SDG 14.5.1 Minimizing alteration of aquatic ecosystems (plan)
In accordance with the regulations of the Waste Disposal Act, the laboratory waste liquid in NCUE is entrusted to be cleaned and treated as industrial waste, and the original sewage treatment facilities are still in normal operation, aimed at minimizing physical, chemical, and biological changes to related aquatic ecosystems.
1. Reduction of water quality changes in NCUE
(1) NCUE manages all generated effluent by routing it through a centralized wastewater treatment plant. The treated water is then discharged through outlets approved and regulated by the authorities. The university complies with the regulations outlined in the Water Pollution Control Act (Link https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?media=print&pcode=O0040001 ) and Water Pollution Control Act Enforcement Rules (Link https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?media=print&pcode=O0040002 ) in handling and reporting the discharge of its wastewater. Every year in July, NCUE submits a report that includes the water quality testing results for both the raw wastewater and the discharged wastewater for the period from January to June of the current year. Additionally, in the following year, by January, NCUE submits a report that covers the water quality testing results for both the raw wastewater and the discharged wastewater for the period from July to December of the preceding year.
The following is a screenshot of NCUE’s reporting on the webpage of the “Waste/Polluted Water Management System for Industrial and Sewage Systems” (WPMIS) of the Ministry of Environment as shown in Figure 1.
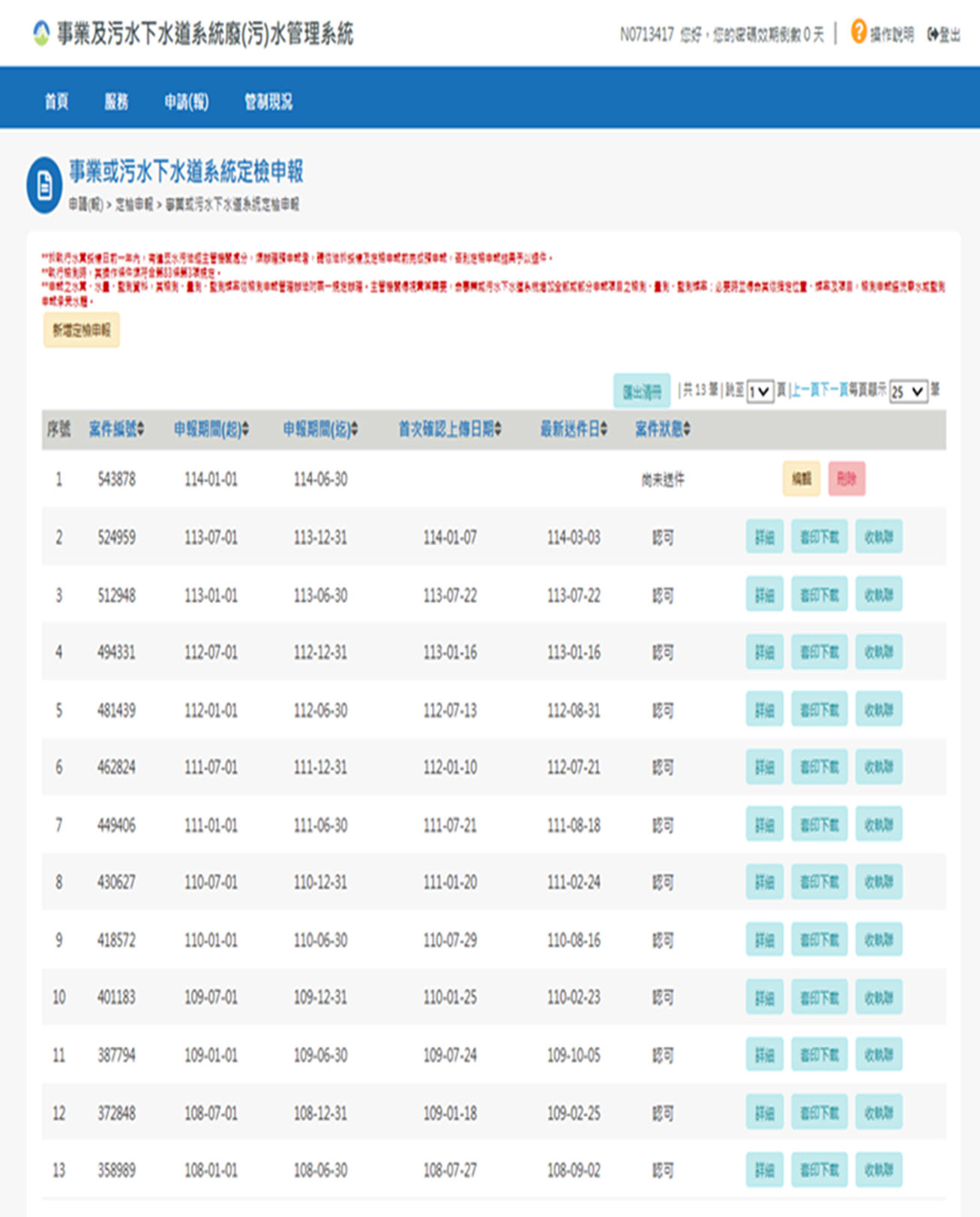
Figure 1. A screenshot of the “Wastewater Management System for Industrial and Sewage Systems” webpage of the Ministry of Environment
(2) The photos of the wastewater treatment plant are shown in Figure 2-5.
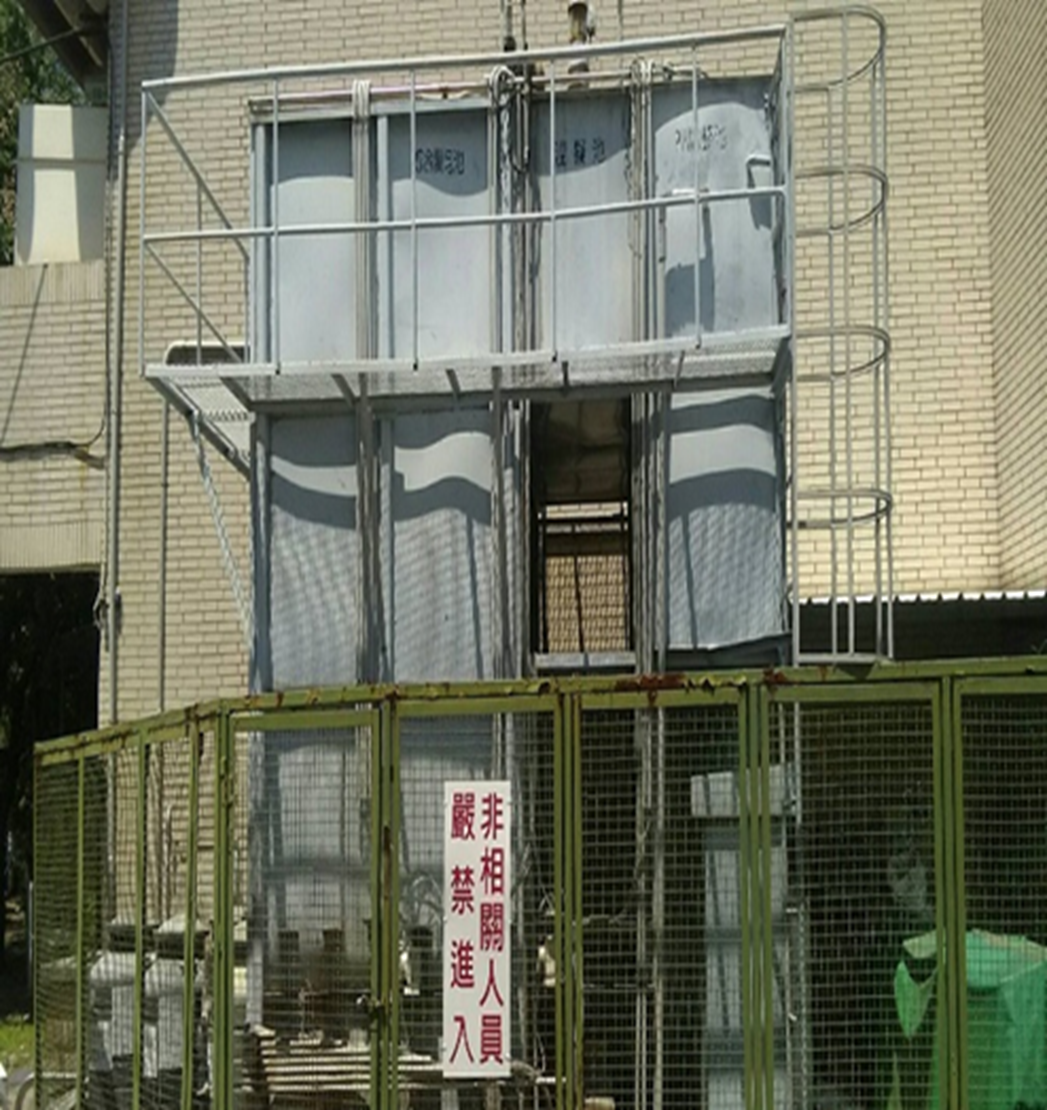
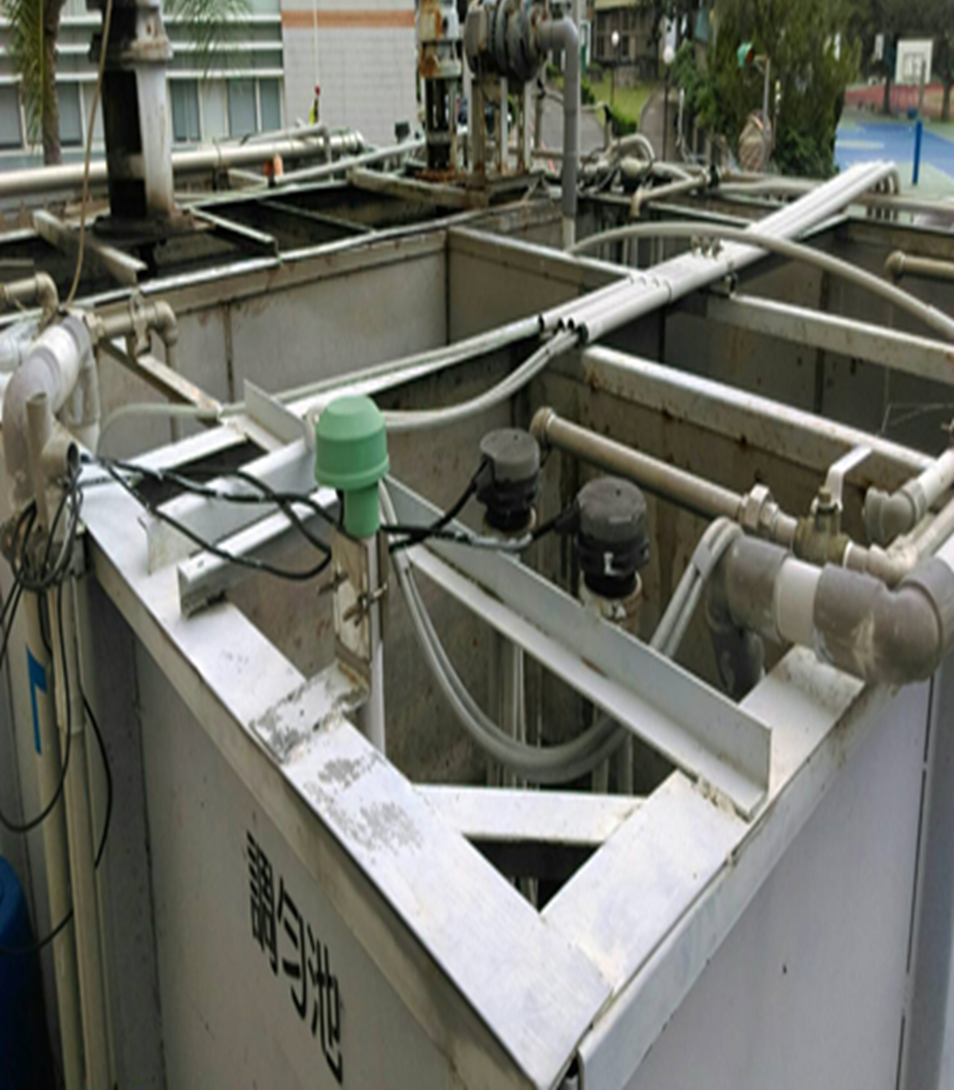


Figure 2-3. Jinde Campus Wastewater Treatment Plant
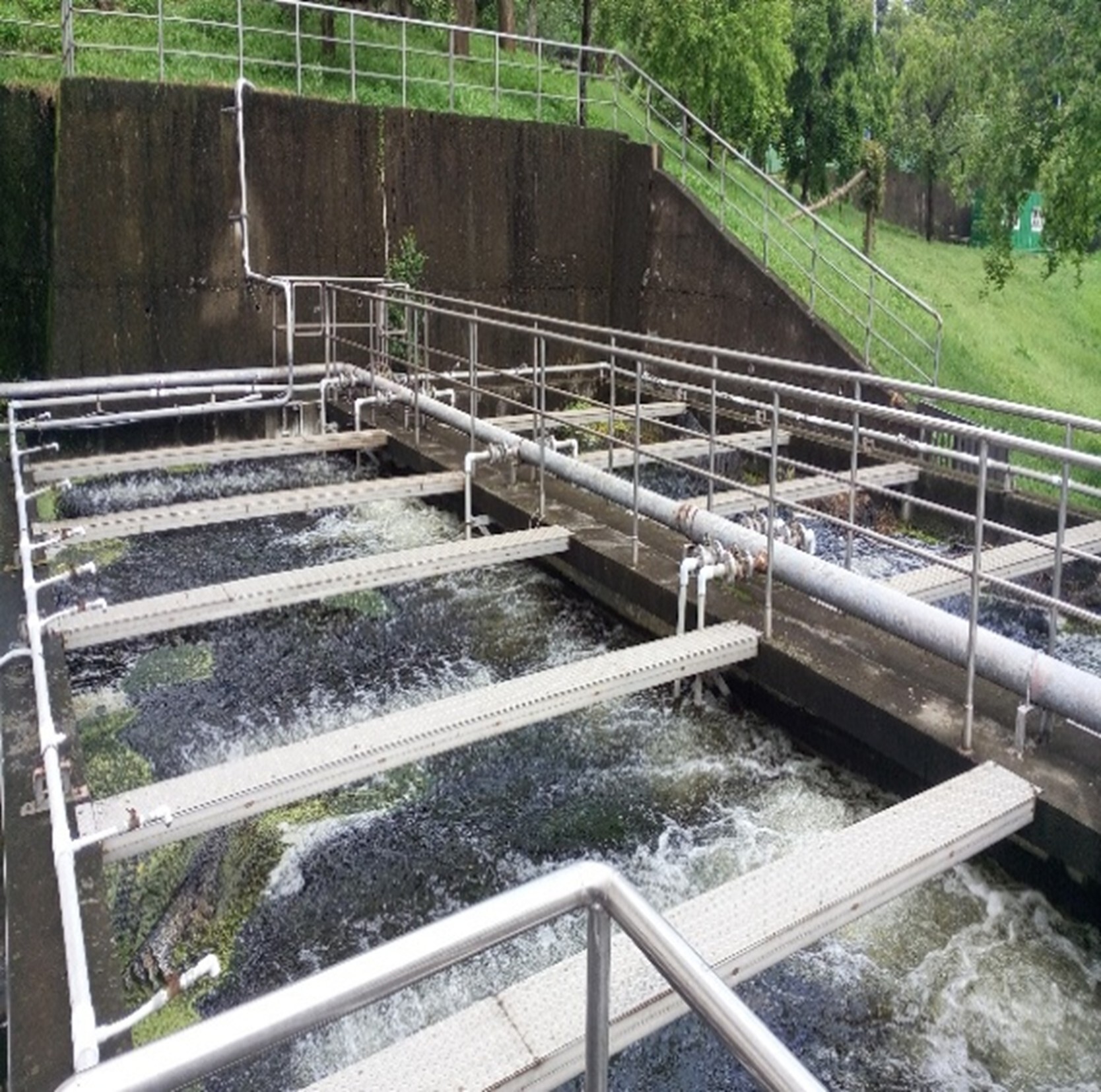
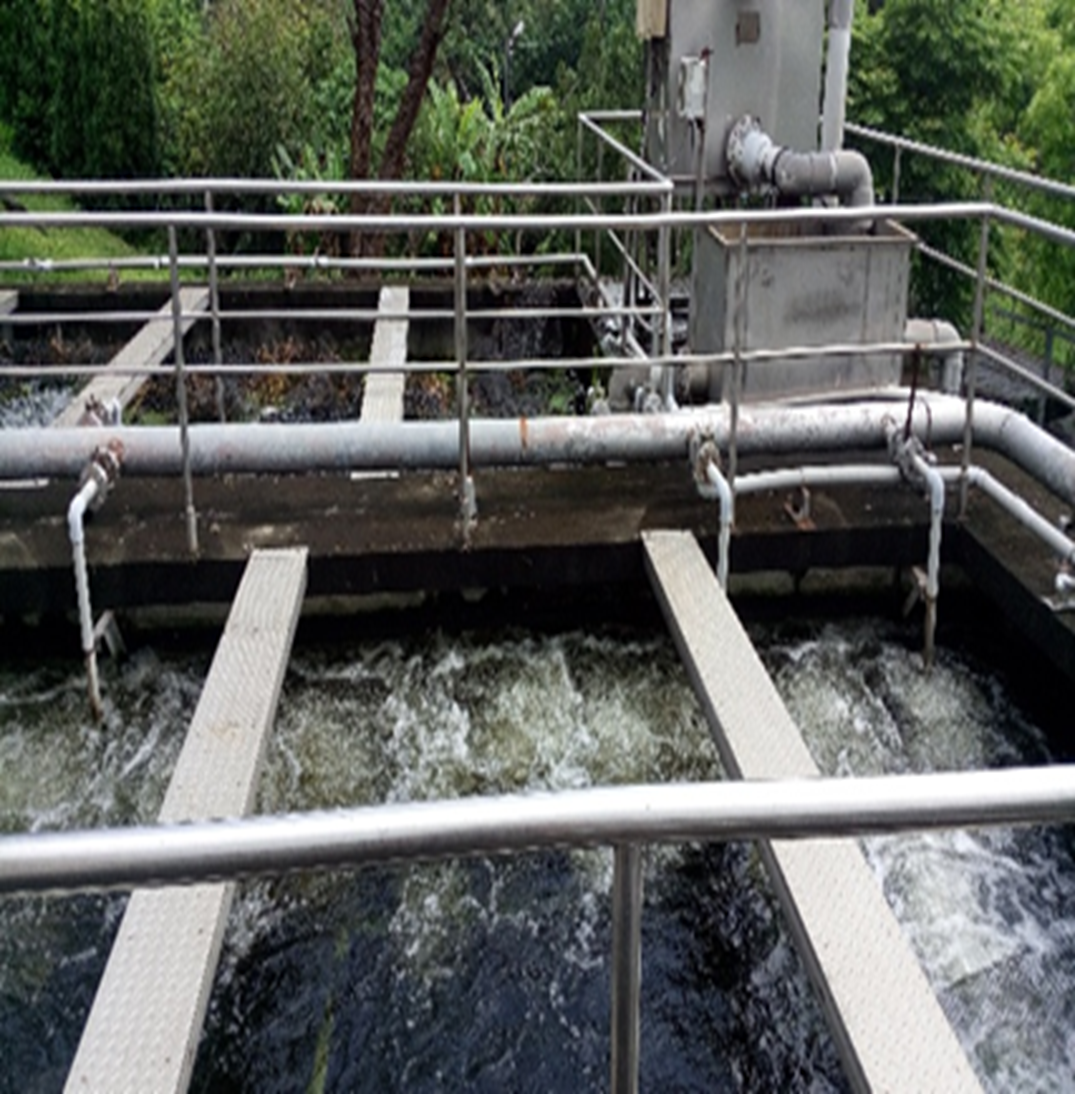


Figure 4-5. Baoshan Campus Wastewater Treatment Plant
(3) In accordance with the Water Pollution Control Act, NCUE’s wastewater treatment plant have to calibrate the water meters annually. The following Figure 5 and Figure 6 are the calibration and correction reports of the school’s wastewater treatment plant effluent water meter, which are issued by an inspection institution accredited by the Ministry of Environment.
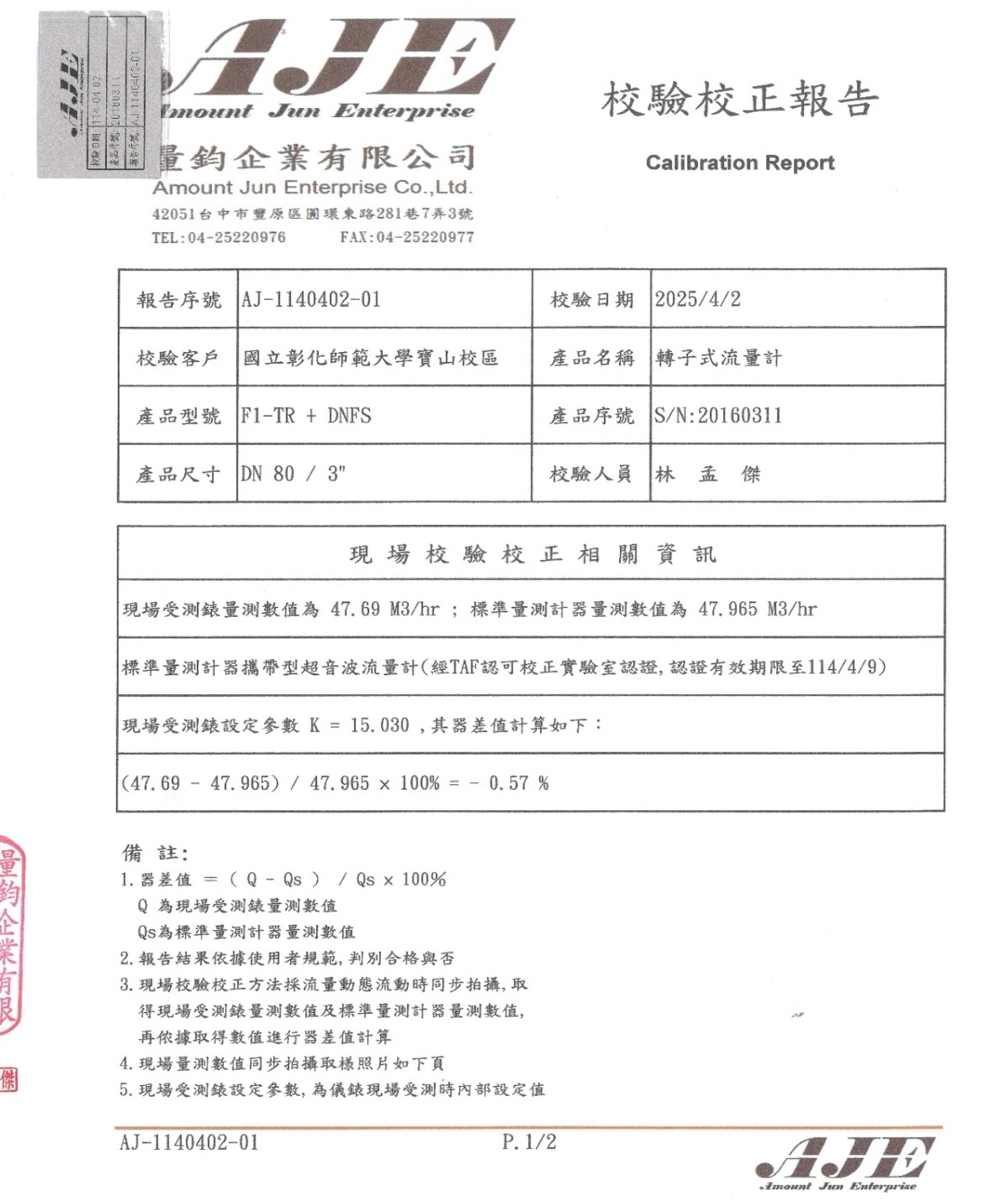
Figure 6. The calibration report of the water meter of NCUE’s wastewater treatment plan (Page 1)
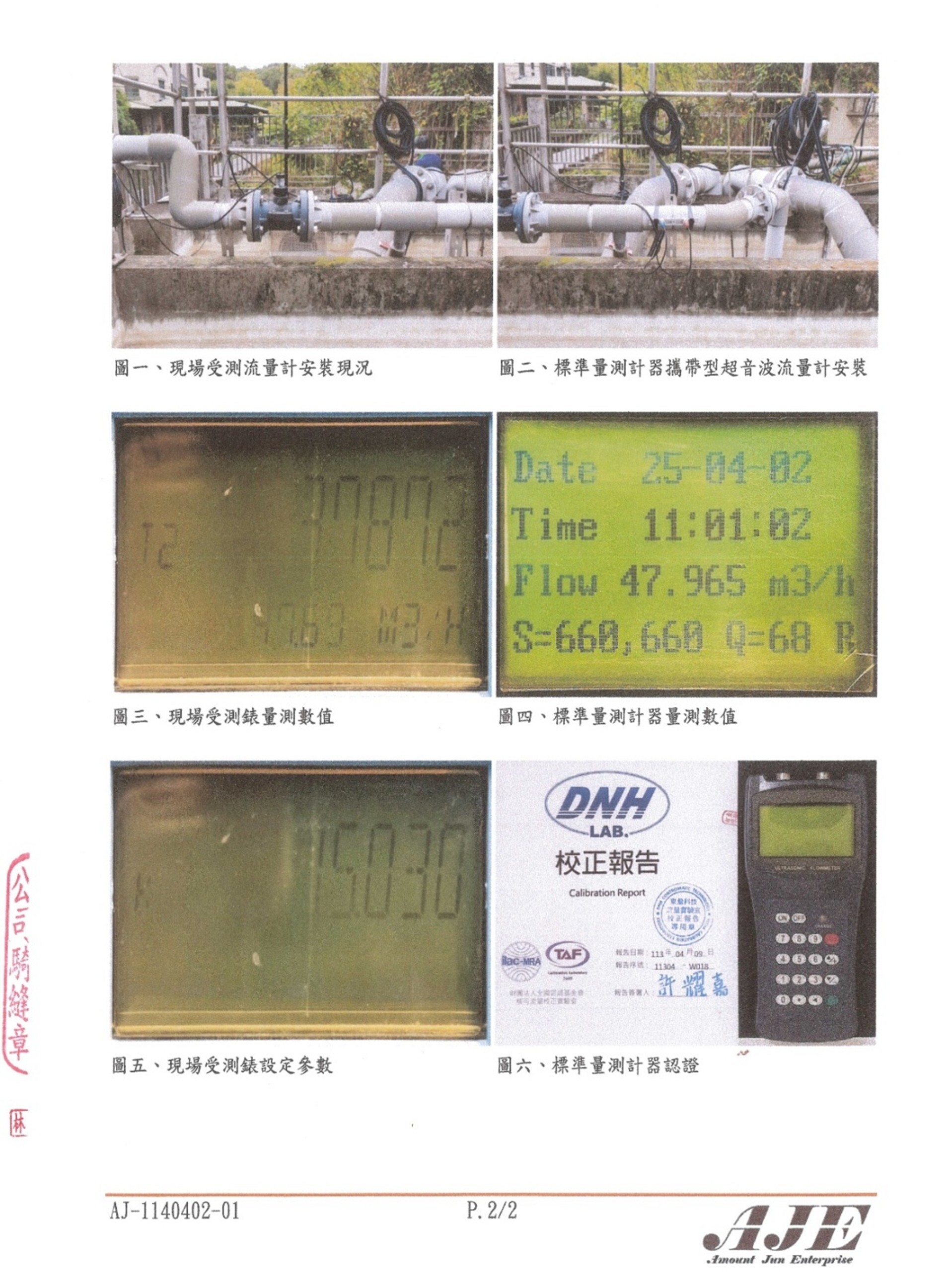
Figure 7. Calibration report of the water meter of NCUE’s wastewater treatment plant (Page 2)
(4) In accordance with the Water Pollution Control Act and Waste Disposal Act, the sludge removal and treatment operations have to be carried out as required, Related photos as shown in Figure 8-11.
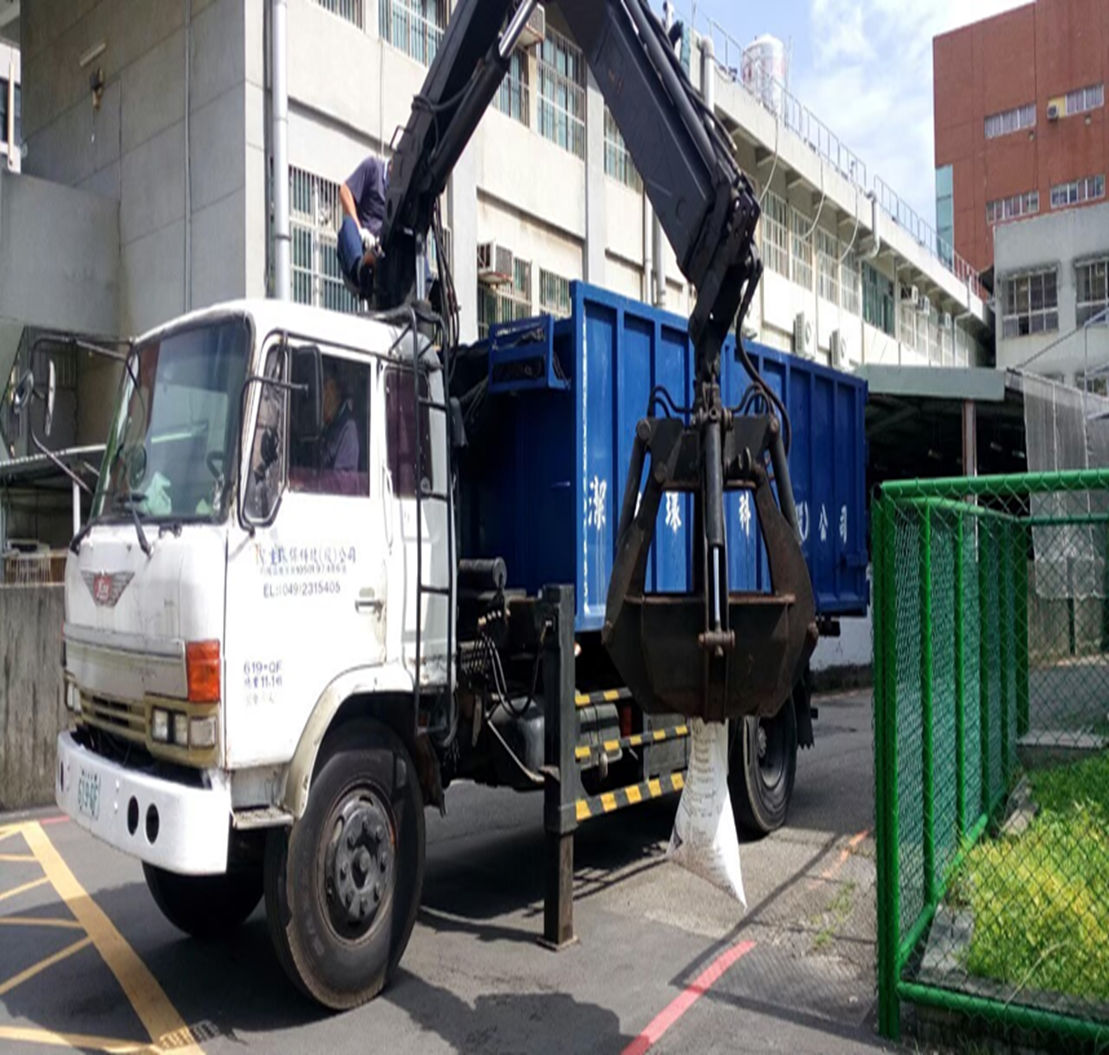
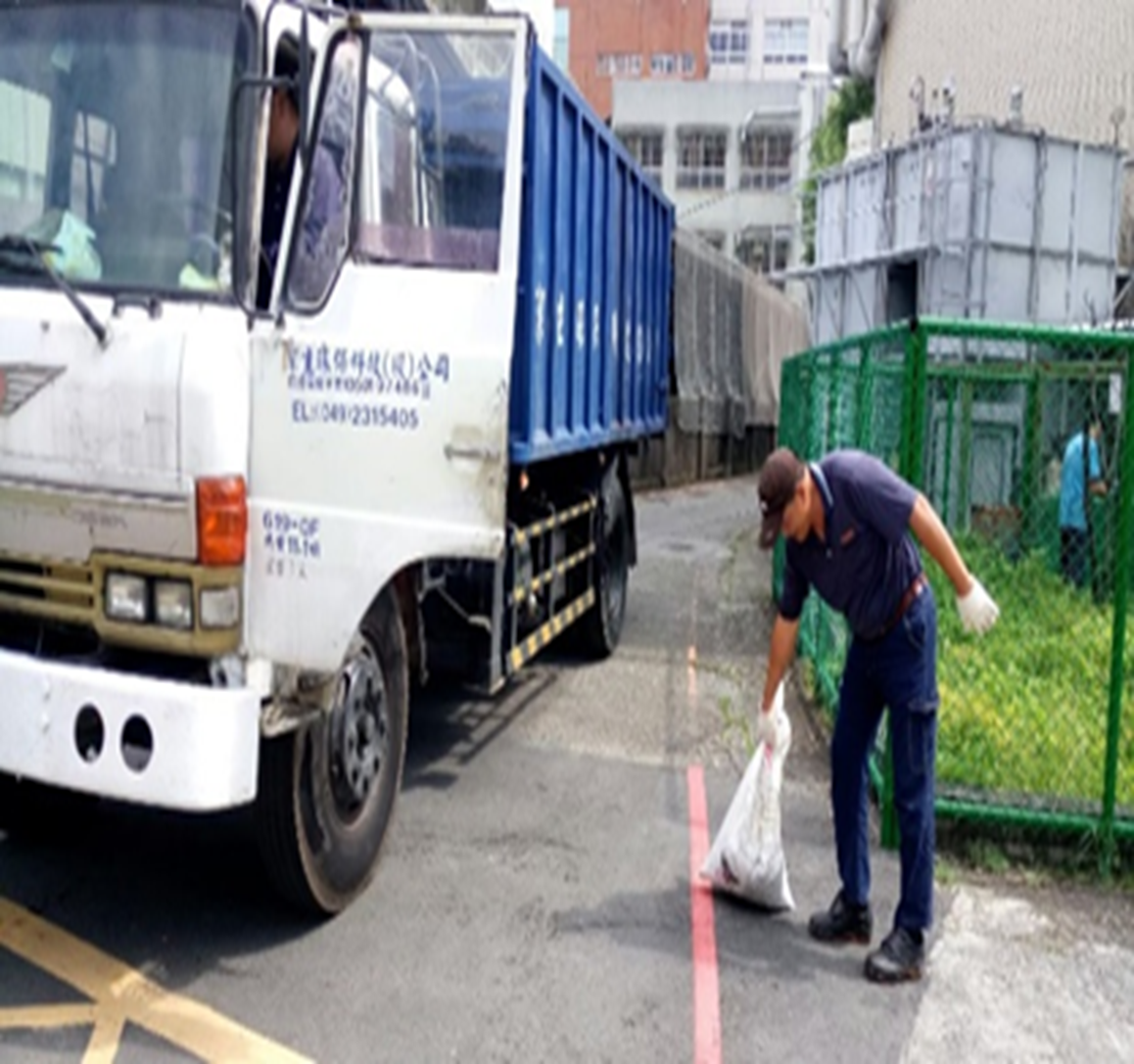


Figure 8-9. Sludge removal and treatment at Jinde Campus
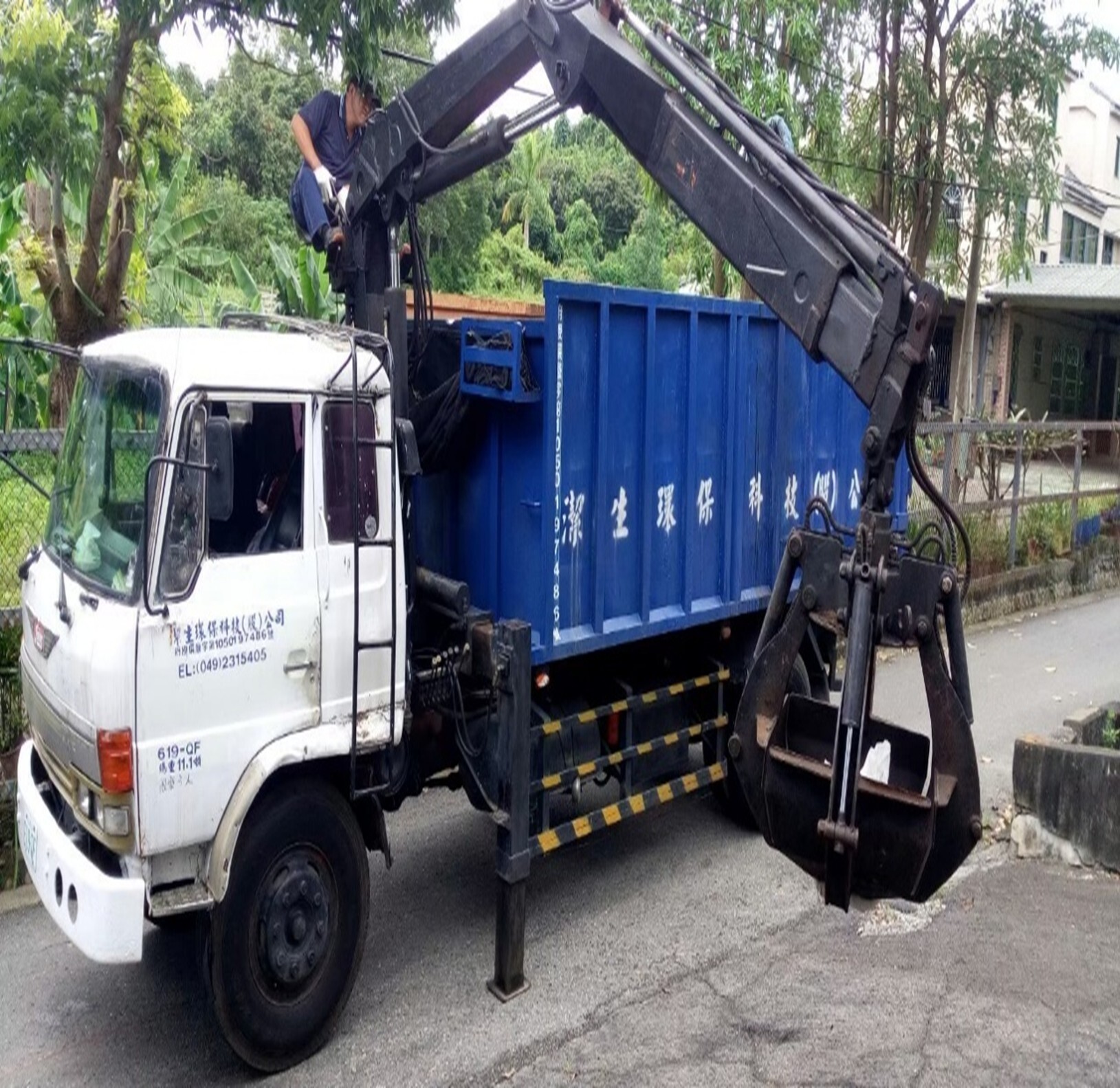


Figure 10-11. Sludge removal and treatment at Baoshan Campus
(5) In accordance with the Water Pollution Prevention and Control Act, water quality inspection is conducted once every six months, and the relevant photos are shown in Figure 12-15.
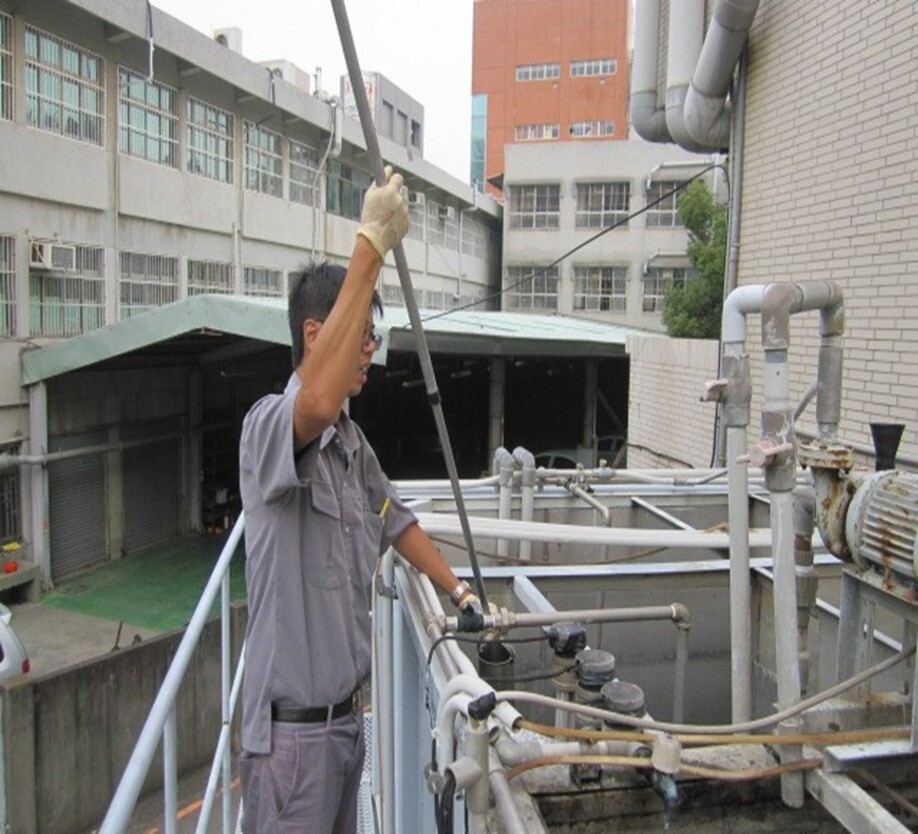
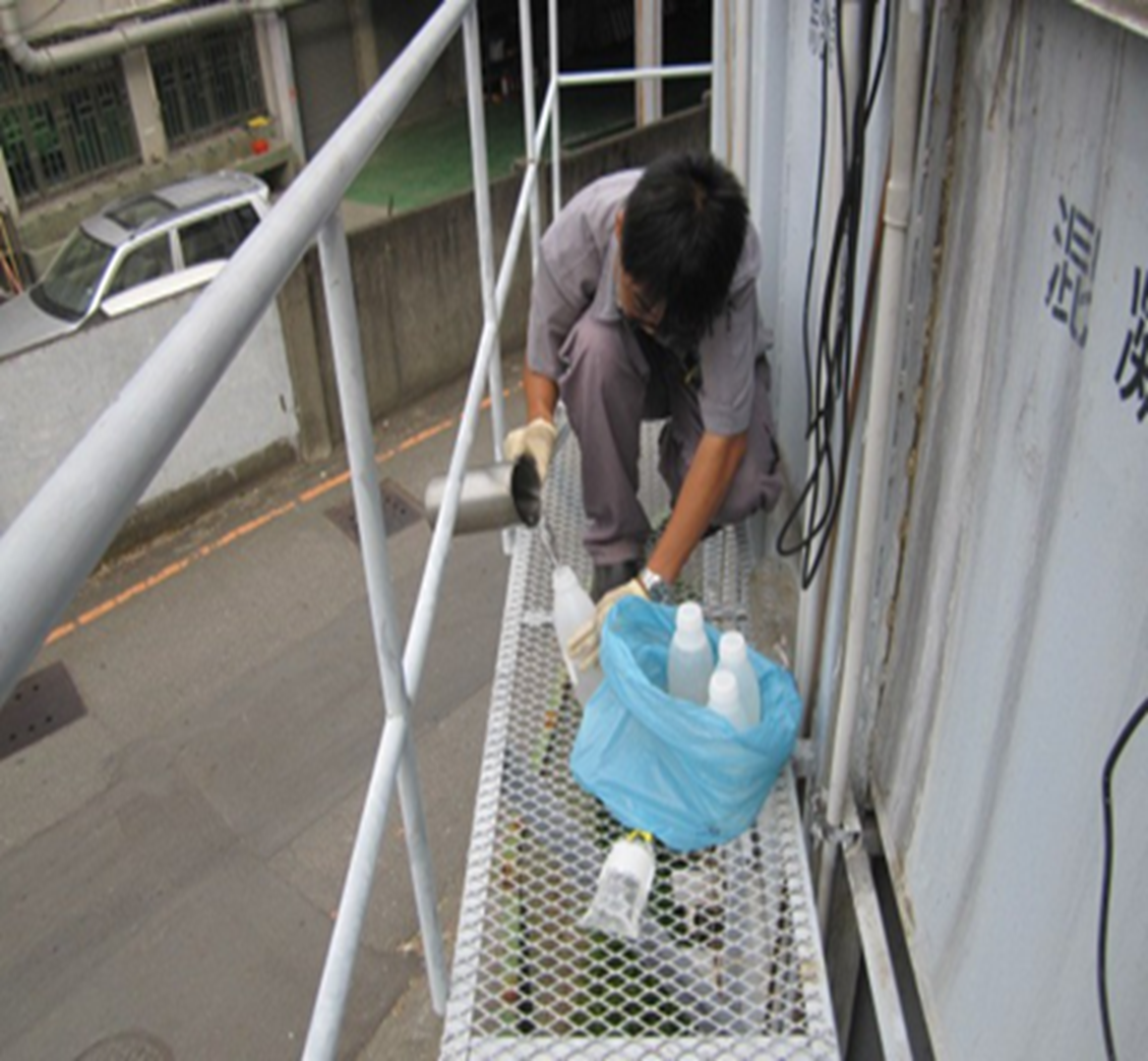


Figure 12-13. Water quality inspection at Jinde Campus
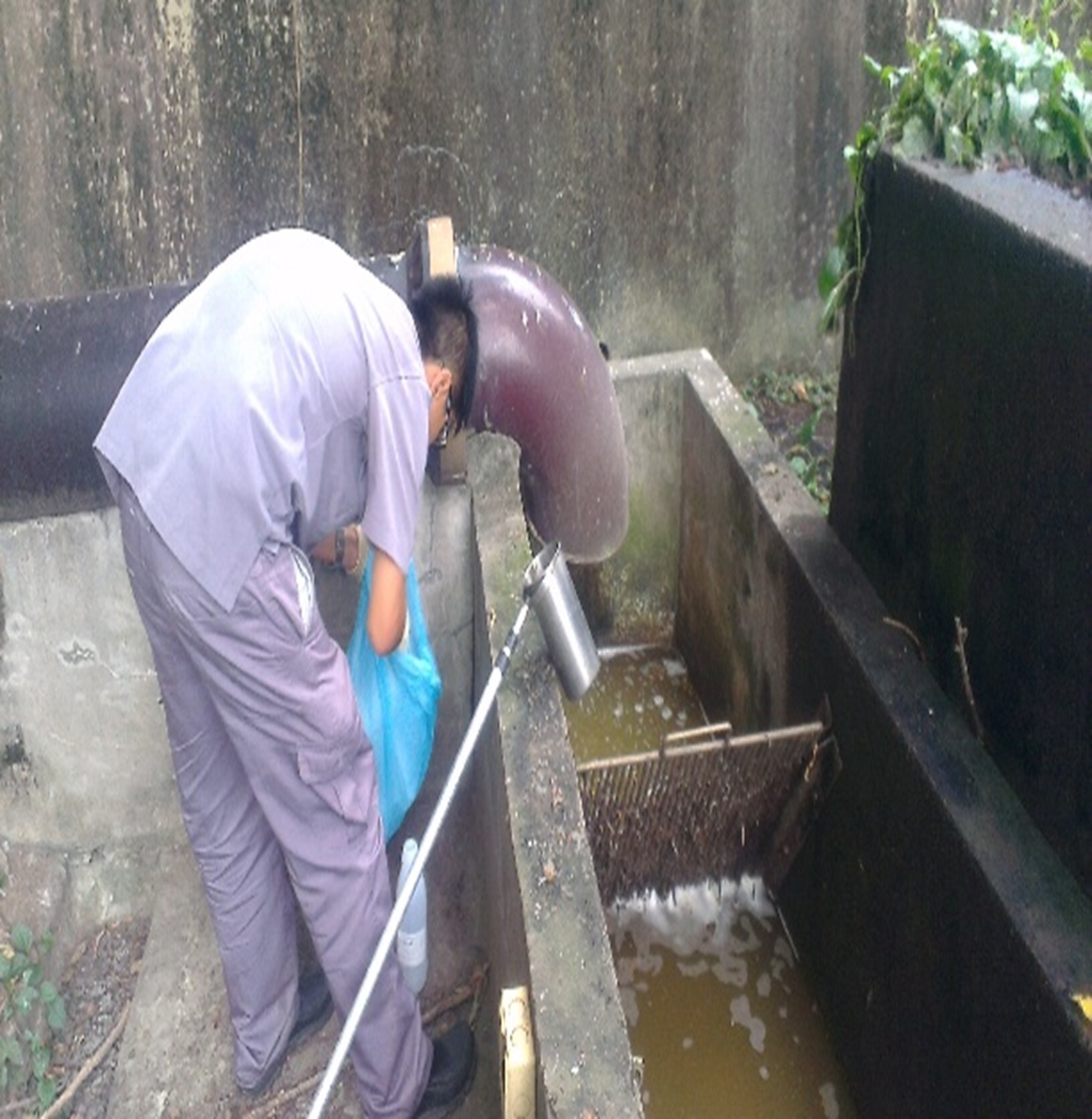
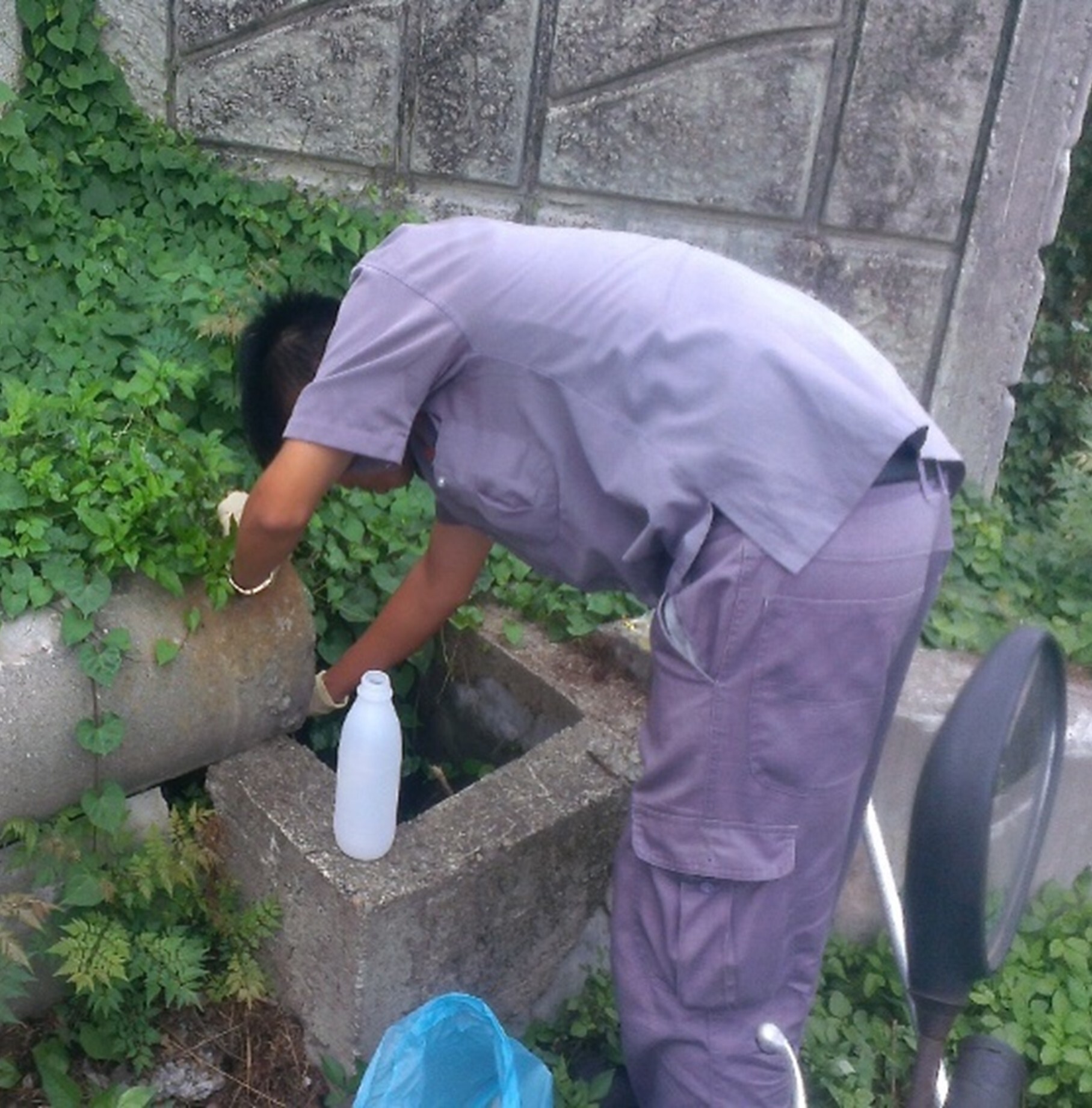


Figure 14-15. Water quality inspection at Baoshan Campus
(6) In 2024, the variety of operations of wastewater treatment plants on both campuses, including water quality inspection and regular reporting all passed the examination.
2. “Beautiful and Treasured Clams in Fangyuan and Dacheng: Sustainable Industry and Environment Project of Changhua’s Two Cities Amid Climate Change” and 2024 Local Marine Conservation Guardianship Program - “Changhua Coastal Hard Clam Habitat Survey and Conservation Education Promotion Project”:
Under the third USR projects, the University offered the courses “Coastal Biological Resources” and “Sustainable Development and Practices of Coastal Biological Resources,” which integrate theories and practices. The curricula covered coastal biodiversity, eco-friendly aquaculture techniques, water and sediment quality testing, fish consumption culture, and the promotion of low-carbon aquaculture. In collaboration with local communities, the courses also advanced marine conservation and sustainable fisheries. In the same year, NCUE carried out the industry–academia collaboration project “Changhua Coastal Hard Clam Habitat Survey and Conservation Education Promotion Project,” conducting a series of marine citizen science courses at Xinbao Wetland and Wanggong Fishing Harbor. Activities included:
(1) Habitat surveys of hard clam (winter, spring, summer, and autumn; four sessions in total, including sediment improvement trials)
(2) Volunteer training for habitat surveys (4 sessions, 41 participants)
(3) “Seed Teacher Training” (3 sessions, 91 participants)
(4) “Little Clam Detectives” educational activities (4 sessions, 185 participants)
The training and practical sessions encompassed water quality testing, biodiversity surveys, bivalve classification, coastal tourism, and conservation education promotion. NCUE also collapsed with Cao-Hu Junior High School, Hanbao Elementary School, and Lukang Elementary School to integrate scientific investigation with local education. Project results show that sediment improvement effectively promotes the growth of coarse-sediment indicator species such as hard clams and corbicula, suppresses the dominance of ring clams, and enhances carbon sequestration potential and benthic biodiversity. In addition, the participation of citizen scientist also effectively increases survey data and strengthens community water resource safety and conservation awareness, successfully establishing a demonstration model that combines scientific research with educational promotion. Relevant photographs are shown in Figure 16.
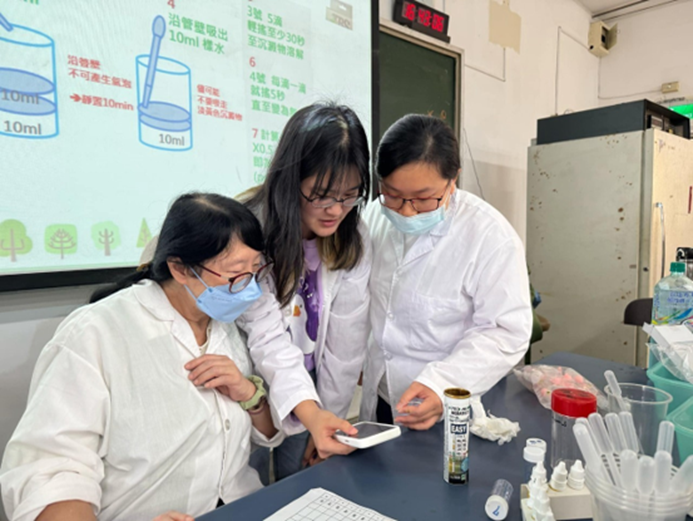

Figure 16. Teachers and students were conducting water and sediment quality assessment in Changhua waters.
Project FB Page Link: https://www.facebook.com/NCUEUSR/

















