SDG 16.3.2 Policy- and lawmakers outreach and education
NCUE faculty members actively assist policymakers and lawmakers by providing outreach activities and courses relating to sustainable development (SDG) concepts such as economics, law, technology, migration, displacement, and climate change. The NCUE faculty members in relevant professional fields serve as advisory members to government agency committees and help implement the agencies’ plans. They ensure that the policymakers and lawmakers recognize and understand the sustainable development concepts and guide them in finding feasible strategies and specific actions toward achieving the United Nations’ 2030 SDGs.
1. In 2023, this increased to 21 faculty members executing a total of 22 government department projects. In 2024, 26 faculty members from NCUE executed a total of 28 government department projects The details are as follows:
(1) Three faculty members assisted with three projects under the "Economy" theme:
(a) Professor Hsien-Chang Huang from the Department of Business Administration is executing the NSTC project (2023/08/01~2024/10/31) titled "Construction of Multidimensional Big Data Prediction Systems in Financial Technology." In recent years, with the rise of 5G mobile communications, Industry 4.0, Internet of Things, Internet of Vehicles, e-commerce, mobile payments, financial technology, and social media. Banks and financial institutions must be able to manage, process, and utilize data for risk management and trading profits. Deep learning has become a popular research field. Current traditional deep learning models (CNN, RNN, LSTM) have many shortcomings. The researcher is dedicated to improving neural network structures by introducing graph topology and shifting to spectral domain predictions to enhance the accuracy of financial multivariate time series data forecasting. This research can effectively improve the network structures of current artificial intelligence and deep learning methods in fintech big data analysis, enhancing predictive performance. It provides society and the nation with superior analytical information and strengthens our country's academic research capabilities (Figure 1).
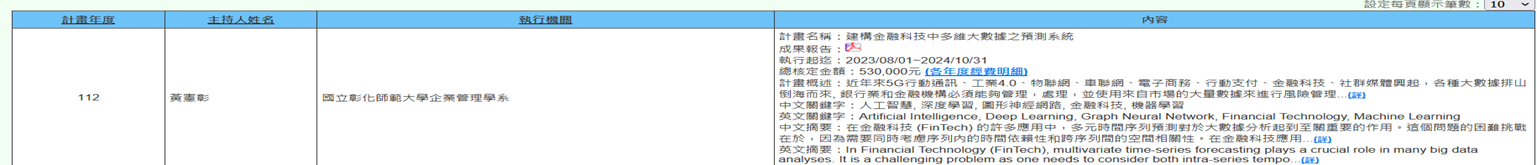
Figure 1. Construction of Multidimensional Big Data Prediction Systems in Financial Technology
(b) Assistant Professor Hsien-Chi Kuang from the Department of Finance and Financial Technology is executing the NSTC FY 2024 project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Good Jumps, Bad Jumps, and VIX Futures Pricing." This project aims to construct an innovative and precise VIX futures valuation model, providing reliable hedging models in today's highly volatile financial markets, making important contributions to financial engineering and investment practices (Figure 2).
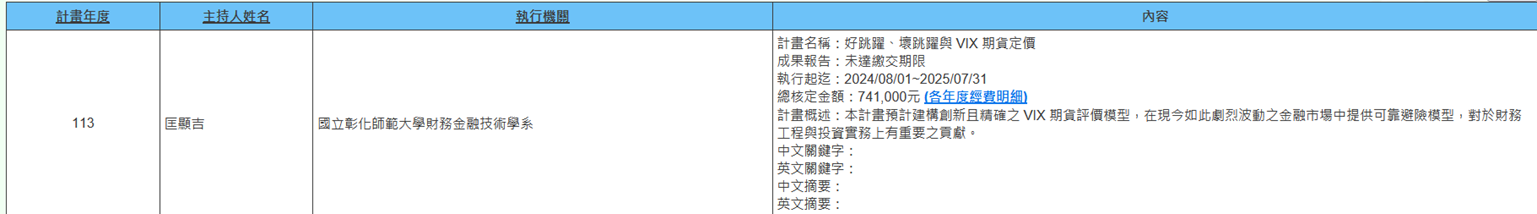
Figure 2. Good Jumps, Bad Jumps, and VIX Futures Pricing
(c) Professor Kai-Chao Yao from the Graduate Institute of Human Resource Management is executing the NSTC project (2024/06/01~2025/05/31) titled "Implementation, Deployment, and Evaluation of Cross-Disciplinary Talent Development Models Using Digital Twin Technology." This project represents pioneering and practical technology and knowledge application research in academia. Following the mechanical computer-aided manufacturing industry chain, from industrial design to CAD/CAM to electrical and information system integration across the upstream and downstream industry chain, it integrates industrial design, mechanical, and electrical-information fields to conduct cross-disciplinary digital twin technology talent development model planning and tool construction. This leverages the cross-disciplinary academic research capabilities of universities and colleges, enhancing talent development capacity in higher education institutions. The established practice-based, cross-disciplinary teaching-oriented digital twin thematic teaching modules will assist in cultivating personnel with cross-industry practical capabilities. It is expected to strengthen domestic digital twin industry talent's practical technology integration abilities in mechanical, electrical-information, and industrial design fields in the future, bringing tremendous benefits to society and the economy. The cross-disciplinary model for digital twin technology addressed by this project can be further extended to talent cultivation in different industries in the future (Figure 3).
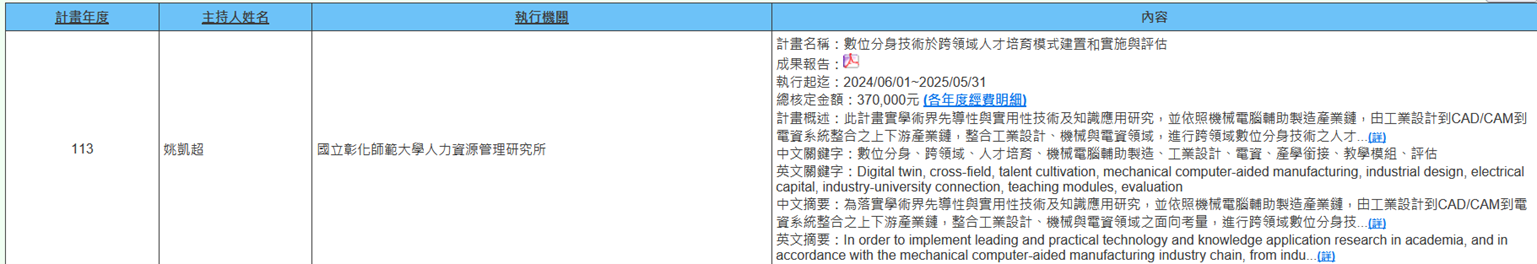
Figure 3. Implementation, Deployment, and Evaluation of Cross-Disciplinary Models Using Digital Twin Technology
(2) Two faculty members are contributing to three projects under the "Law" theme:
(a) Professor Wen-Jing Chang from the Department of Accounting is executing an NSTC project (2023/11/01-2024/10/31) titled "Can Audit Litigation Improve Audit Quality?" In audit academic research, Chy et al. (2021) call for future research to explore more about the relationship between legal environment and auditor behavior, and the evidence in this study can respond to their call. Furthermore, this study supplements the empirical evidence for the "litigation avoidance" theory (Khurana and Raman 2004). There is little empirical evidence on whether litigation systems can alert negligent parties to improve their audit quality. More importantly, current audit litigation literature only provides evidence at the accounting firm or office level (Lennox and Li 2014; Schmidt 2009), and this study extends the evidence of audit litigation impact to the partner level. In practical implications, investors wishing to evaluate auditor audit quality should collect not only their past error records but also information about their disciplinary actions (such as being sued) to comprehensively assess future changes in audit quality (Figure 4).
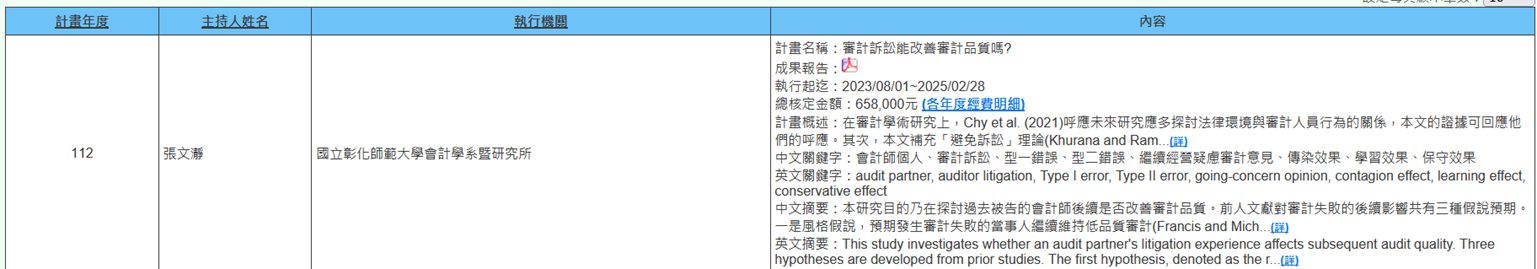
Figure 4. Can Audit Litigation Improve Audit Quality?
(b) Associate Professor Huan-Yi Li from the Department of Accounting is executing an NSTC project (2023/08/01-2025/06/30) titled "The Impact of the Implementation of the Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industry Development Act and Amendments to the Industrial Innovation Act on Corporate Innovation, Investment Efficiency, and Firm Value in Taiwan." The Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industry Development Act was officially implemented in 2022, incorporating biotechnology contract manufacturing into the scope of tax incentives, adding equipment investment credits and including subsidies for advanced medical technologies. The Industrial Innovation Act has undergone multiple amendments since its implementation in 2010. The tax incentives provided by both acts play important roles in Taiwan's corporate R&D investment and industrial development. This project will analyze the impact of the implementation of the Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industry Development Act and important amendments to the Industrial Innovation Act on the innovation, investment efficiency, and firm value of Taiwan's listed companies. The research results can serve as a reference for government formulation of investment credit-related tax policies and corporate tax management (Figure 5).
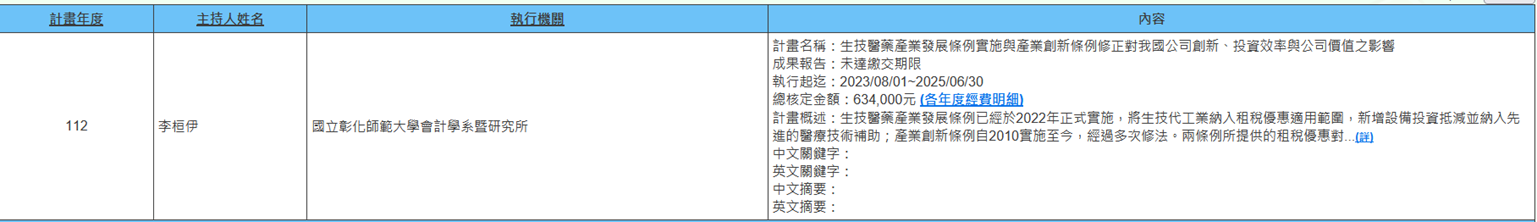
Figure 5. The Impact of the Implementation of the Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industry Development Act and Amendments to the Industrial Innovation Act on Corporate Innovation, Investment Efficiency, and Firm Value in Taiwan
(c) Professor Wen-Jing Chang from the Department of Accounting is executing an NSTC project (2024/08/01~2026/06/30) titled "Research on the Impact of Audit Litigation on Auditor Reputation." The purpose of this research is to explore whether auditors involved in audit litigation suffer reputational damage and consequently lose other clients. In auditing academic research, this study makes several contributions. First, Anantharaman et al. (2016) and Chy et al. (2021) call for future research to explore more about the relationship between legal environment and auditor behavior, and the evidence in this study can respond to their call. Second, there is little empirical evidence from previous research based on accounting firms exploring audit litigation leading to reputational capital damage (Allen et al. 2005, Lennox 1999), and the evidence is inconsistent. This study can add archival empirical evidence on whether audit litigation damages auditor’s reputation. Finally, evidence of audit litigation damaging auditor reputation still lacks evidence at the individual accountant level, and this study can fill this gap in literature (Figure 6).
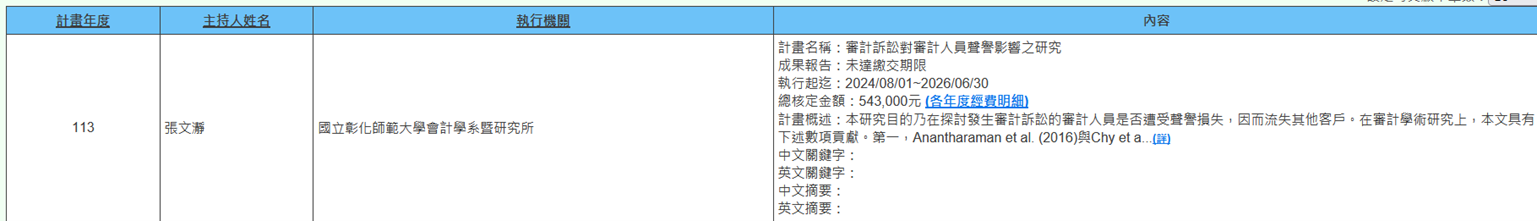
Figure 6. Research on the Impact of Audit Litigation on Auditor’s Reputation
(3) 15 faculty members assisted with 15 projects under the "Technology" theme:
(a) Assistant Professor Jia-Xuan Wu from the Department of Electrical and Mechanical Technology is executing the NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Three-Phase Interleaved Wireless Charging System with Battery Voltage Balancing Function." The contributions of this project are as follows: a. Academically, this project will investigate the input ripple improvement of three-phase interleaved wireless charging systems while studying the control of the proposed architecture in series battery balancing algorithms. b. In industrial applications, wireless charging systems have been increasingly widely used in electric vehicle fields. The goal of this project is to develop wireless charging systems for electric buses, which have industrial development value as it does not require additional battery balancing circuits (Figure 7).
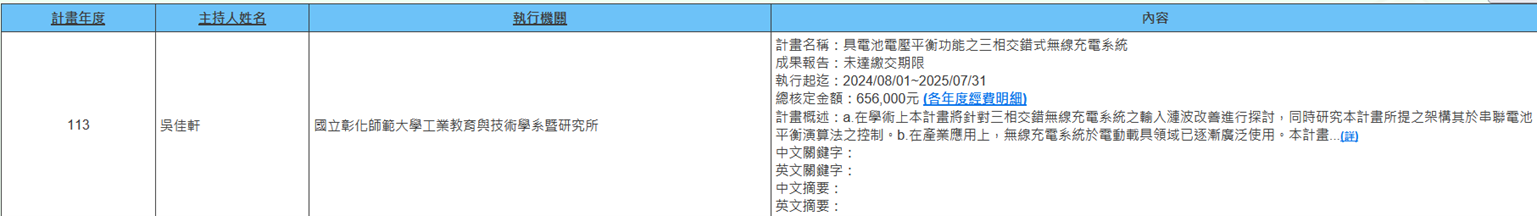
Figure 7. Three-Phase Interleaved Wireless Charging System with Battery Voltage Balancing Function
(b) Professor Chao-Chin Wu from the Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering is executing the NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Adaptive Scheduling Strategies for Automatic Hyperparameter Tuning Tasks of Deep Learning Models with Population Evolution Characteristics in Heterogeneous Computing Environments." In automated machine learning, since each training task requires different training durations and computing nodes have vastly different training capabilities, work allocation plays a key role, and self-scheduling strategies can often provide excellent load balancing. However, training tasks in Ray's population evolution have unique characteristics, and key limitations must first be resolved to fully exploit the efficiency of self-scheduling strategies. In the first year, the project aims to design new population evolution processes, develop new self-scheduling strategies, and train a model that can estimate training task workloads. In the second year, based on population size, estimated workloads, generated node numbers, and differentiated resource allocation of each working node, combined with new evolution processes, we will integrate high-performance self-scheduling strategies (Figure 8).
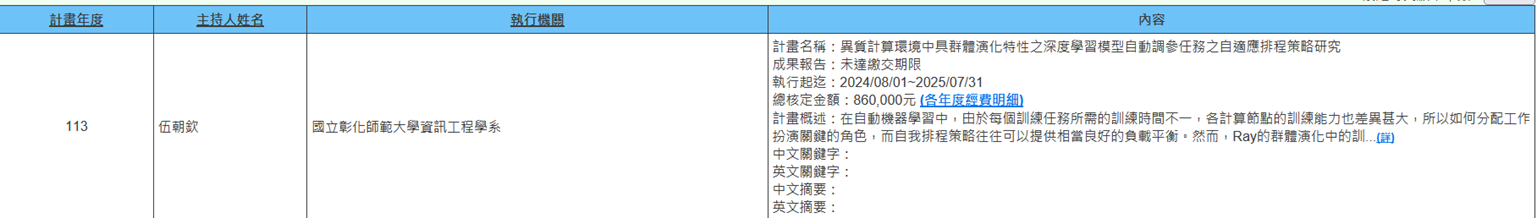
Figure 8. Adaptive Scheduling Strategies for Automatic Hyperparameter Tuning Tasks of Deep Learning Models with Population Evolution Characteristics in Heterogeneous Computing Environments
(c) Professor Ming-Hua Ho from the Department of Electronic Engineering is executing the NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/10/31) titled "Investigation of Miniaturized Substrate Integrated Coaxial Cavity Structures and Their Applications in Balanced or Unbalanced Filter Circuit Design, and Applications of Substrate Integrated Coaxial Structures in Phase Inverter and Magic-T Circuit Design." The research focuses on developing various microwave circuits with miniaturized substrate integrated coaxial cavity structures. These structures not only effectively reduce the resonant frequency of traditional substrate integrated waveguide cavities but also achieve extreme area reduction effects, used for miniaturized balanced or unbalanced bandpass filters, dual-band filters, and diplexer designs. Substrate integrated coaxial lines transform traditional 3D coaxial structures into planar structures and can be manufactured using existing PCB technologies, such as substrate integrated coaxial filter, inverters, and magic-T circuits. All circuits described here can be realized through PCB manufacturing, with allows for mass production and cost reduction, which are indispensable technologies in the commercialization process of modern microwave circuits. Academically, most of these circuit structures are currently fields urgently awaiting development, extremely challenging and forward-looking (Figure 9).
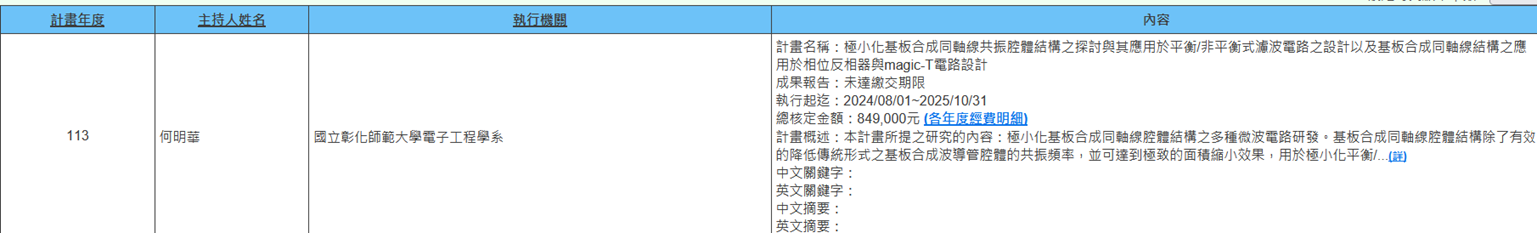
Figure 9. Investigation of Miniaturized Substrate Integrated Coaxial Cavity Structures and Their Applications in Balanced or Unbalanced Filter Circuit Design, and Applications of Substrate Integrated Coaxial Structures in Phase Inverter and Magic-T Circuit Design
(d) Professor Chia-Chi Liu from the Department of Physics is executing the NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "High-Performance Synthesis of Novel Thermoelectric Thick Films and Bulk Organic-Inorganic Composite Materials and Manufacturing of Thermoelectric Generators (1/3)." Reducing energy consumption by synthesizing thermoelectric materials is beneficial for promoting widespread use of thermoelectric materials in energy harvesting. Although the conversion efficiency of thermoelectric generators (TEGs) for power generation is currently inferior to solar panels, minimizing the energy consumption in manufacturing thermoelectric materials may make the net power generation of TEGs comparable to solar panels. Additionally, thermoelectric modules have the following advantages: high reliability and long durability. Recently developed high-performance thermoelectric materials with zT > 2 promise even greater conversion efficiency (Figure 10).
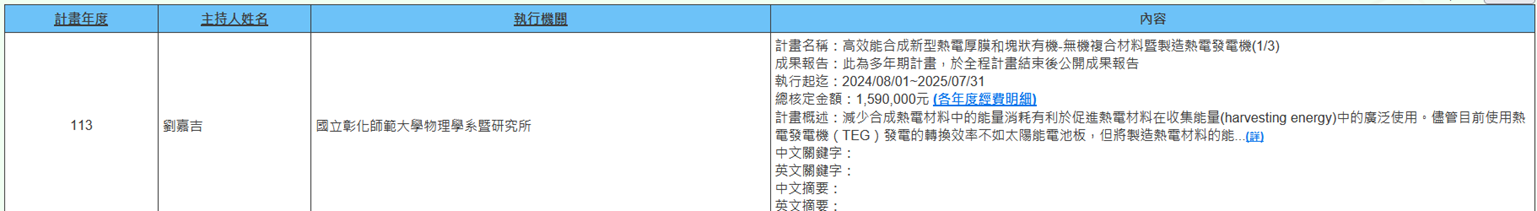
Figure 10. High-Performance Synthesis of Novel Thermoelectric Thick Films and Bulk Organic-Inorganic Composite Materials and Manufacturing of Thermoelectric Generators (1/3)
(e) Professor Cheng-Kai Liu from the Department of Mathematics is executing the NSTC project (2024/08/01~2026/07/31) titled "Invariants of Skew Derivations on Semiprime Rings and Polynomial Identities." Invariants of skew derivations on rings have always been a very active research topic in ring theory. In this project, we mainly characterize the structure of integer q-skew derivations on semiprime rings and explore whether a semiprime ring is also a PI ring when the invariant subring of integer q-skew derivations on the semiprime ring is a PI ring. Additionally, the study investigates necessary and sufficient conditions for invariants of algebraic q-skew derivations on prime rings to become prime or semiprime rings and explore the relationship between the PI-degree of the invariant subring and the PI-degree of the prime ring. The results obtained from this project are believed to receive attention and recognition from scholars in the ring theory field (Figure 11).
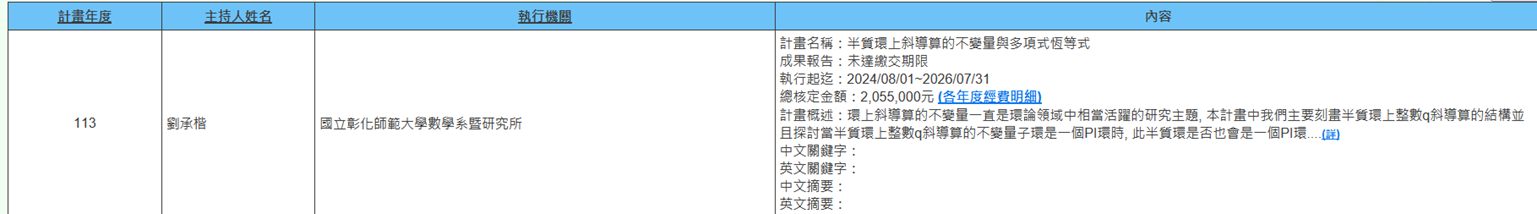
Figure 11. Invariants of Skew Derivations on Semiprime Rings and Polynomial Identities
(f) Assistant Professor Yong-Qian Zhou from the Department of Mechatronic Engineering is executing NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Magnetically Levitated Control Wireless Capsule Endoscopy Based on Three-Dimensional Scene Reconstruction". This project aims to accurately control the position and orientation of wireless capsule endoscopes to enhance the controllability of capsule endoscopy during internal organ examinations in the human body. In academic research, very few studies have simultaneously achieved three-dimensional scene reconstruction and magnetic levitation control of capsule endoscopes, and there is no position-based magnetic levitation control of capsule endoscopes that can control both position and orientations of capsule endoscopes to achieve high-quality internal organ imaging. Currently, among commercial products, very few companies have developed magnetically controlled wireless capsule endoscopy systems. However, these can only control the position of capsule endoscopes within human organs but cannot precisely control orientation. Academically, there are few sensor-less capsule endoscope position and orientation control technologies. This project will construct an experimental platform, conduct actual experiments, and make improvements based on test results, aiming to achieve practicality and user-friendliness. Therefore, this research has considerable value (Figure 12).
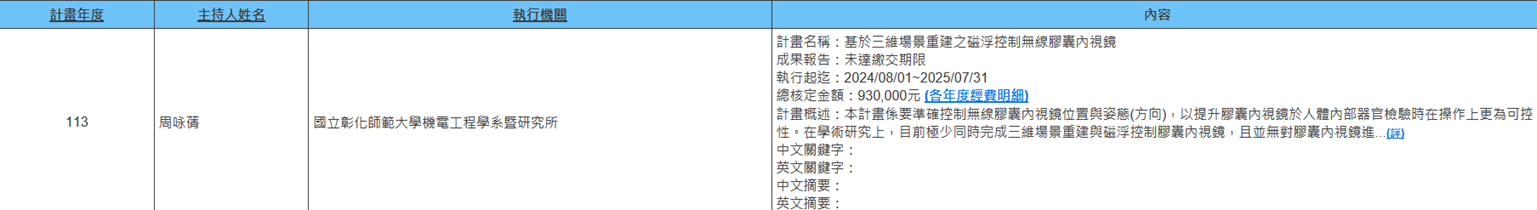
Figure 12. Magnetically Levitated Control Wireless Capsule Endoscopy Based on Three-Dimensional Scene Reconstruction
(g) Professor Chih-Wei Chang from the Department of Chemistry is executing NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Preparation of Silver Nanoclusters Protected by DNA, Polymers, Carbon Quantum Dots, and Glutathione and Investigation of Their Special Spectroscopic Properties". This project aims to understand the special spectroscopic properties of silver nanoclusters labeled on DNA, polymers, carbon quantum dots, and glutathione. Through this research, we can better understand the influence of different protecting groups on the spectroscopic properties of silver nanoclusters. Such related knowledge is very important for future applications of silver nanoclusters in biological imaging, ion or molecular sensor design, and optical components. This project not only cultivates students' ability to prepare metal nanoclusters but also trains them to use many material analysis instruments such as: TEM, XPS, FT-IR, HPLC, high-resolution ESI mass spectrometer, steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectrometers. This will be very helpful for future development in materials chemistry, spectroscopy, and analytical chemistry fields (Figure 13).
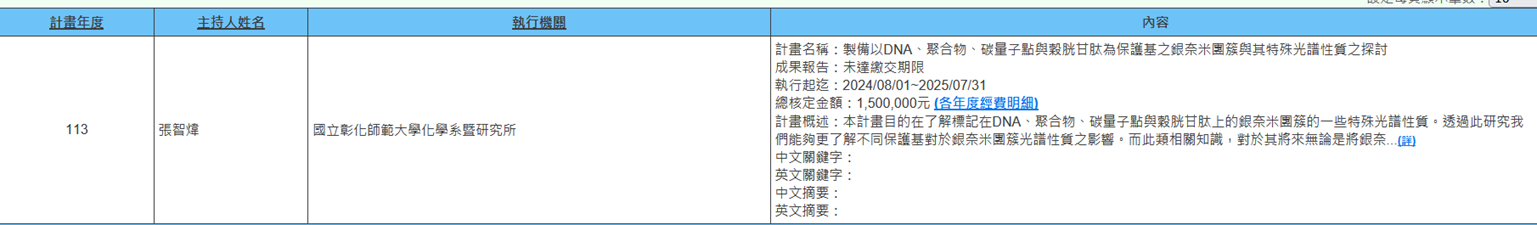
Figure 13. Preparation of Silver Nanoclusters Protected by DNA, Polymers, Carbon Quantum Dots, and Glutathione and Investigation of Their Special Spectroscopic Properties
(h) Professor Yu-Min Tseng from the Department of Mathematics is executing NSTC project (2024/08/01~2026/07/31) titled "Design of Anonymous Heterogeneous Multi-Receiver Encryption Schemes with Seamless Compatible Public Key System Transformation". Based on various public key systems, many anonymous multi-receiver encryption (AMRE) mechanisms have been proposed, which is an important cryptographic application. However, existing anonymous multi-receiver encryption mechanisms are only applicable to single public key systems and are not suitable for heterogeneous public key systems. In this project, our goal is to design four anonymous heterogeneous multi-receiver encryption mechanisms with seamless compatible public key system transformation (AHMRE-SCPST), of which two are lightweight AHMRE-SCPST mechanisms suitable for IoT applications with limited computational resources, and the other two are AHMRE-SCPST mechanisms with leakage-resilient characteristics that can resist side-channel attacks. All four mechanisms are proposed for the first time, which will help enhance the international visibility of Taiwan's academic community and provide information security applications for the industry (Figure 14).
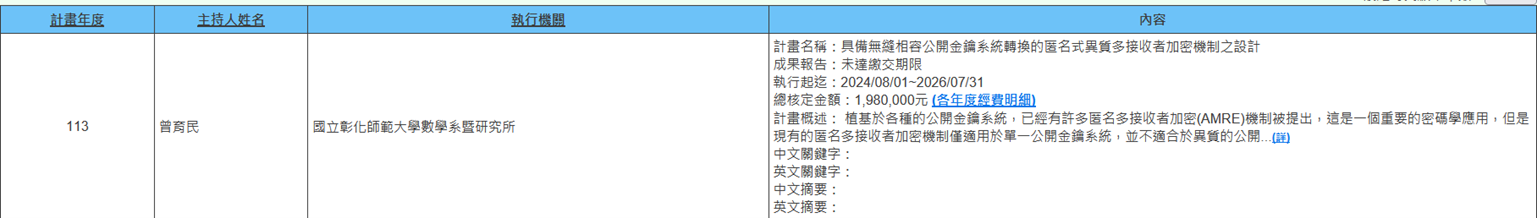
Figure 14. Design of Anonymous Heterogeneous Multi-Receiver Encryption Schemes with Seamless Compatible Public Key System Transformation
(i) Associate Professor Li-Wei Tseng from the Department of Mechatronic Engineering is executing NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) "Study on Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Non-equiatomic FeNiCoAlCrB and FeNiCoAlTiB High-Entropy and Shape Memory Alloys". FeNiCoAlCrB and FeNiCoAlTiB alloys possess high strength and high ductility, with wide application ranges: biomedical industry, precision machinery industry, mold industry, and automotive industry. Their soft magnetic characteristics can be applied in electrical and electronic industries for motor cores, solenoid valves, high-frequency soft magnetic thin films, and various sensors. The latest research results of these novel alloys provide important reference for future academic research and industrial material processing (Figure 15).
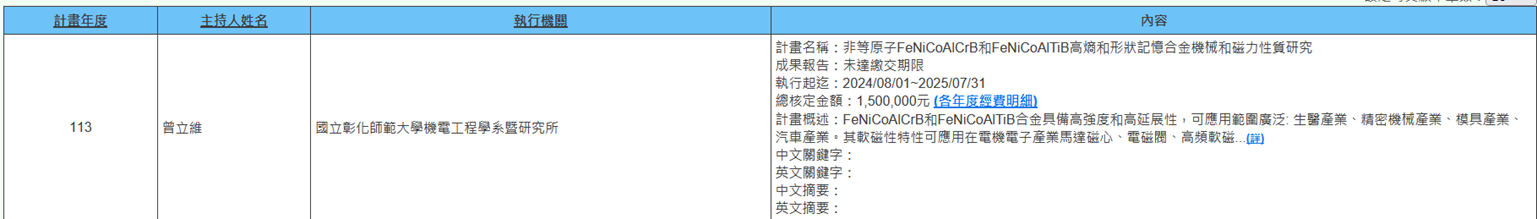
Figure 15. Study on Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Non-equiatomic FeNiCoAlCrB and FeNiCoAlTiB High-Entropy and Shape Memory Alloys
(j) Professor Han-Wen Li from the Department of Chemistry is executing NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Development of Efficient Late Transition Metal Catalysts and High Proton Conductivity Coordination Polymers (1/3)". The focus of the first part is to develop late transition metal complexes that can effectively catalyze organic transformations. In the second part, the emphasis is on non-porous coordination polymers with high proton conductivity, hoping to develop new proton conductive materials to replace Nafion membranes in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Our concept is novel, and we are optimistic that a considerable portion of this project can be published in high international standard journals, thereby contributing to Taiwan's scientific research development. Additionally, successful execution of this project proposal will promote the scientific training of participating students. These young people will receive comprehensive scientific professional training, equipped with rich scientific knowledge, enabling them to assume leadership or R&D positions in Taiwan's high-tech industries (Figure 16).
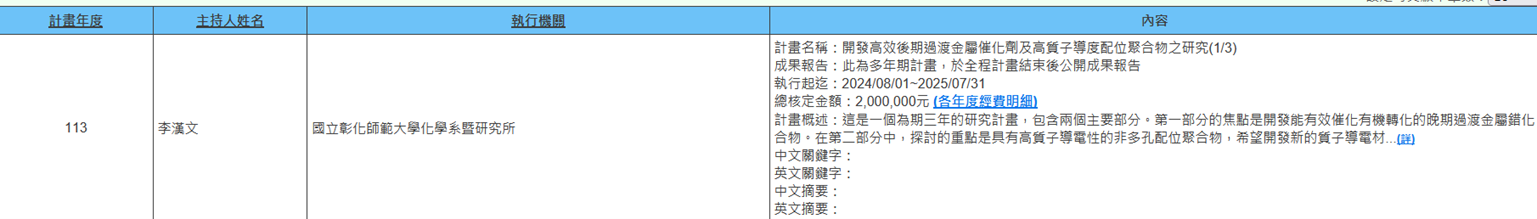
Figure 16. Development of Efficient Late Transition Metal Catalysts and High Proton Conductivity Coordination Polymers (1/3)
(k) Professor Chi-Ying Li from the Department of Biology is executing a National Science and Technology Council project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Endocrine Basis of Feminization of Male Hosts by Parasitic Barnacle Polyascus planus." This research project explores the endocrine networks that induce host feminization during parasite-host interactions. The expected major academic discovery is the first understanding of the molecular mechanisms by which parasitic barnacles feminize their hosts, which holds significant importance for fundamental biology. In terms of applications, understanding the mechanisms of sexual development and sex change in decapod animals can be used to develop sex conversion and reproductive control in economically important aquaculture animals (Figure 17).
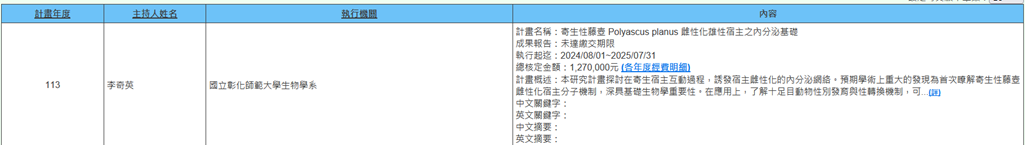
Figure 17. Endocrine Basis of Feminization of Male Hosts by Parasitic Barnacle Polyascus planus
(l) Professor Shih-Yun Lin from the Department of Physics is executing a National Science and Technology Council project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Interaction of Relativistic Single Electron Wave Packets with Electromagnetic Field Vacuum: Quantum Information and Quantum Radiation (2/3)." The results of this project will enrich and refine the understanding of quantum field theory in curved spacetime, relativistic quantum information, and quantum electrodynamics. We will compare the results with experiments using electron microscopy and accelerators, and attempt to predict experimental results of strong-field laser verification of the Unruh effect. Future work may also touch upon quantum computing using free electrons as quantum bit carriers (Figure 18).
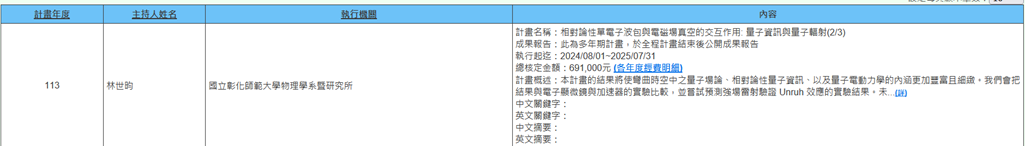
Figure 18. Interaction of Relativistic Single Electron Wave Packets with Electromagnetic Field Vacuum: Quantum Information and Quantum Radiation (2/3)
(m) Associate Professor Si-Lin Lin from the Graduate Institute of Vehicle Technology is executing a National Science and Technology Council project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Research and Development of Non-Line-of-Sight Imaging Technology Using Artificial Intelligence and Doppler Radar." This research project aims to develop non-line-of-sight imaging technology combining artificial intelligence and Doppler radar to enhance the safety of autonomous vehicles in complex traffic environments. This technology will enable vehicles to identify and track objects obscured by obstacles, such as pedestrians or other vehicles around corners, thereby reducing traffic accidents. In terms of humanities and society, this technology will improve public traffic safety, particularly in urban environments, and enhance public trust in autonomous vehicles. Economically, it is expected to drive the development of the autonomous vehicle industry, creating new markets and employment opportunities. Furthermore, the commercialization of this technology will promote growth and innovation in related industries. This project will promote interdisciplinary research, deepen understanding of advanced imaging technology and autonomous driving systems, and enhance the quality and innovation capacity of academic research. In summary, this project has significant expected impacts on improving traffic safety, promoting economic development, and advancing academic research (Figure 19).
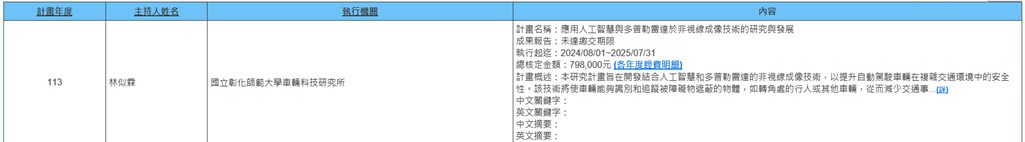
Figure 19. Research and Development of Non-Line-of-Sight Imaging Technology Using Artificial Intelligence and Doppler Radar
(n) Professor De-Yu Lin from the Department of Electronic Engineering is executing a National Science and Technology Council project (2024/08/01~2025/12/31) titled "Growth of Silver Selenide and Silver Sulfide Films and Investigation of Their Optoelectronic and Thermoelectric Properties." In this research, we will use different thin film growth methods to grow silver selenide (Ag2Se) and silver sulfide (Ag2S) films. First, we will use thermal evaporation to grow silver films, then use CVD method to selenide or sulfurize the silver films into Ag2Se or Ag2S films. These two types of films possess good conductive properties, are confirmed to be n-type semiconductors, and have high See beck coefficients, making them applicable to thermoelectric thin film devices. This project aims to improve silver films to single crystal form before film growth to reduce resistivity. Additionally, this project will also combine CVT methods to first grow Ag2Se and Ag2S single crystals, then fabricate them into films using thermal evaporation or spin coating methods to obtain high-quality continuous films. These can also be combined with p-type semiconductor materials to form heterostructures, applicable to thin film solar cells, thermoelectric devices, diode devices, and wearable sensing devices (Figure 20).
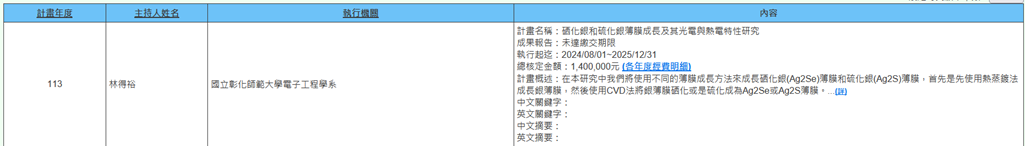
Figure 20. Growth of Silver Selenide and Silver Sulfide Films and Investigation of Their Optoelectronic and Thermoelectric Properties
(o) Professor Yi-Cheng Lin from the Department of Mechatronic Engineering is executing a National Science and Technology Council project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Application of SCAPS Software for Sb2Se3 Solar Cell Simulation and Machine Learning Data Mining Establishment." With the recent rise of AI and ML, the combination of materials engineering with AI and ML has attracted considerable attention. However, during the data mining phase of AI and ML, experimental-based materials engineering struggles to rapidly provide thousands of reliable data points. This research utilizes SCAPS simulation of Sb2Se3 solar cells combined with experimental validation to supplement the shortage of materials science data and assist in AI/ML model training. This accelerates the integration of materials science with AI and promotes new developments in the solar cell field (Figure 21).
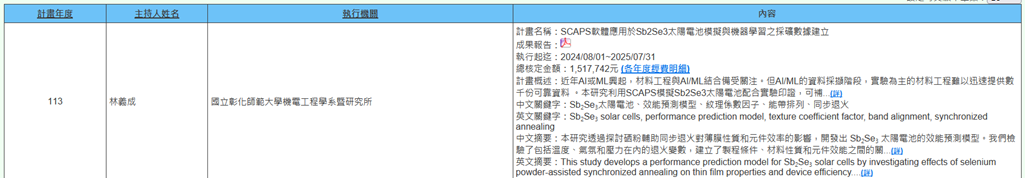
Figure 21. Application of SCAPS Software for Sb2Se3 Solar Cell Simulation and Machine Learning Data Mining Establishment
(4) 1 faculty member is contributing to 1 project under the "Immigration and Displacement" theme: Professor Yi-Han Wang of the Department from Guidance and Counseling is executing a National Science and Technology Council project from 2023/08/01 to 2025/07/31, titled “The experiences of social participation and empowerment of female new immigrants and an Action Research practice: The case of new immigrant organizations.”
This research has two main focuses:
(a) To explore the social participation and empowerment experiences of new immigrant women in Taiwan, using new immigrant groups as case studies.
(b) To identify factors and methods that promote the empowerment of new immigrant women in social participation. Based on the findings, the study will collaborate with new immigrant groups to develop an empowerment program aimed at enhancing social participation.
The expected outcomes of this research are:
(a) Enriching the academic research landscape.
(b) Leading empirical research and practical fields to focus on social participation and empowerment work for new immigrant women.
(c) Serving as a reference for relevant units in planning and implementing empowerment programs for new immigrant groups or new immigrant women in the future.
(d) Contributing to promoting social participation, diversifying empowerment experiences, and maintaining the rights and well-being of new immigrant women in Taiwan.
This study addresses important issues related to the integration and empowerment of immigrant women, which is crucial for fostering an inclusive society and ensuring the well-being of diverse populations (Figure 22).
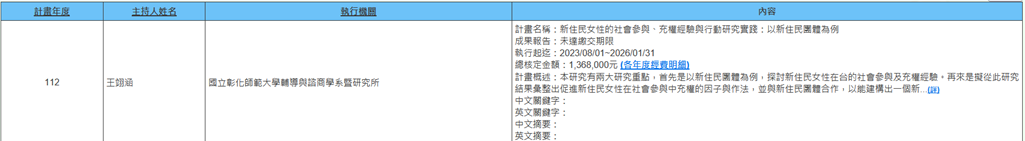
Figure 22. The experiences of social participation and empowerment of female new immigrants and an Action Research practice: The case of new immigrant organizations
(5) Five faculty members assisted with Six projects under the "Climate Change" theme:
(a) Professor Su-Fen Wang of the Department of Geography is executing the NSTC FY 2024 project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Constructing a Framework for Assessing Large-Scale Landscape Changes and Ecosystem Services Using Remote Sensing Technologies (Sub-project II) (3/3)". This project focuses on the impact of land use change on ecosystem services as its core issue. Through remote sensing as a tool, it quantifies the relationship between land use change processes and ecosystem services, which can serve as a foundation for future transformation of ecological function values into economic output estimates. The ecosystem service assessment methodology established through remote sensing technology is suitable for large-scale, spatially-explicit estimation; the integrated use of multi-temporal feature image interpretation techniques can also resolve dynamic change in land cover classification, enabling more accurate quantification of environmental impacts caused by land use patterns. The ecological value assessment of agricultural and fishery land as well as natural wetlands can ensure domestic agricultural food production supply and the maintenance of local industrial patterns; the ecological benefits of non-economic values can provide estimates of potential environmental silent costs caused by development. Linking with other sub-projects will introduce scientific data into local communities and local governments, strengthening the academic purpose of knowledge practice and avoiding inappropriate land use development (Figure 23).
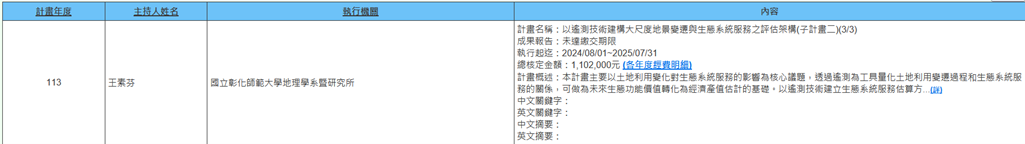
Figure 23. Constructing a Framework for Assessing Large-Scale Landscape Changes and Ecosystem Services Using Remote Sensing Technologies (Sub-project II) (3/3)
(b) Professor Su-Fen Wang of the Department of Geography is executing the NSTC FY 2024 project (2024/10/01~2025/09/30) titled "Monitoring of Socio-Ecological Systems in Coastal Wetlands along Taiwan's Western Coast - Phase II (1/2)". This project aims to establish core long-term ecological monitoring data for the semi-agricultural and semi-fishery socio-ecological systems along Taiwan's southwestern coast, providing baseline data for long-term changes in socio-ecological systems and understanding the impacts of related green energy policies on coastal socio-ecological systems (Figure 24).
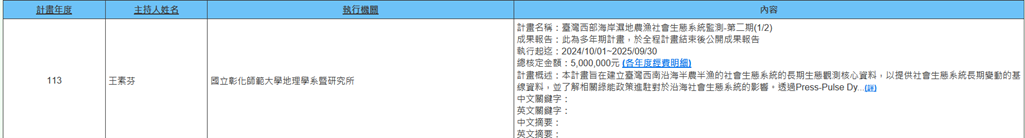
Figure 24. Monitoring of Socio-Ecological Systems in Coastal Wetlands along Taiwan's Western Coast - Phase II (1/2)
(c) Associate Professor Yi-Ching Chen of the Department of Geography is executing the NSTC FY 2024 project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Observation of Coastal Geomorphological Changes and Their Environmental Control Factors in Changhua Coast (Sub-project I) (3/3)". Tidal flat geomorphology serves as an important foundation for the ecological and agricultural-fishery social systems of Changhua coast. This project will use multi-scale aerial remote sensing technology to establish nearly 30 years of tidal flat geomorphological changes along Changhua coast, as well as the impacts of natural environmental changes and artificial structures (such as elevated walkways, mangroves, wind and solar power facilities) on tidal flat geomorphology. Expected outcomes of this project include: (1) coastal shoreline interpretation and geomorphological modeling modules; (2) establishment of 30-year long-term coastal geomorphological observation and spatial distribution of coastal erosion and accretion along Changhua coast; (3) correlation of tidal flat geomorphology with river sediment transport, and the impact of artificial structures on coastal geomorphology; (4) production of high-resolution digital terrain models for nearshore coasts using UAV photogrammetry to analyze the impact of mangroves on tidal flat geomorphology; (5) integration of natural ecological and socio-cultural aspects to assess climate change and artificial structure impacts, providing a basis for the social-ecological resilience and vulnerability of Changhua coast (Figure 25).
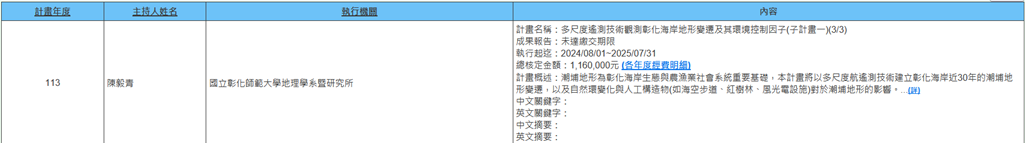
Figure 25. Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Observation of Coastal Geomorphological Changes and Their Environmental Control Factors in Changhua Coast (Sub-project I) (3/3)
(d) Professor Chien-Yi Tu of the Department of Geography is executing the NSTC FY 2024 project (2024/08/01~2025/10/31) titled "Impact of Large-Scale Circulation Changes on Precipitation in Asian Monsoon Regions under Global Warming (III)". Taiwan is located within the most significant monsoon region globally. The long-range water vapor transport accompanied by vigorous southwest airflows in summer often brings abundant precipitation to Taiwan, sometimes causing disasters. Therefore, understanding the long-term changes of the monsoon system is important. This project plans to start from observational data analysis and connect to assess the possible impacts of Asian monsoon circulation changes on regional rainfall under future warming scenarios. The research outcomes can help us further understand the possible impacts of monsoon circulation changes on monsoon region precipitation and assist Taiwan's future disaster prevention and water resource allocation (Figure 26).
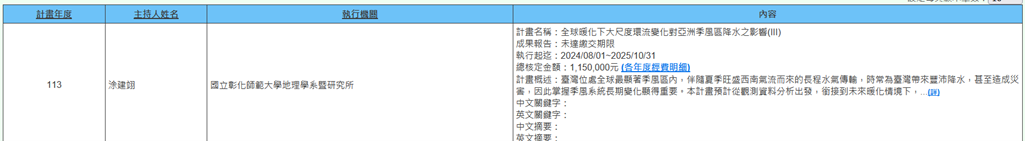
Figure 26. Impact of Large-Scale Circulation Changes on Precipitation in Asian Monsoon Regions under Global Warming (III)
(e) Professor Yu-Ling Song of the Department of Geography is executing the NSTC project (2024/08/01~2025/07/31) titled "Tragedy of Artifacts? -- Networks and Changes in the Socio-Ecological System of Fangyuan Coast in Changhua Intervened by Elevated Walkways (Main Project and Sub-project VI) (3/3)". This research explores a coastal society that has repeatedly been intervened by artifacts during its development process as a government strategy for revitalizing the development of Fangyuan Township in Changhua County, and how the actor networks connected by artifacts impact the socio-ecological system. This research is based on an integrated social-ecological actor network as an analytical framework, conducted over three years, and integrates other sub-projects in aspects of coastal geomorphology, regional climate, land use, ecological service systems, marine spatial planning, and benthic ecological diversity for interdisciplinary analysis of the development and impacts of peripheral coastal society (Figure 27).
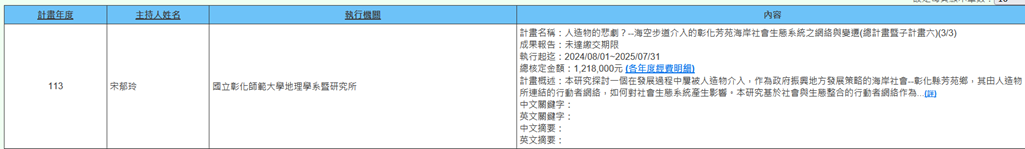
Figure 27. Tragedy of Artifacts? -- Networks and Changes in the Socio-Ecological System of Fangyuan Coast in Changhua Intervened by Elevated Walkways (Main Project and Sub-project VI) (3/3)
(f) Professor Tsung-Chi Lin of the Department of Biology is executing the NSTC project (2024/11/01~2025/10/31) titled "Using Artificial Intelligence and Citizen Scientists for Urban Environmental Vector Surveillance and Monitoring (1/2)". In recent years, global dengue fever outbreaks have continued to spread, with this year already exceeding ten million cases. Taiwan experienced major dengue fever outbreaks in 2015 and 2023, with cases exceeding ten thousand in both instances. Vector mosquitoes are affected by climate change - warming has altered vector mosquito distribution. Urban ecosystems often harbor disease vectors that expand and outbreak along with urban development systems, making it necessary to establish early detection and warning systems. This project will develop corresponding mobile applications or LINE bots, which will be used and validated by citizen. This can enable early response before dengue fever case distribution changes, specifically when Aedes aegypti colonizes new locations but has not yet established stable populations (Figure 28).

Figure 28. Using Artificial Intelligence and Citizen Scientists for Urban Environmental Vector Surveillance and Monitoring (1/2)
2. In 2024, 4 faculty members joined the list, for a total of 5 serving on seven government committees. These faculty members provide policymakers with recommendations for practical strategies and concrete actions to achieve specific sustainable development goals:
(1) Assistant Professor Hsing-Kuo Liao from the Department of Electrical and Mechanical Technology was seconded to serve as Principal Secretary at the Ministry of Education from September 1, 2020, to May 19, 2024. He assisted the Minister of Education in coordinating inter-ministerial affairs and actively planned and promoted important educational policies and regulations, making significant contributions to improving the educational environment. He was recognized as an Exemplary Civil Servant by the Ministry of Education in 2023. Website: https://www.ncue.edu.tw/p/406-1000-23435,r93.php?Lang=zh-tw
(2) Professor Wei-Tzer Huang from the Department of Industrial Education and Technology serves as a member of the Electric Reliability Council of the Ministry of Economic Affairs from September 27, 2022, to September 26, 2024, participating in meetings concerning Taiwan’s long-term power load forecasting, renewable energy development, and power system operation reliability (Figure 29).

Figure 29. Professor Wei-Tzer Huang serves as a member of the Electric Reliability Council of the Ministry of Economic Affairs
(3) Professor Chung-Chi Lin from the Department of Biology serves as the executive director of the National Red Imported Fire Ant Control Centre of the Council of Agriculture and is responsible for planning and implementing professional technical support and emergency control plans. The National Red Imported Fire Ant Control Centre was established in November 2004 to provide overall notifications and control actions on RIFA infestations. The Centre also researches effective monitoring methods and control strategies suitable for Taiwan’s ecological environment, cooperates with communal and non-governmental organizations to educate the public about the problems, and helps train teachers to help the government mitigate the spread of RIFAs (Figure 30). Website: https://fireant.aphia.gov.tw/RedFireAnt/AboutUs
Figure 30. Professor Chung-Chi Lin serves as the executive director of the National Red Imported Fire Ant Control Centre of the Council of Agriculture
(4) Associate Professor Pei-wen Lu from the Department of Geography serves as a committee member on the National Spatial Planning Council, the Ministry of the Interior. In this role, she contributed to: Reviewing the drafting or modification of national spatial plans, Evaluating national defense and major public facility or public utilities that span more than two national land functional zones, Soliciting opinions for the national land white paper, Reviewing and improving the national spatial plan, and Addressing other matters related to the deliberation or coordination of national spatial planning (Figure 31). Link:
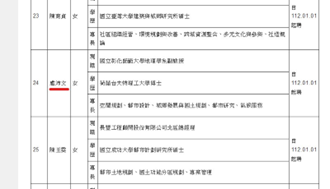
Figure 31. Documentation of Associate Professor Pei-wen Lu 's appointment as a committee member of the National Spatial Planning Council, Ministry of the Interior
(5) Associate Professor Pei-wen Lu of the Department of Geography serves as a committee member on the Construction and Planning Development Fund Management Committee, the Ministry of the Interior from February 1 to January 31, 2025. In this role, she assists the government in effectively managing the income, expenditures, safekeeping, and utilization of the Construction and Planning Development Fund, contributing to the promotion and development of national construction projects (Figure 32). Website:

Figure 32. Appointment letter for Associate Professor Pei-wen Lu of the Department of Geography as a committee member of the Construction and Planning Development Fund Management Committee, Ministry of the Interior

















