SDG 6.5.6 Promoting conscious water usage on campus
1. NCUE has established smart campuses that operate on a sustainable living platform and has implemented various strategic measures in accordance with the United Nations’ sustainable development indicators. Regarding water resources, conductivity and pH values are monitored at the three wells on campus. Real-time data are obtained through water quality detection sensors, and the detected data are then transmitted to the water resources monitoring system in real time on the Internet. These facilitate the effective management of the wells’ water quality and the optimal distribution and utilization of the water resources. The sustainable living platform allows staff and students to grasp real-time water monitoring data, understand the importance of water resources management, and learn to value water resources.
2. We promote an awareness of water conservation regularly through public announcements (Figure 1) and requests that all staff and students assist by reporting water leakages of any equipment inside the buildings via the internal maintenance system. This leads to the timely and effective elimination of faulty and leakage issues. In addition, campus electricians conduct daily readings of the main water meters. Upon detecting any abnormal readings, they will initiate a campus-wide inspection to determine if there are any leaks. If a leak is found, immediate action is taken to address the issue (Figure 2). Water Conservation Awareness Announcements:
https://apss.ncue.edu.tw/odedi/doc_page.php?id=./6221/-63/.0-
Figure 1. 10 Great Water-Saving Habits

Figure 2: water meter readings, which are recorded by NCUE electrical staff daily
3. For facilities with higher levels of water consumption, water utilization measures are adjusted according to demand. For example, the sprinkler irrigation system will not activate when it detects rain, and the lease contract of the campus swimming pool requires the tenant to cooperate with the government’s water conservation measures. These measures ensure the rational utilization of water (Figure 3).

Figure 3: The above picture shows that NCUE uses rain sensors to control the sprinkler irrigation system to achieve the benefits of effective use of water resources.
4. To cultivate awareness of reasonable water use and water resource sustainability among faculty and students, NCUE actively integrates "water resource conservation" and "environmental sustainability" issues into curricula and practical experiences. Through courses, experimentation, field research, and service learning, students develop correct concepts and action capabilities for water use. Related measures are as follows:
(1) Center for General Education Courses
(a) The "Water Resources and Human Civilization" course offered by the General Education Center in 2024 focuses on introducing global and Taiwan's water resource challenges. Through this course, students explore the historical and contemporary significance of water for human society and its key role in sustainable development. The course examines the impact of water resource changes on human history. Students learn how to understand sustainable water use and reflect on how individuals and society should conserve water in daily life.
(b) The " Water and Electricity Energy Saving in Modern Life " course introduces students to the basic principles of water resources and power sources to understand their importance and environmental impact, while cultivating students' water and electricity conservation capabilities.
(c) Related course syllabus information:
i. https://webap0.ncue.edu.tw/DEANV2/UploadDEAN/SUBJECT/1131/00243_0CCGE0175120.pdf(PDF)
ii. https://webap0.ncue.edu.tw/DEANV2/UploadDEAN/SUBJECT/1122/0232_0CCGE0178720.pdf(PDF)
(2) Courses from the "Beautiful and Treasured Clams in Fangyuan and Dacheng: Sustainable Industry and Environment Project of Changhua's Two Cities Amid Climate Change"
(a) The project offers "Coastal Biological Resources" and "Sustainable Development and Practice of Coastal Biological Resources" courses, which combine theory and practice. By introducing coastal environmental characteristics, marine ecological diversity, and human environmental impact, students could understand the limitations and vulnerability of water resources, thereby establishing concepts of cherishing and reasonable utilization. The courses cover friendly aquaculture techniques, water quality and sediment testing (Figure 4), fish-eating culture, and low-carbon aquaculture promotion, allowing students to understand the importance of water resource monitoring and management through practical operations, and NCUE even cooperates with local communities to promote marine conservation and sustainable fisheries.
(b) Course syllabus information:
i. https://webap0.ncue.edu.tw/DEANV2/UploadDEAN/SUBJECT/1131/24004_1SCBI0220930_EN.pdf(PDF)
ii. https://webap0.ncue.edu.tw/DEANV2/UploadDEAN/SUBJECT/1132/24004_1SCBI0221030_EN.pdf(PDF)
(c) Project activity Facebook page link: https://www.facebook.com/NCUEUSR/

Figure 4. Coastal Biological Resources Sustainable Development and Practice course: teachers and students were conducting water quality and sediment testing in Changhua waters
(3) Department of Geography "Hydrology" Course Geographic Field Investigation: In the first semester of Academic Year 2024, a hydrology course was offered in the Department of Geography with approximately 43 students enrolled. The course content covered understanding of water cycles and water resource balance, along with field investigations. The investigation site was the Zhongguakeng Stream watershed in Nantou County (as shown in Figure 5), observing the crises faced by mountain streams under the impact of climate change and possible actions to take. Nature-based solutions are an adaptive strategy option for responding to climate change. Through the activity, students learned the advantages and disadvantages of nature-based solutions for stream governanceand understand sustainable wild stream governance strategy options available for consideration today.
Zhongguakeng Stream is a tributary of the Wu River. In the past, traditional engineering caused damage to the stream environment. Now, concrete is being removed to create a naturally friendly environment, seeking a win-win outcome for both humans and natural ecology. Students on-site can fully appreciate the pleasure that natural streams bring to people and observe water flow velocity, water depth, and aquatic organisms. The field investigation activity reflects on how individuals and society should respond to climate change impacts and the possible effects of response strategies from a sustainable perspective.
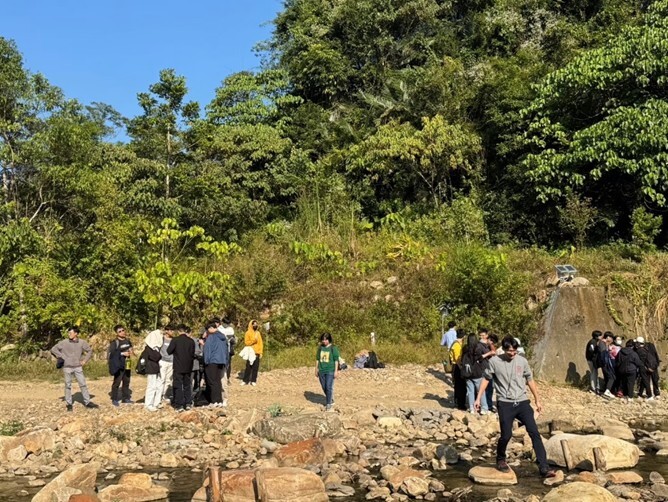

Figure 5. Group discussions at the Zhongguakeng Stream.
5. Smart Water Meter Installation and Enhanced Water Management
NCUE plans to install 7 ultrasonic smart water meters at the Jinde Campus and add 23 new ones at the Baoshan Campus by the end of 2025 (schematic diagram shown in Figure 6). At the Baoshan Campus, each building will be equipped with groundwater and tap water meters to monitor water usage data for each building. The university can evaluate the water usage patterns by analyzing the water consumption and event data wirelessly transmitted from smart water meters. The flow trend charts automatically generated by the management system can be used to detect abnormal water usage. Real-time data obtained from smart water meters enables effective management of on-campus water usage and provides instant water resource monitoring information. By installing smart water meters across the campus, NCUE can consolidate various water resource data throughout the campus to serve as a basis for water resource balancing, allocation, leak detection, and management.

Figure 6. Smart water meter diagram
6. Through diverse measures including smart water meter installation, smart campus sustainable life platform real-time monitoring, public announcements, repair reporting systems, and water-saving facility adjustments, NCUE has not only effectively strengthened campus water resource management mechanisms but also enabled faculty and students to grasp water resource conditions in real-time, enhancing awareness of water resource conservation and reasonable utilization. In addition, the university integrates "water resource conservation" and "environmental sustainability" concepts into curriculum teaching, field investigations, and community cooperation, allowing students to develop from knowledge understanding to action practice, cultivating civic literacy that combines professional capabilities with sustainability awareness, promoting reasonable campus water use and water resource sustainability.

















