SDG 14.4.1 Water discharge guidelines and standards
Water quality and drainage standards are set for both NCUE campuses; the Environmental Education Center organize related activities.
1. NCUE has two campuses, Jinde and Baoshan, and the procedure is as follows:
(1) In accordance with the regulations of the Waste Disposal Act, the laboratory waste liquid of the Jinde campus is supposed to be cleaned and disposed of as industrial waste. Following application, the Environmental Protection Bureau of Changhua County Government approved the cancelation of the water pollution prevention and control permit of the Jinde campus and removed it from the management list of the government. The original sewage treatment facilities are still in normal operation.
(2) The Baoshan campus mainly treats general domestic sewage.
NCUE manages all generated effluent by routing it through a centralized wastewater treatment plant. The treated water is then discharged through outlets approved and regulated by the authorities. The university complies with the regulations outlined in the Water Pollution Control Act (Link: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?media=print&pcode=O0040001) and Water Pollution Control Act Enforcement Rules (Link: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?media=print&pcode=O0040002) in handling and reporting the discharge of wastewater. Every year in July, the University submits a report that includes the water quality testing results for both the raw wastewater and the discharged wastewater for the period from January to June of the current year. Additionally, in the following year, by January, the University submits a report that covers the water quality testing results for both the raw wastewater and the discharged wastewater for the period from July to December of the preceding year. These regular reports show compliance with the reporting obligations set forth in the Water Pollution Control Act and its implementing regulations.
Reporting website: Environmental Management System of Ministry of Environment (https://ems.moenv.gov.tw/)
The following is a screenshot of NCUE’s reporting on the webpage of the “Waste/Polluted Water Management System for Industrial and Sewage Systems” (WPMIS) of the Ministry of Environment as shown in Figure 1:
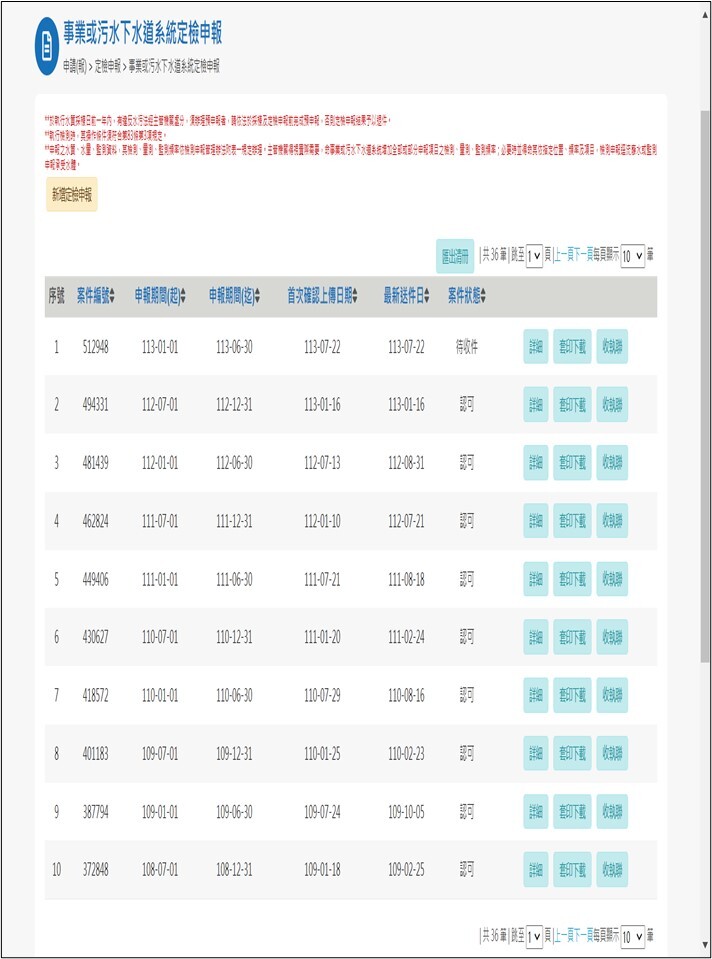
Figure 1. A screenshot of the “Wastewater Management System for Industrial and Sewage Systems” webpage of the Ministry of Environment
(3) The photos of the wastewater treatment plant are shown in Figure 2-3.
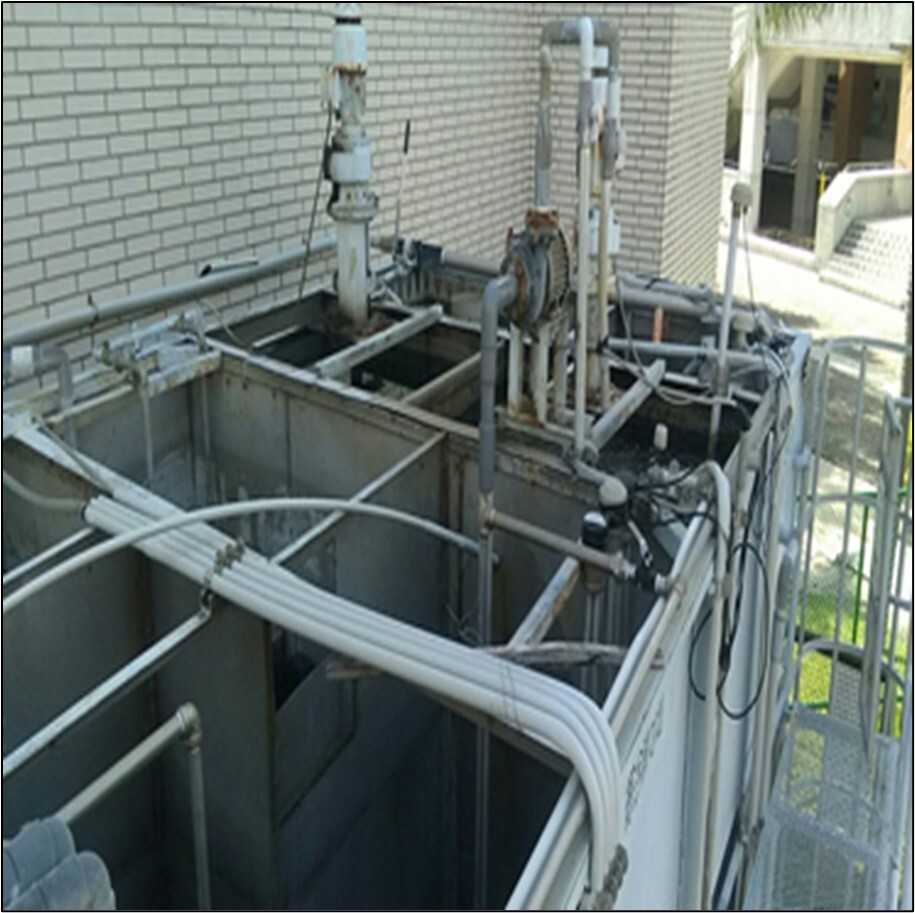

Figure 2. Jinde Campus Wastewater Treatment Plant
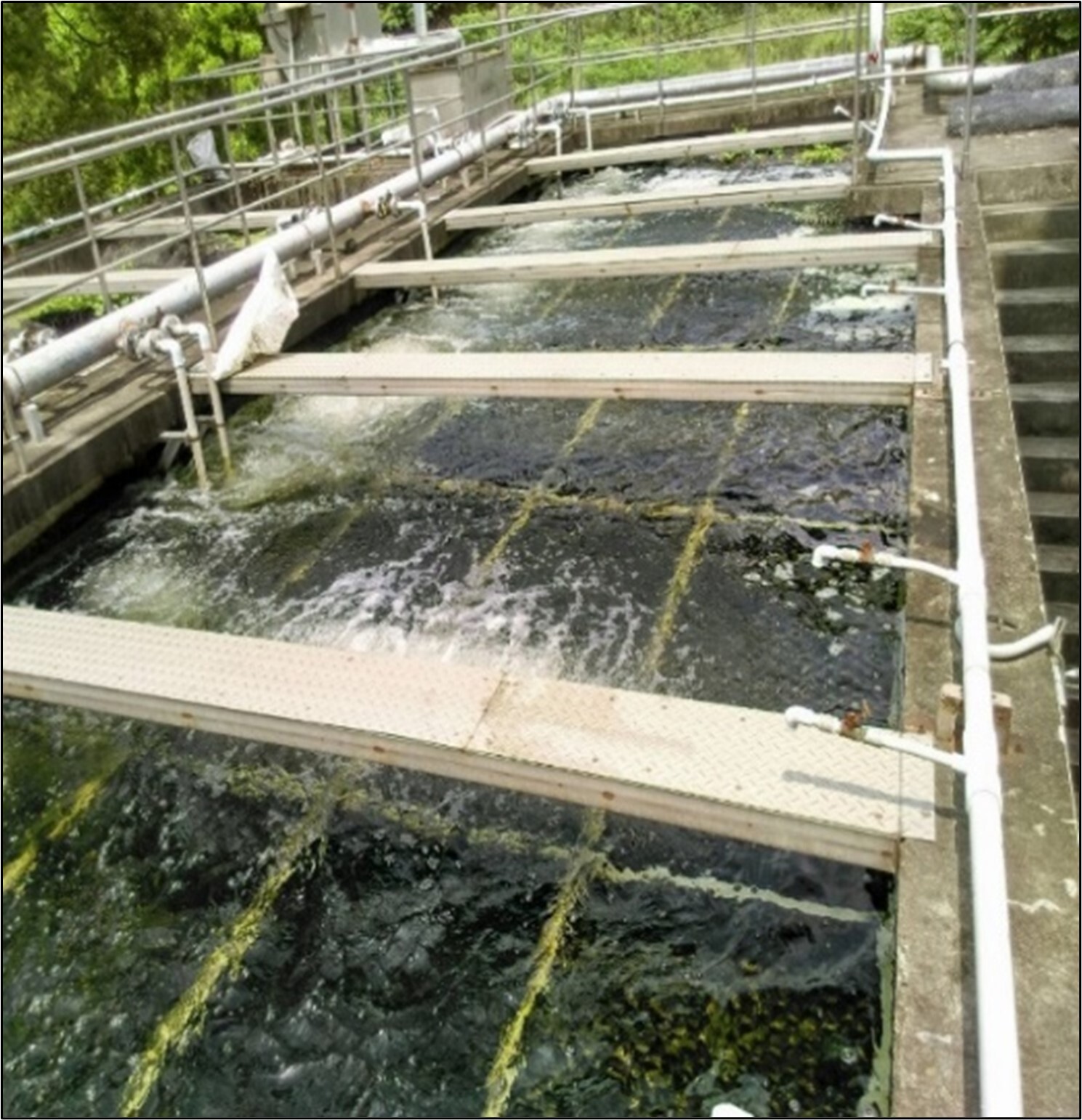

Figure 3. Baoshan Campus Wastewater Treatment Plant
(4) The Water Pollution Control Act requires annual calibration of the water meter for the effluent of the school’s wastewater treatment plant. The following Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the calibration and correction report of the school’s wastewater treatment plant effluent water meter issued by an inspection institution accredited by the Ministry of Environment.
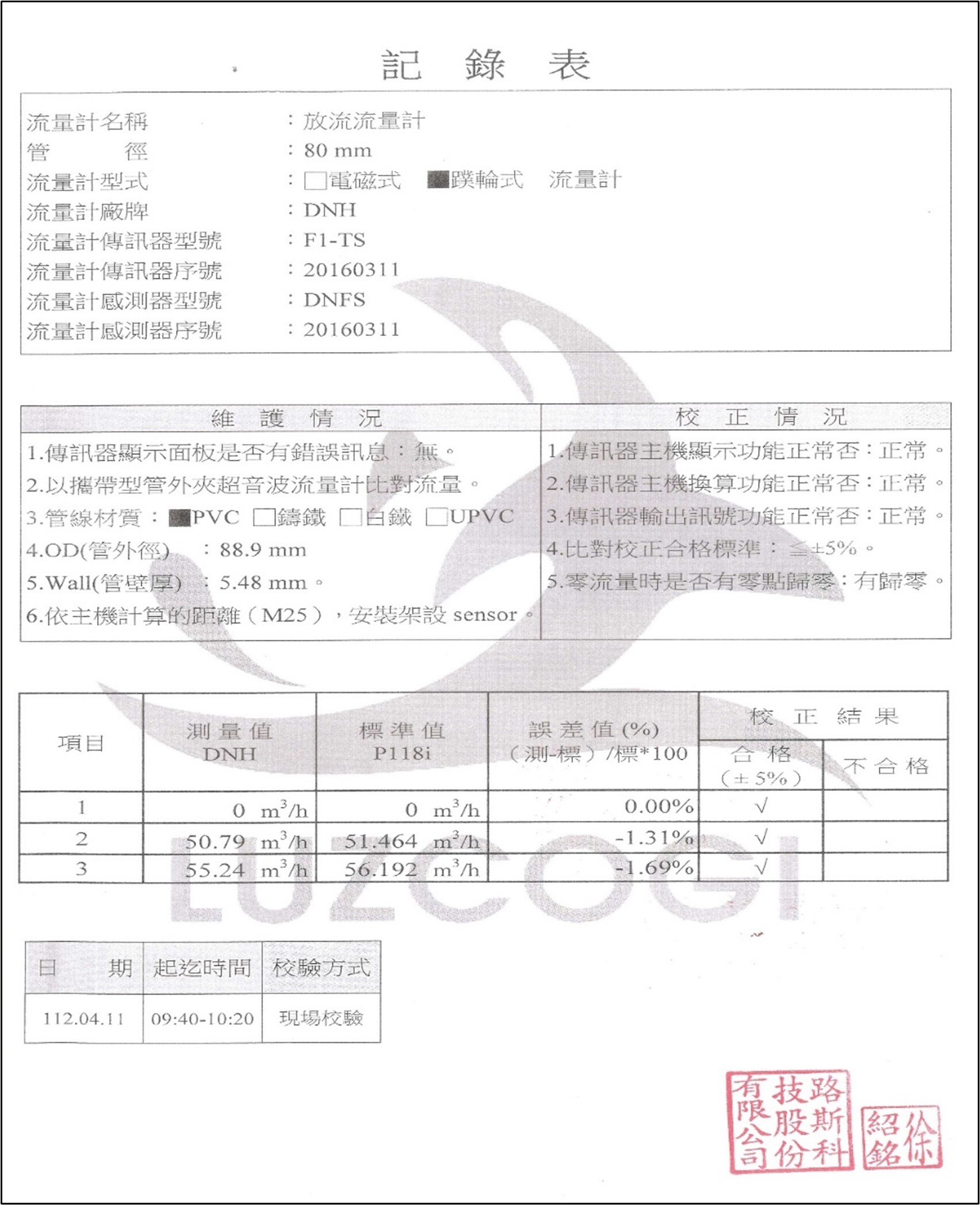
Figure 4. Calibration report of the water meter of NCUE’s wastewater treatment plant effluent water meter (Page 1)
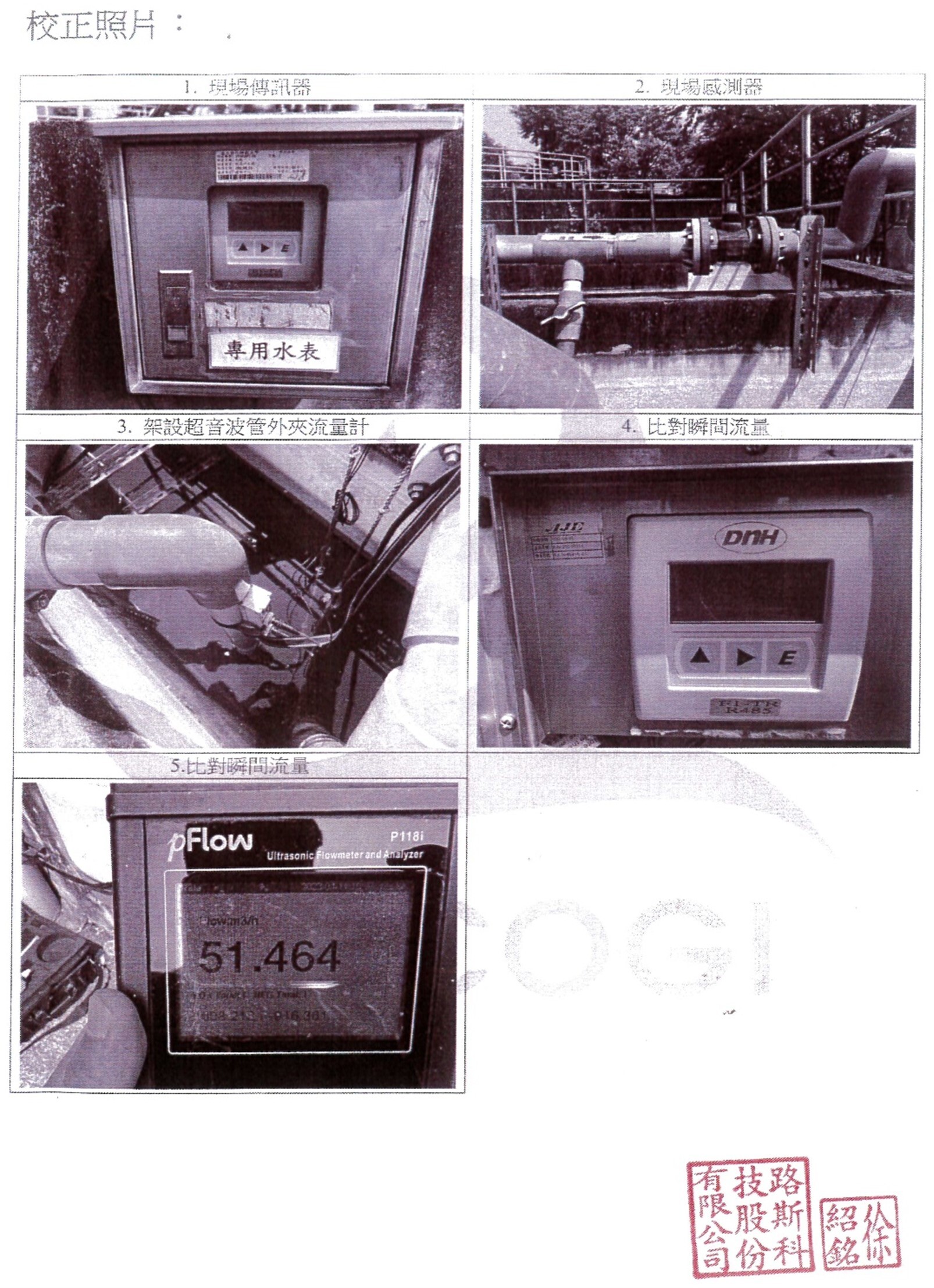
Figure 5. Calibration report of the water meter of NCUE’s wastewater treatment plant effluent water meter (Page 2)
(5) In accordance with the Water Pollution Control Act and Waste Disposal Act, the sludge removal and treatment operations have been carried out as required, Related photos as shown in Figure 6-7.
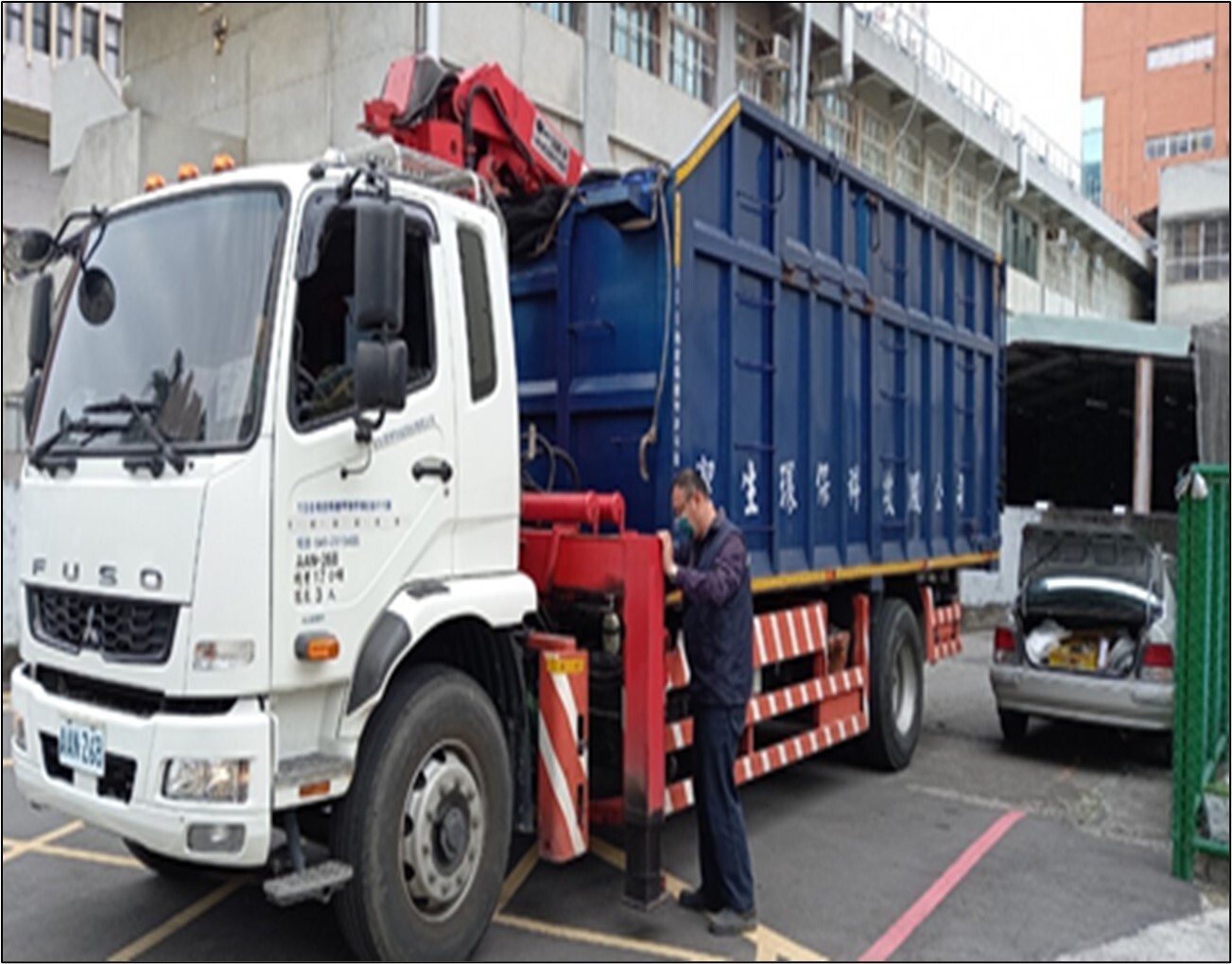

Figure 6. Sludge removal and treatment at Jinde Campus of NCUE
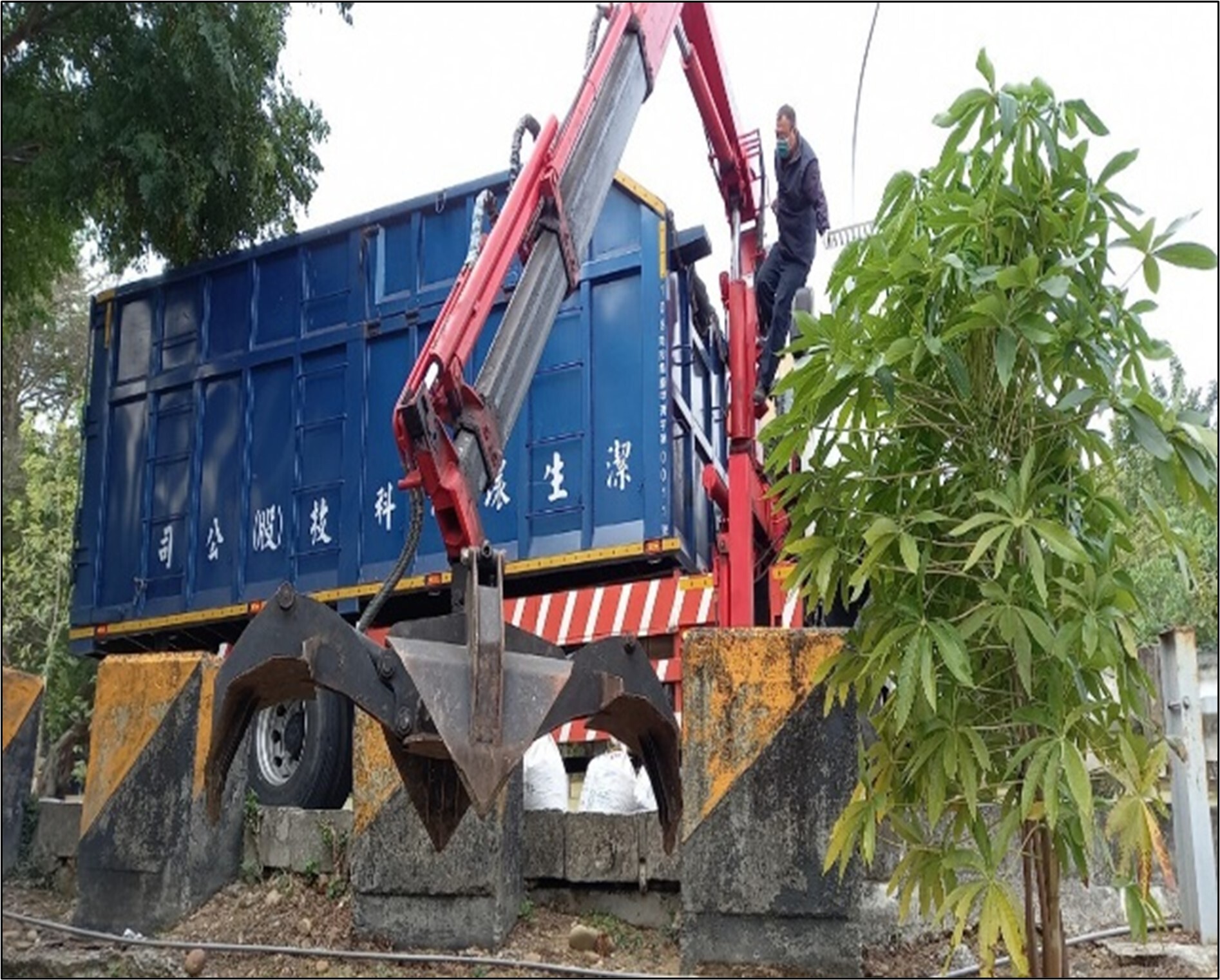

Figure 7. Sludge removal and treatment in Baoshan Campus of NCUE
(6) According to the Water Pollution Prevention and Control Act, water quality inspection is conducted once every six months, and the relevant photos are shown in Figure 8-9.
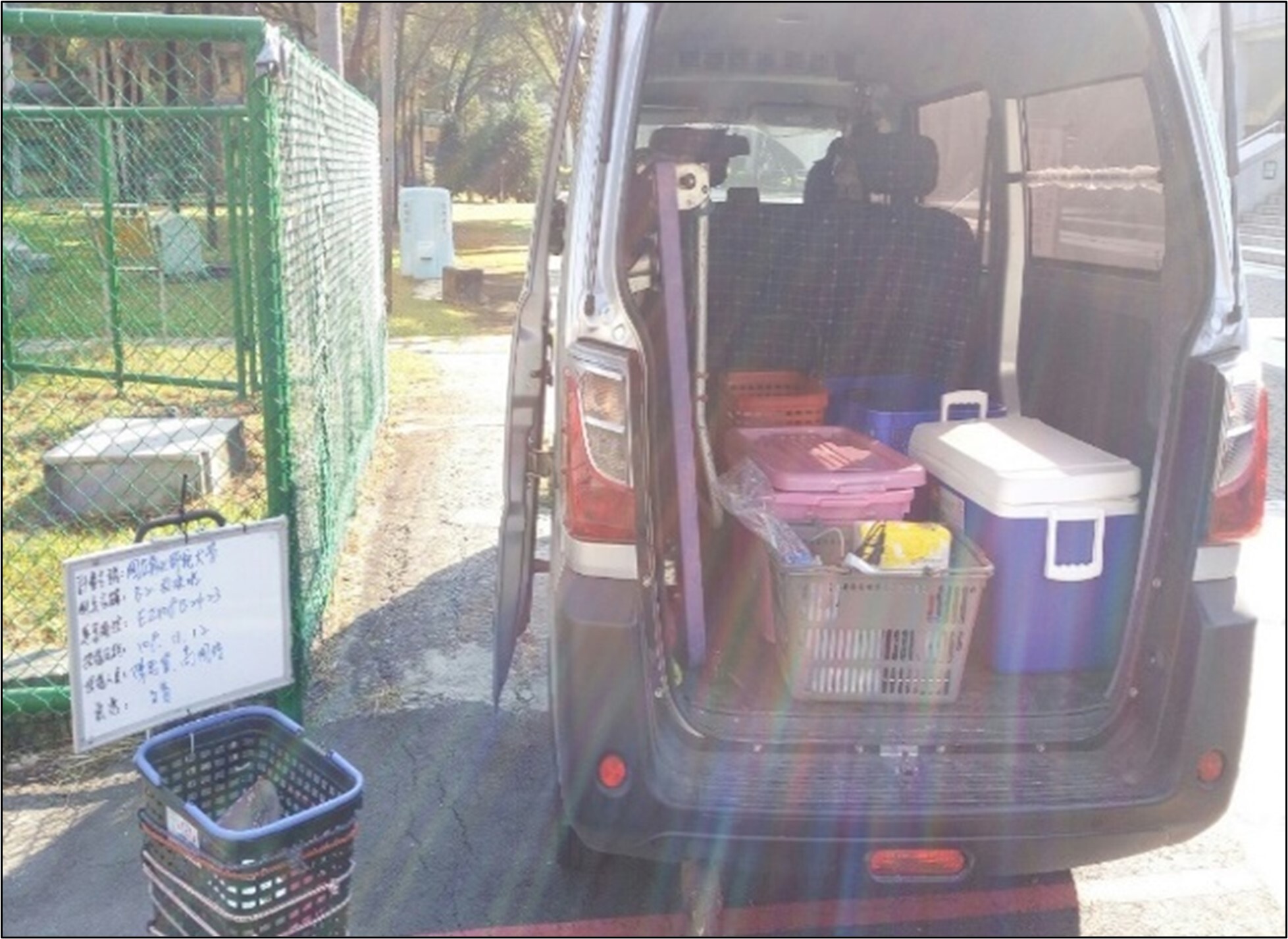

Figure 8. Water quality inspection at Jinde Campus
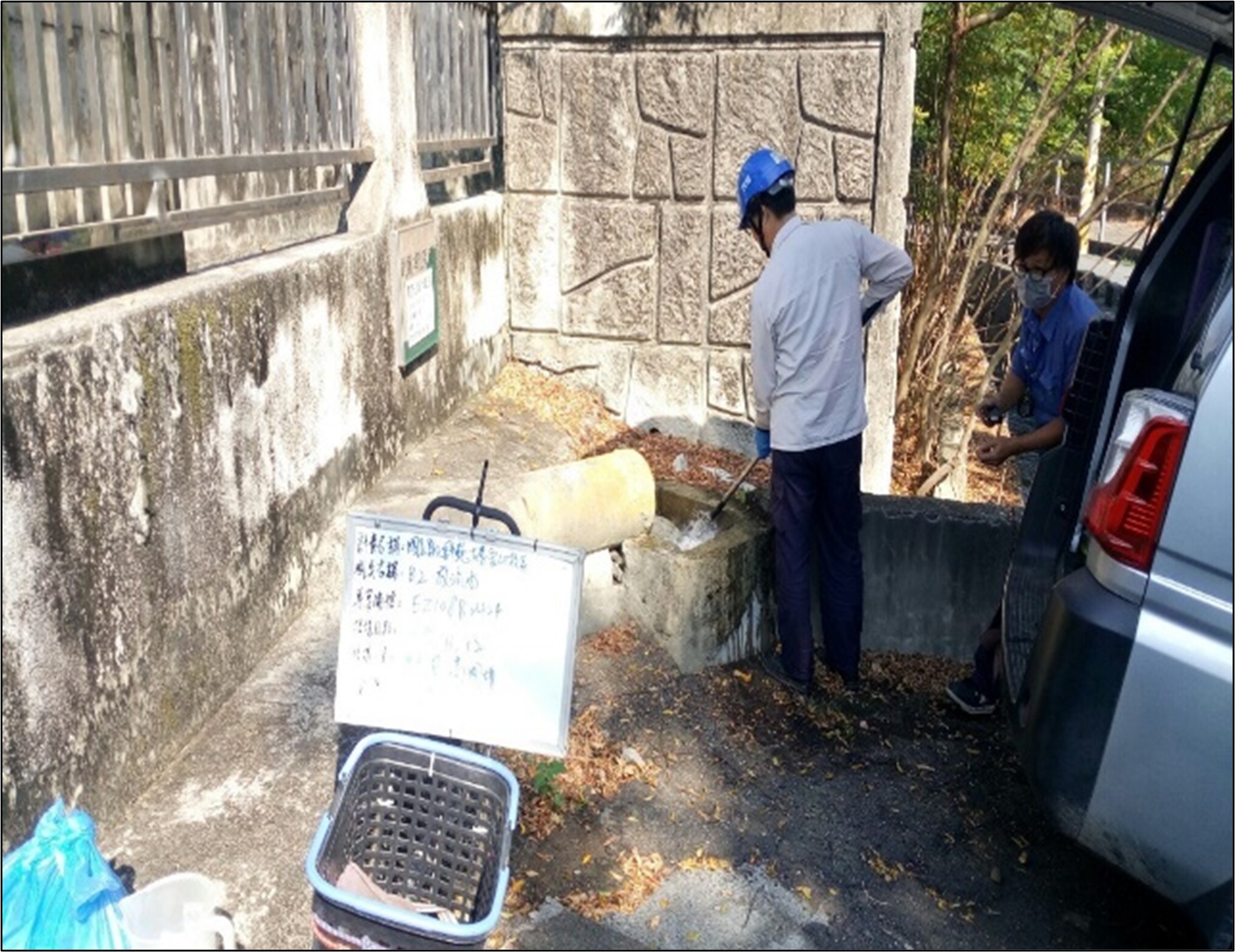

Figure 9. Water quality inspection at Baoshan Campus
2. The Environmental Education Centre implements the “Beautiful and Treasured Clams in Fangyuan and Dacheng: Sustainable Industry and Environment Project of Changhua’s Two Cities Amid Climate Change”
Aquaculture production of Asian hard clams is environmentally friendly as carbon dioxide is absorbed in the process, thus curbing greenhouse gases and carbon emissions. Polyculture based on ecosystem functions can reduce the use of baits, save water, and decrease waste. Risks can be lowered, and quality and quantity can be improved with the use of intelligent aquaculture, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics. New technologies form the core of the project, which helps implement innovative teaching that combines research courses, and teacher-student learning services, together with in-depth development and operation of aquaculture tourism in the fishing village to create and exploit new values of urban and rural development for both NCUE and the local industries, related event photos as shown in Figure 10.
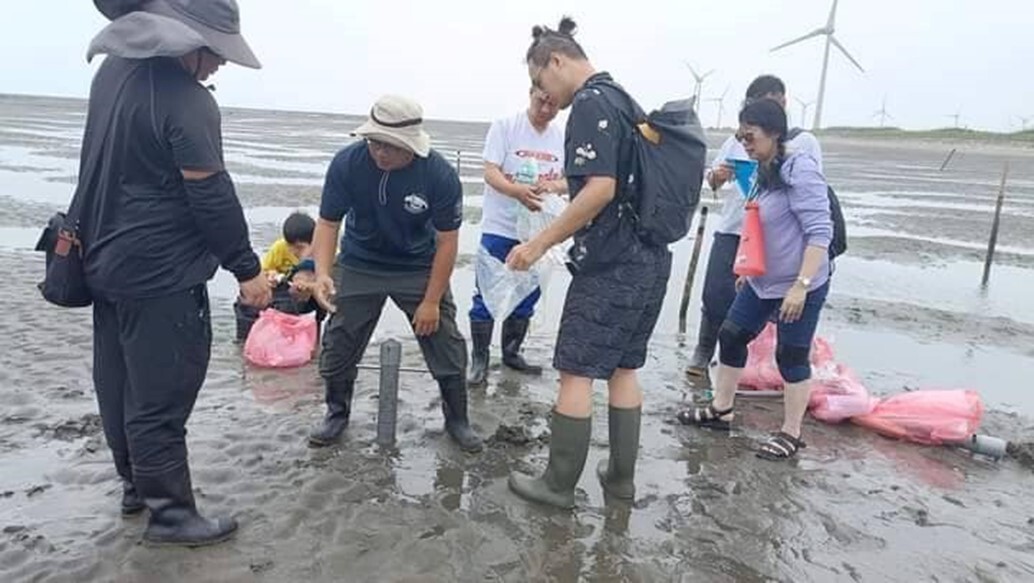

Figure 10. NCUE’s teachers and students partnered with members of local groups to conduct a survey on the ecosystem and organisms in the coastal wetlands to establish a marine ecological database and monitor information related to economic fishery resources
Facebook fan page of project-related activities: https://www.facebook.com/NCUEUSR/photos/?tab=album&ref=page_internal

















