SDG 7.2.3 Carbon reduction and emission reduction process
In accordance with the Ministry of Education and national net-zero transition policies, NCUE has established a comprehensive carbon management and emission reduction framework. This initiative encompasses multiple measures, including the development of energy-saving systems, the installations of renewable energy facilities, the application of energy storage technologies, vehicle electrification, and the promotion of public transportation. Through systematic planning and implementation, NCUE has effectively reduced external power purchases and carbon dioxide emissions while enhancing the low-carbon operational efficiency of the campus and surrounding communities. The sustained efforts mark steady progress toward realizing a sustainable, green energy campus.
1. Achievement of Annual Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction Targets
In accordance with the Ministry of Education’s regulations, NCUE has achieved electricity saving of at least 1% annually, thereby effectively reducing the amount of carbon dioxide emissions.
2. Institutionalized Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction Management
NCUE have formulated “NCUE's Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction Implementation Guidelines”, which focus on management measures for power and water conservation, energy saving for lighting and air conditioning, as well as incorporating environmental education courses. The purpose is to reduce our carbon footprint and carbon dioxide emissions. Please refer to Annex 7.2.3A(PDF): NCUE's Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction Implementation Guidelines
3. Carbon Reduction through Photovoltaic Power Generation
NCUE has completed the installation of 2558.375 kWp and 571.5 kW photovoltaic solar power at its Jinde and Baoshan Campuses respectively. Based on the average daily sunlight duration of 3.5 hours in the Changhua region, the total energy production can be calculated as (2558.375+571.5)×365×3.5= 3,998,415 kWh (14,394 GJ). According to the 2024 carbon emission factor for electricity published by the Ministry of Economic Affairs at 0.474kg of CO2 per kWh, this would result in a reduction of approximately 3,998,415×0.474=1,895,249 kg of carbon emission.
4. Energy Storage Systems for Peak Shaving and Valley Filling to Assist Emission Reduction
NCUE's Baoshan Campus is equipped with a 1 MW/1.26MWh energy storage system (Figure 1), along with two additional 100 kW/50 kWh energy storage systems that support the operation of the campus microgrid (Figure 2).
(1) This system allows for the storage of energy during off-peak nighttime hours and its release during daytime peak periods, effectively achieving load shifting (Figure 3). This approach reduces the output of coal-fired power plants during peak hours, thereby decreasing carbon emissions from power generation. Additionally, using energy storage for peak shaving and valley filling helps to smooth the daily load curve, reduces peak line currents, and consequently decreases power transmission losses by approximately 3%, contributing to energy conservation and carbon reduction.
(2) NCUE utilizes an energy storage system to reduce the contract capacity from 835 kW to 785 kW (Figure 4), decreasing overall external power purchases.
5. Integration of Electric Vehicles with Energy Storage
In addition, NCUE has purchased a 30 kW/78 kWh electric bus to replace traditional internal combustion engine vehicles (Figure 5). This not only aligns with the EV100 initiative’s objectives but also allows us to use the electric bus as an energy storage system during periods of inactivity, thereby supplementing the aforementioned load-shaving and valley-filling benefits.
6. Promotion of Public Transportation and Low-Carbon Commuting
Since 2014, the main entrance of NCUE's Jinde Campus has provided space for the Changhua County Government to establish public bicycle stations (YouBike and MOOVO systems). The service contract was renewed in 2024 and is scheduled to continue through 2026 for the MOOVO system (see Figure 6). In 2025, NCUE coordinated with the Changhua County Government to evaluate the feasibility of installing three additional public bicycle stations near the Baoshan and Jinde campuses. This expansion not only provides faculty, staff, and students with greater convenience and options for short-distance transportation but also encourages broader adoption of public transportation. Ultimately, these measures support the goals of low-carbon, environmentally friendly, and energy-efficient commuting.
7. Charging Infrstructure and Transportation Decarbonization
In accordance with government net-zero transition policies, NCUE has actively advanced vehicle electrification and transportation decarbonization initiatives as part of its carbon managementframework. In November 2024, car charging stations were completed at both the Jinde and Baoshan campuses (2 stations at Jinde Campus, 1 station at Baoshan Campus; see Figures 7-9). These facilities serve not only campus users but also nearby community residents, promoting clean energy vehicles and reducing transportation-related carbon emissions. At the same time, NCUE's security team has taken the lead in adoptingsmart green energy electric motorcycles (Figures 10-11) as the primary mode of patrol and campus security transportation. The transition has reduced carbon emissions while improving patrol efficiency and minimizing noise. Moving forward, NCUE will continue to enhance campus campus electrification infrastructure by integrating, charging facilities with vehicle management systems, progressively establishing a low-carbon and sustainable transportation environment.
Through the integrated promotion of institutionalized management, renewable energy development, smart energy storage applications, and transportation decarbonization strategies, NCUE has established a comprehensive carbon emission reduction management process. This initiative not only fulfills annual energy conservation and carbon reduction goals, but also creates a demonstrative and sustainable low-carbon environment for both the community and campus.

Figure 1. Baoshan Campus 1 MW/1.26 MWh Energy Storage System

Figure 2. 100 kW/50 kWh Energy Storage System
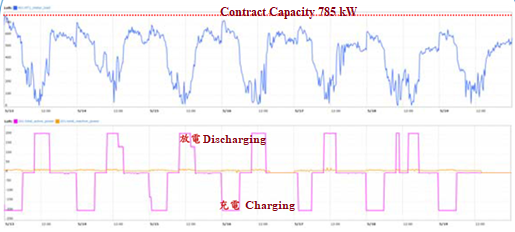
Figure 3. Effect of Load Shifting
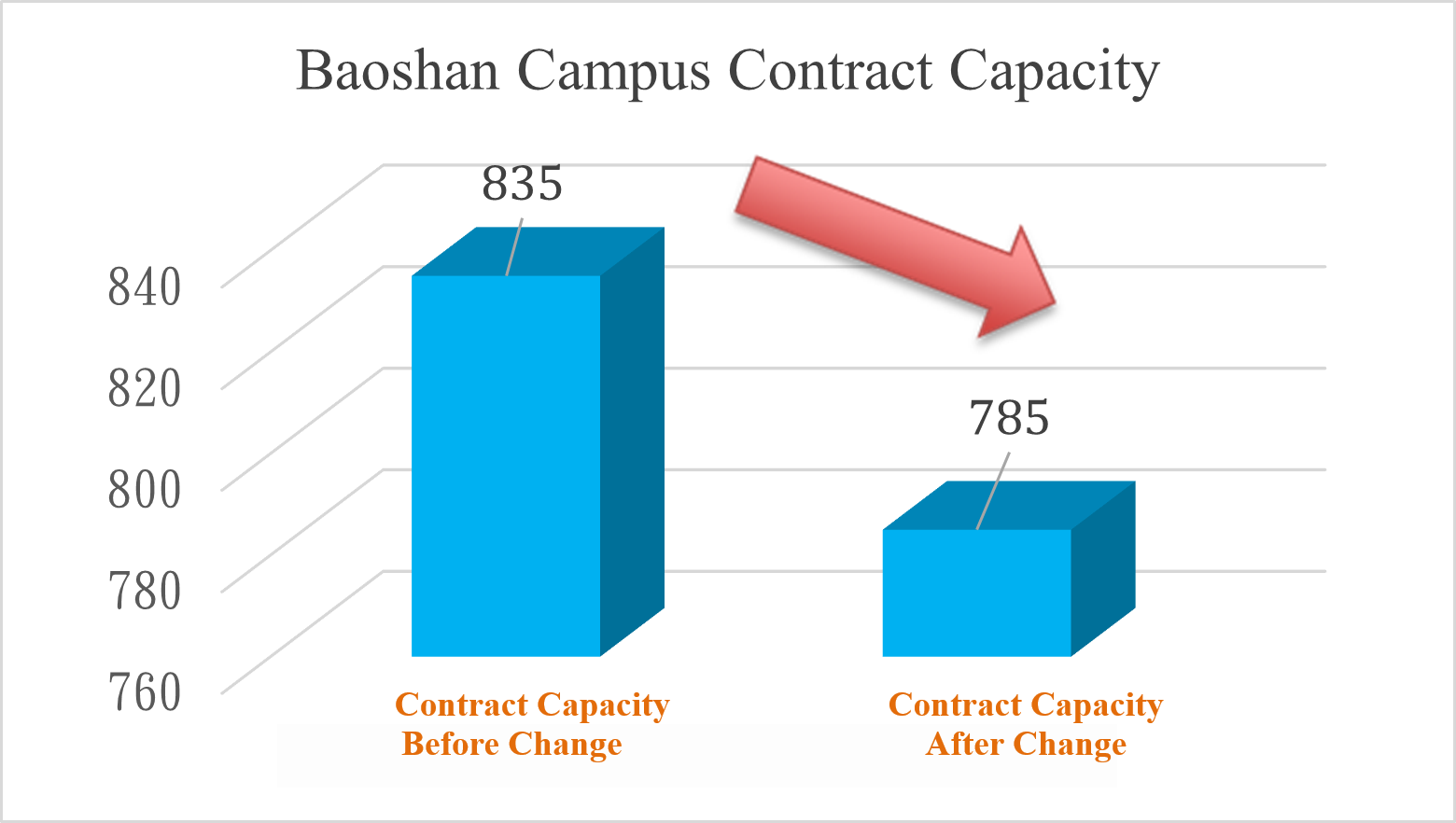
Figure 4. Reduction of Contract Capacity in Baoshan Campus

Figure 5. 30 kW/78 kWh Electric Bus

Figure 6. MOOVO Public Bicycle Station at the Main Entrance of Jinde Campus
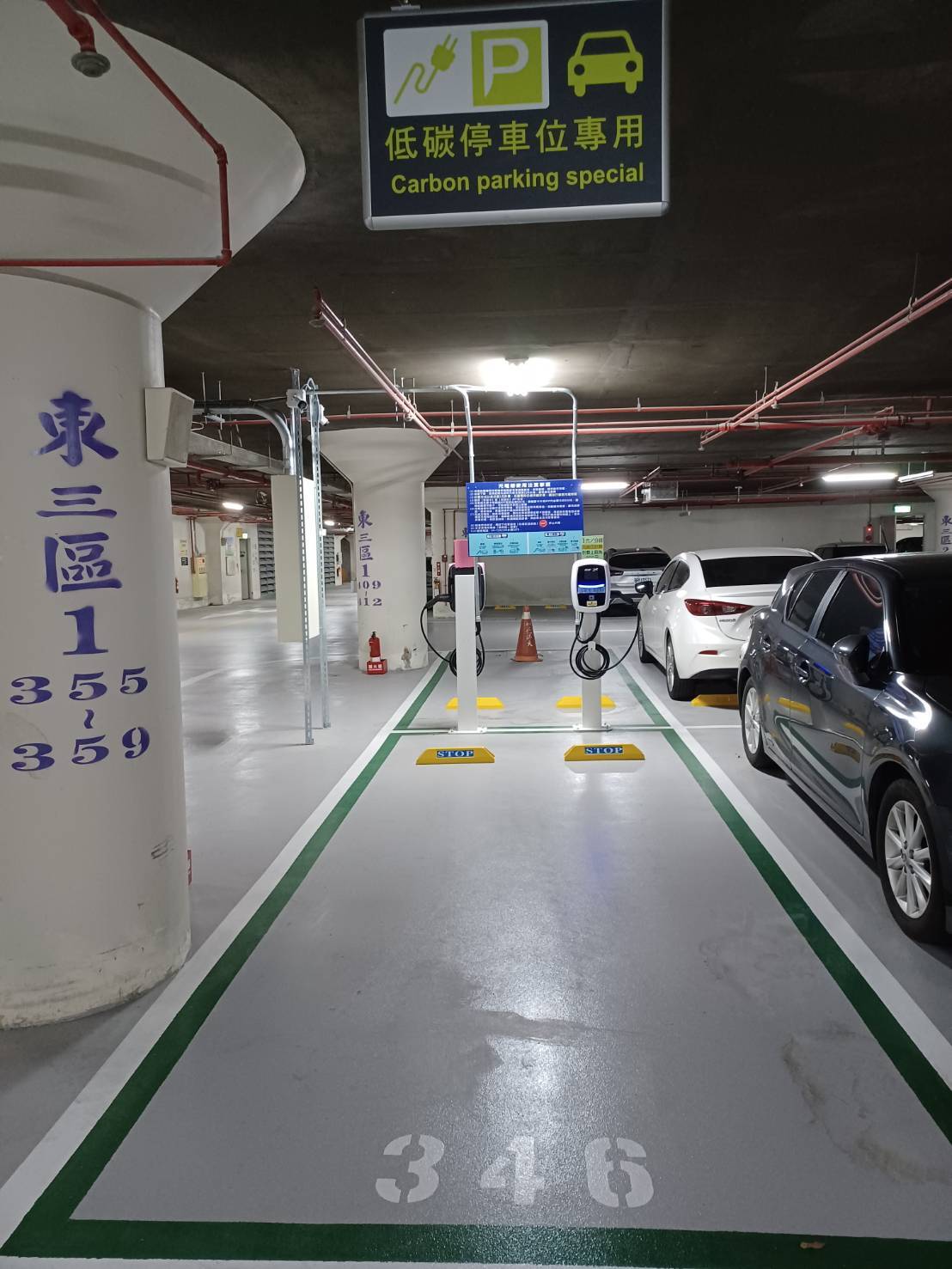

Figure 7. Charging Equipment at Jinde Campus Parking Spaces
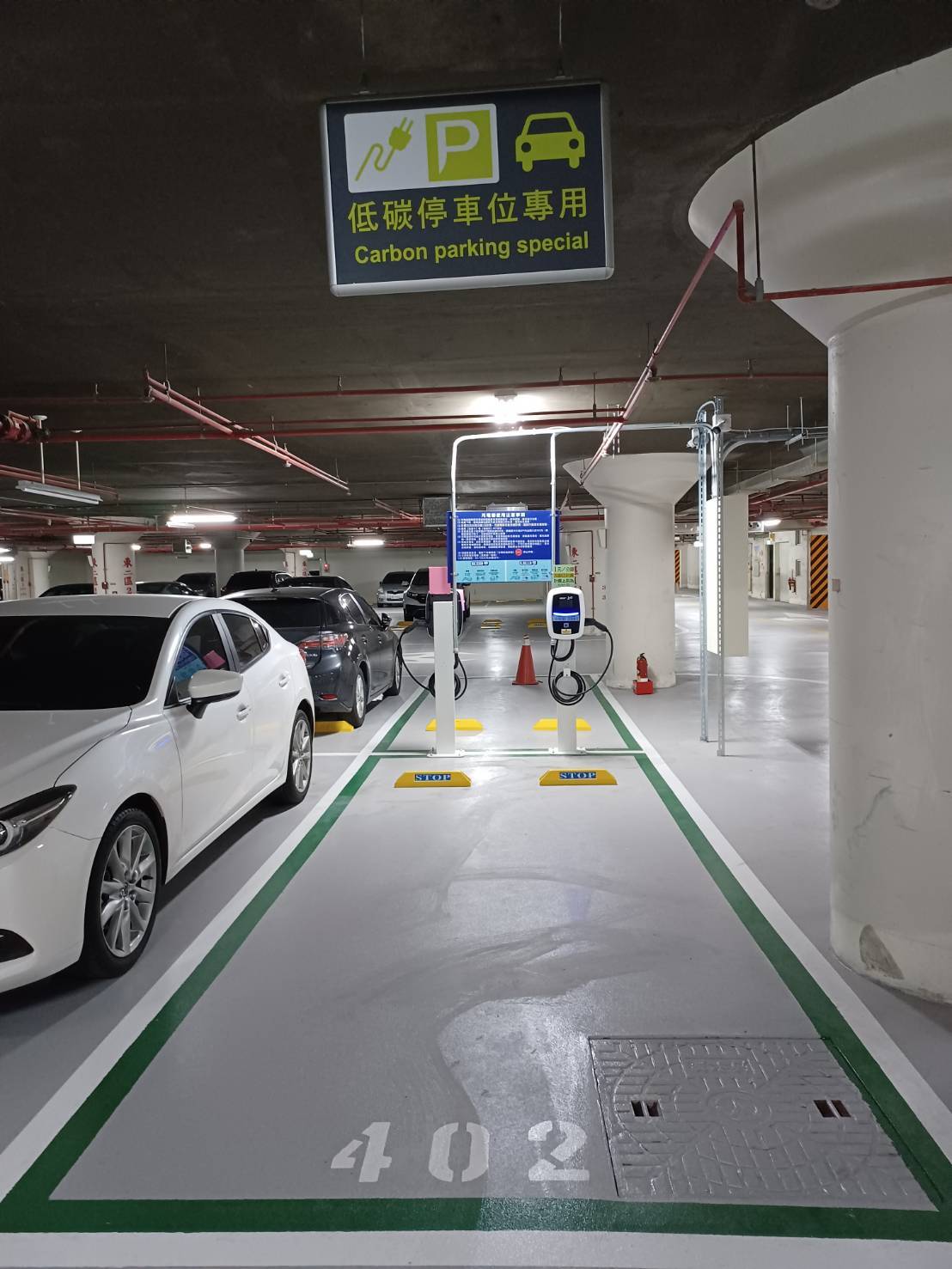

Figure 8. Charging Equipment at Jinde Campus Parking Spaces
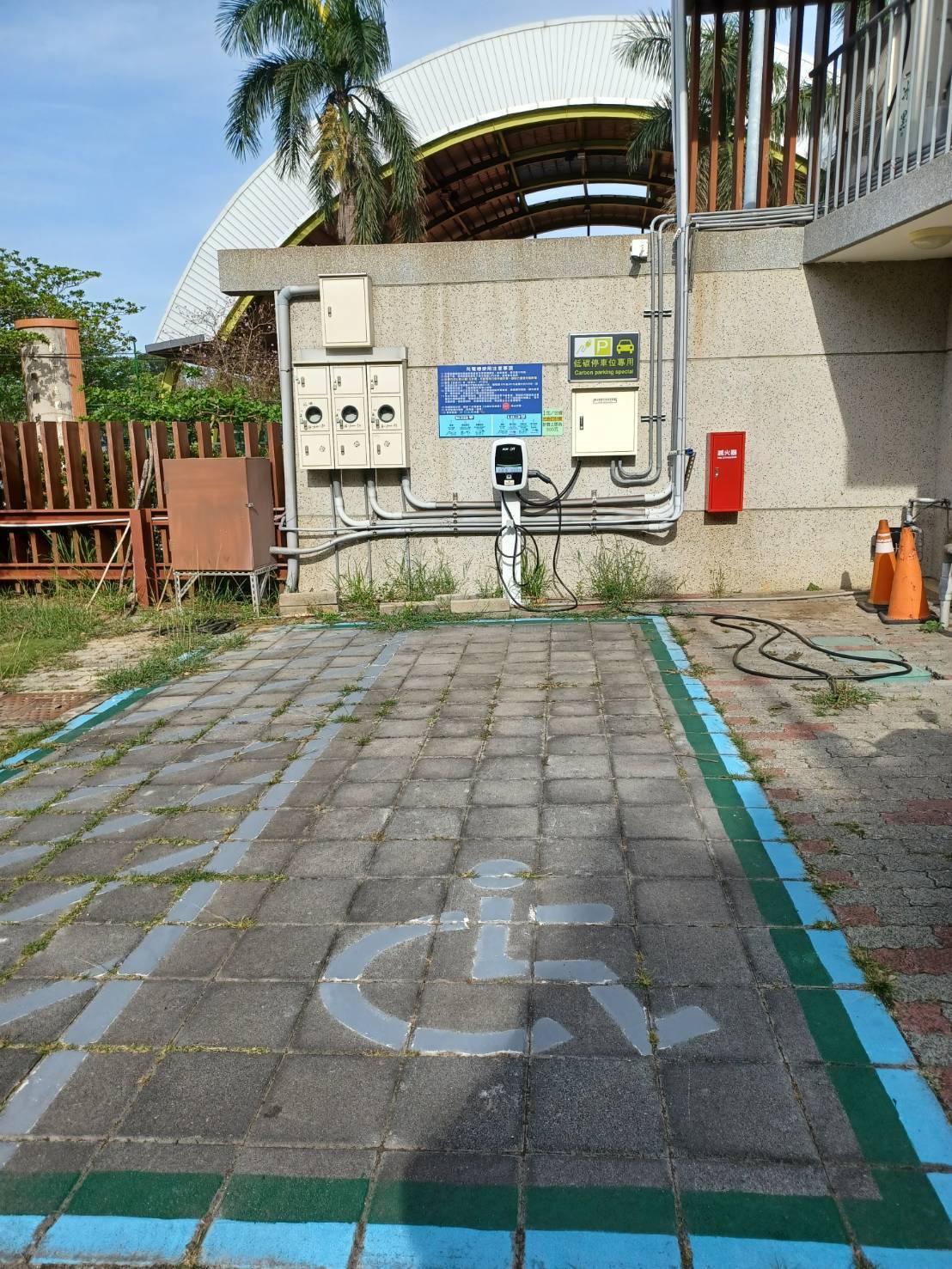

Figure 9. Charging Equipment at Baoshan Campus Parking Spaces

Figure 10. Security Team Riding Electric Patrol Motorcycles at Jinde Campus
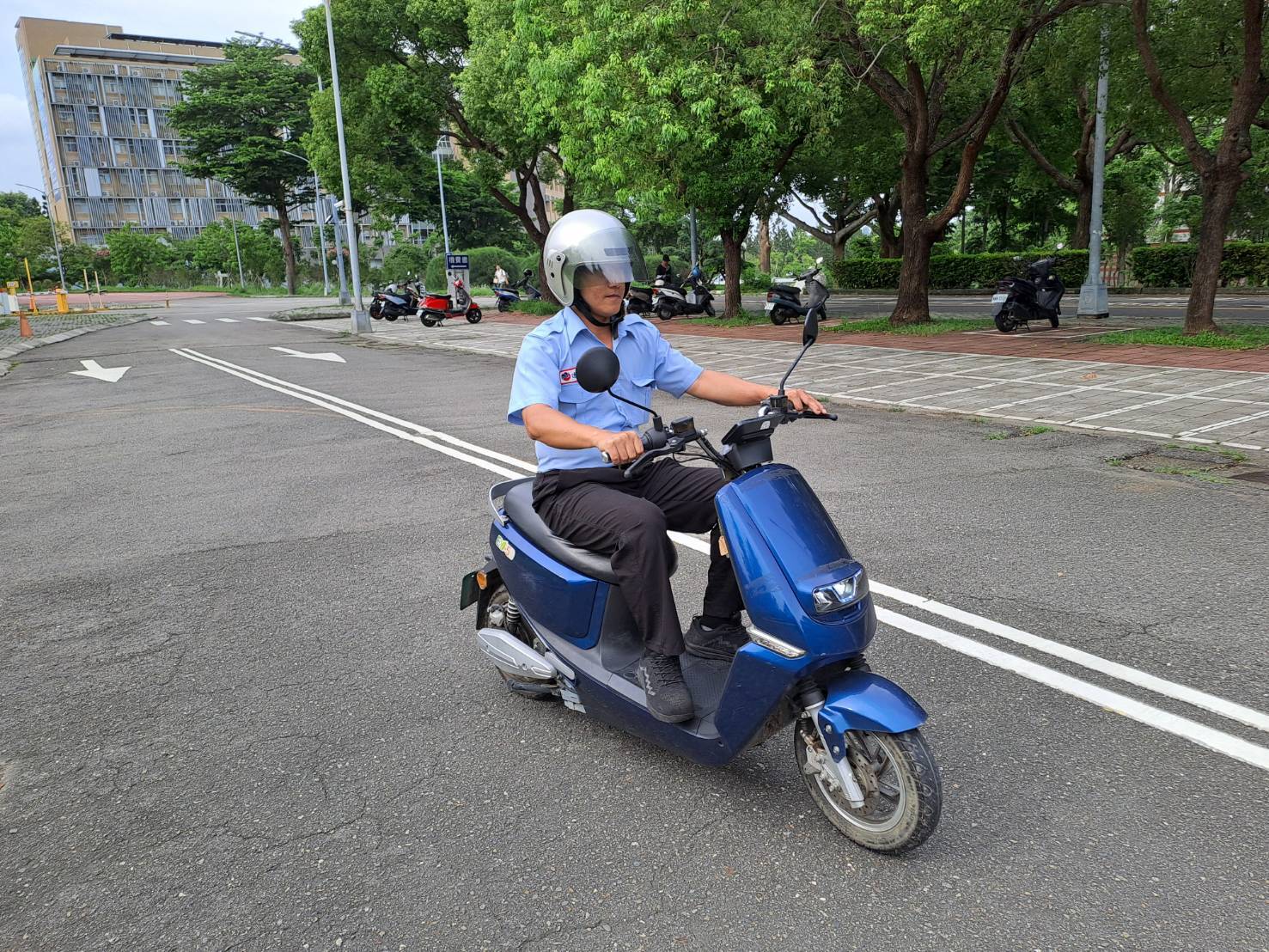

Figure 11. Security Team Riding Electric Patrol Motorcycles at Baoshan Campus

















