SDG 15.3.5 Collaboration for shared land ecosystems
NCUE has multiple ongoing projects and activities, including the Environmental Education Centre’s “Project of Taoyuan International Airport Corporation/Entrusted Planning and Design for Red Imported Fire Ants (RIFA) Control”, the Department of Geography’s “Monitoring Agricultural and Fishery Socio-Ecosystems in the Wetland Stretches along the West Coast of Taiwan”, “Changing Landscapes in Changhua Coastal Area: Man-Made Features Driving Cross-Scale Spatial Development and Socio-Ecological System Analysis - Developing a Large-Scale Landscape Change and Ecosystem Services Assessment Framework Using Remote Sensing Technology”; Biology Department’s “Project of the Division of Science and Technology/Discussion and Solution Strategies on the Ant Infestation Problems in Qianshan Caused by the Impact of Climate Change on the Ecology of Qianshan and the Changes in the Community”, and a project of the Division of Science and Technology “Reshape the Prevention and Control of Global Invasive Species: Positioning Taiwan as a Hub for the Prevention and Control, Prediction and Education of RIFA in Asia”, “Agriculture Bureau of Kaohsiung City Government/Kaohsiung City Evaluation Plan for Implementing Survey, and Control Strategies for Flying Ant Control”, as listed in Table 1. These will be described briefly in the following section.
Table 1. Related projects and events
|
Project activities |
Subsidized units |
|
Project of Taoyuan International Airport Corporation/Entrusted Planning and Design for Red Imported Fire Ants (RIFA) Control |
Taoyuan International Airport Corporation |
|
Monitoring of Agricultural and Fishery Social and Ecological Systems in the Coastal Wetlands of Western Taiwan |
National Science and Technology Council |
|
Changing Landscapes in Changhua Coastal Area: Man-Made Features Driving Cross-Scale Spatial Development and Socio-Ecological System Analysis - Developing a Large-Scale Landscape Change and Ecosystem Services Assessment Framework Using Remote Sensing Technology |
National Science and Technology Council |
|
Discussion and Solutions to the Problem of Pest Ant Damage Caused by the Impact of Climate Change on the Lowland Ecology and the Change of the Lowland Community |
Ministry of Science and Technology |
|
Reshape the Prevention and Control of Global Invasive Species: Positioning Taiwan as a Hub for the Prevention and Control, Prediction and Education of RIFA in Asia |
Ministry of Science and Technology |
|
Fire Ant Hazard Survey and Control Strategy Assessment Project in Kaohsiung City |
Agriculture Bureau of Kaohsiung City Government |
1. “Project of Taoyuan International Airport Corporation/Entrusted Planning and Design for RIFA Control”:
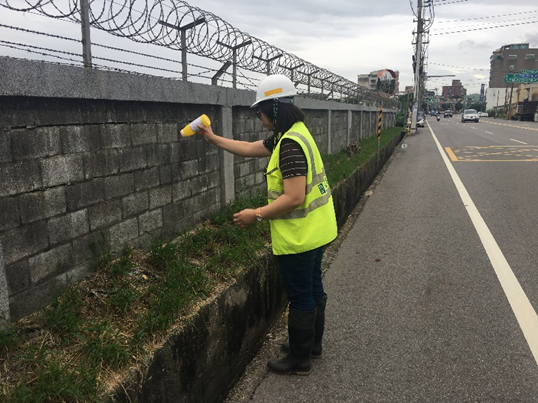
Taoyuan International Airport is located in the Dayuan District. In 2004, Taoyuan International Airport determined that the area around Taoyuan Airport, the airport traffic lane, and some parts of the lawn that divide the running chute were invaded by RIFA. The project team has achieved remarkable results after years of prevention and control work. The entire airport area has been lifted from the list of management by the government in May 2018. However, because Taoyuan International Airport is located in the Dayuan District of Taoyuan City, and the current RIFA population distribution and density in Dayuan District is still relatively serious, Taoyuan International Airport is still in an area susceptible to RIFA recurrence. The goal of the project team is to continue to assist Taoyuan International Airport in the prevention and control of RIFA in the entire airport area, including the manpower planning and execution in the control and investigation field operation, planning for the types of prevention and control agents, method suggestion and execution, RIFA monitoring execution and control rate reporting, assistance in reports required by the competent authorities, and checking related matters on the prevention and control of RIFA. In addition, the project team also assists the RIFA prevention and control operations in Dayuan District, related photos as shown in Figure 1.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 1. Taoyuan International Airport RIFA control team of NCUE assisting in RIFA prevention and control operations in the Dayuan District, Taoyuan City, outside Taoyuan Airport |
Link for reference information: https://www.facebook.com/NCUEEEC/videos/a.1053897732014001/549273452851485.
2. Monitoring of Agricultural and Fishery Social and Ecological Systems in the Coastal Wetlands of Western Taiwan:
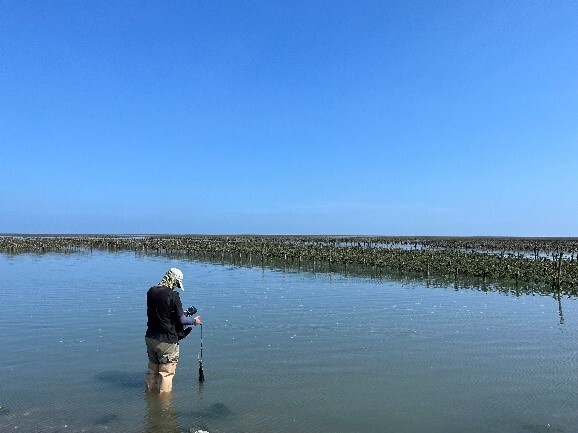
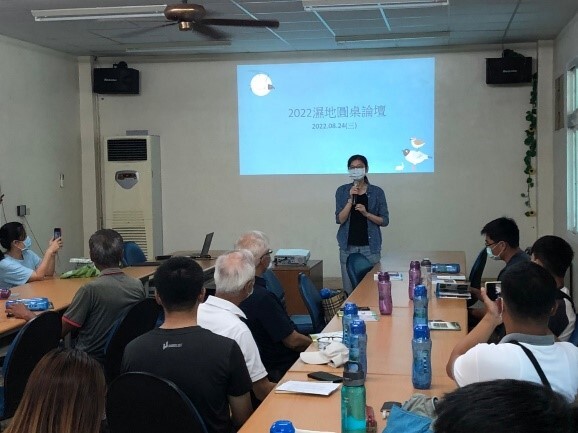
The Department of Geography of NCUE undertook the National Science and Technology Council’s “Monitoring of Agricultural and Fishery Social and Ecological Systems in the Coastal Wetlands of Western Taiwan (2/3)” project. The project is centered around Fangyuan and focuses on establishing a local research demonstration initiative for long-term, fundamental, and critical observations of core aspects of the socio-ecological system. As part of the long-term socio-ecological core observation, NCUE has set up the Changhua Station for observation. The environmental and ecological surveys at the Yongxing Wanggong Aquaculture Area’s canals involve monthly water quality monitoring. These surveys were conducted from February 2022 to July 2023, and we plan to continue these monitoring activities in the future. In-depth interviews with key local stakeholders are a vital component of the social research conducted at our observation station. These interviews help expand the platform’s local social network and involve representatives from various local stakeholders, including governing bodies, cultural organizations, industry groups, developers, producers, and others. Through these interviews, the project team collects systematic information about different roles, functions, and relationships of these stakeholders and their experiences and observations regarding the complex changes in the local society and ecology. This information forms the essential foundation of social-ecological data for the LTSER platform. Staff from the station actively participate in local events to discover relevant issues and collaborate with local communities. We aim to ensure that our long-term observational data can simultaneously address local needs, related photos as shown in Figures 2-3.
|
|
|
Figure 2. Water quality observation at the observation station along the coast of Fangyuan after the algal bloom incident |
|
|
|
Figure 3. Attending the Wetland Roundtable organized by Changhua Bird Watcher’s Association in Fangyuan |
Link for reference information: https://www.facebook.com/LTSER_Changhua-107002388661252/.
3. Changing Landscapes in Changhua Coastal Area: Human-Made Features Driving Cross-Scale Spatial Development and Socio-Ecological System Analysis - Developing a Large-Scale Landscape Change and Ecosystem Services Assessment Framework Using Remote Sensing Technology (Sub-Project 2):
The Department of Geography at NCUE is undertaking a subproject of the National Science and Technology Council’s research project titled “Changing Landscapes in Changhua Coastal Area: Human-Made Features Driving Cross-Scale Spatial Development and Socio-Ecological System Analysis - Developing a Large-Scale Landscape Change and Ecosystem Services Assessment Framework Using Remote Sensing Technology (Sub-Project 2)”.This project focuses on the typical agricultural and fishing community of Fangyuan Township in Changhua. Historically, this region has faced challenges due to its remote location and the relatively low economic value of its farmland, leading to shifts in land use influenced by policy changes. These shifts have had an impact on the composition of the local agricultural landscape. This project integrates Landsat, SPOT, and Sentinel-2 images to stack time-series image sets, and imports temporal features and multi-criteria classification methods for land use classification to provide foundational data for estimating the service value of agricultural landscape ecosystems. The results of the classification indicate a decrease in cultivated land of 593.06 hectares over the past two decades. Abandoned farmland has led to an increase of 4.48% in grassland and approximately 2.30% increase in building coverage ratio. Government agricultural statistics indicate that the total planted area for agricultural products has decreased by over 3,200 hectares from 2000 to the present. This reduction in cultivated land reflects a decline in land use intensity or efficiency in agriculture. Although the local agricultural landscape still maintains a complex structure with diverse crops and crop rotation systems, there has been a significant decrease in the utilization of arable land. This decline is further exacerbated by recent solar energy policies and economic incentives, which have increased the pressure to convert agricultural land into other forms of development.
Reference link: https://data.depositar.io/dataset/ltserchanghuaresearch.
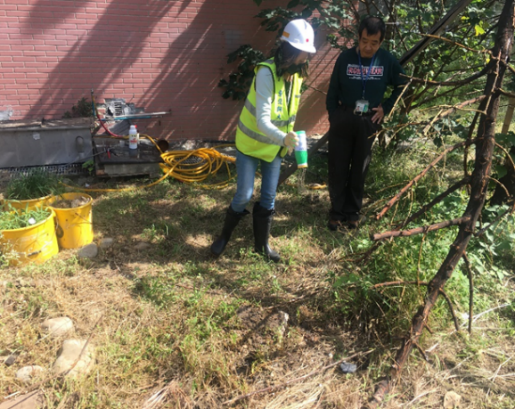
4. Project of the Division of Science and Technology: “Discussion and Solution Strategies on the Ant Infestation Problems in Qianshan Caused by the Impact of Climate Change on the Ecology of Qianshan and the Changes in the Community”:
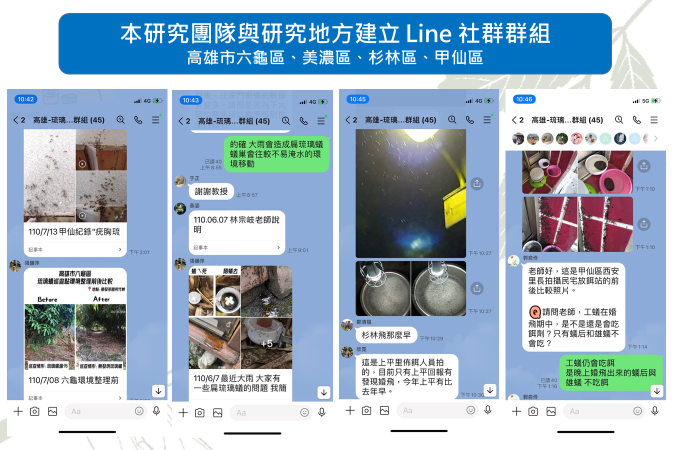
Natural disasters on slopes arising from climate change and man-made development pressures have caused landscape fragmentation, ecological fragmentation, and habitat loss, causing slopes in Qianshan, Taiwan, an ecologically fragile area. Recently, emerging ant infestation problems have appeared in Qianshan towns in southern-central Taiwan. Ants flood pour into houses like streams, and flying ants infest homes like black mists. Such abnormal ecological responses are signs of the gradual loss of the ecological health in Taiwan. This project integrates multiple domains. It takes the ant infestation problem of the Qianshan residents as the starting point to comprehensively examine the hidden landscape fragmentation, ecological loss, and development pressure. Using the ecosystem service on the slopes as the research framework, key biofacies in habitat are investigated, landscape changes are analysed, indicators are established, environmental fragility and ecological potential are examined. In addition, in response to the impact of the ant infestation problem on the industry and tourism in the mountain village communities, a Qianshan agricultural production system with potential for ecosystem services and human well-being are established considering the climate change background. This project has currently established immediate contact with the district offices in the research area (Liougui District, Meinong District, Shanlin District, and Jiaxian District of the Kaohsiung City) and relevant personnel via a Line group (Kaohsiung-Dolichoderus thoracicus-Epidemic Prevention Group), which includes district chiefs, office staff, community directors, production and sales team leaders, and personnel in the homestay industry, etc. The communication software used can establish a long-term interaction mechanism with the community, and it can answer and solve problems in real time. This instant contact Line group is employed to sort out the related questions asked by the community, and analyze the feelings and concerns regarding the ant infestation hazards from people in public affairs, residents, agriculture, and tourism. Related photos are shown in Figure 4.
Link for reference information: https://www.facebook.com/media/set/?vanity=NCUEEEC&set=a.1053897732014001.
|
|
|
Figure 4. The Line group established with the local community by the research team |
5. Project of the Division of Science and Technology: “Reshape the Prevention and Control of Global Invasive Species: Positioning Taiwan as a Hub for the Prevention and Control, Prediction, and Education of RIFA in Asia”.
This study further uses data model analysis and establishment of an innovative RIFA invasive platform for the ongoing scientific debate on the causes of the global invasion of RIFA, making significant contributions to the RIFA prevention, its agricultural and economic impacts, and the development of science in Taiwan. This study successfully discovered the pattern of the RIFA elimination in Taiwan and revealed their proliferation hotspots and paths. In addition, a smart RIFA notification platform was developed, and a harmful ant detection and AI image automatic identification app system was introduced to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the detection of front-line investigators, volunteers, farmers, and the public, so that the sources of infection can be detected early for prevention and control. Through GIS, social network analysis, and foreign and domestic RIFA distribution information, this study has made the following major discoveries: (1)RIFA are mainly distributed across general roads, rice fields, and storage. (2)The way of invasion is through ports with high shipping volume and those having tight connections with high-shipping-volume ports. (3)The main proliferation reasons of island-type proliferation in Kinmen are road construction, regional construction, and city development. Therefore, a major part of this research involves assisting the Bureau of Inspection and Quarantine in distributing epidemic prevention resources. This team has been participated in the inter-departmental meetings of the Bureau of Inspection and Quarantine, and to manage citizen forums. Related photos are shown in Figure 5.
Link to forum information as reference: http://pa.ntu.edu.tw/News_Content_n_15078_s_68772.html.
|
|
|
Figure 5. Expert Speakers of the Forum “Development and Opportunities of Citizen Science” |
6. Agriculture Bureau of Kaohsiung City, Government/Kaohsiung City Evaluation Plan for Implementing Survey and Control Strategies for Flying Ant Control:
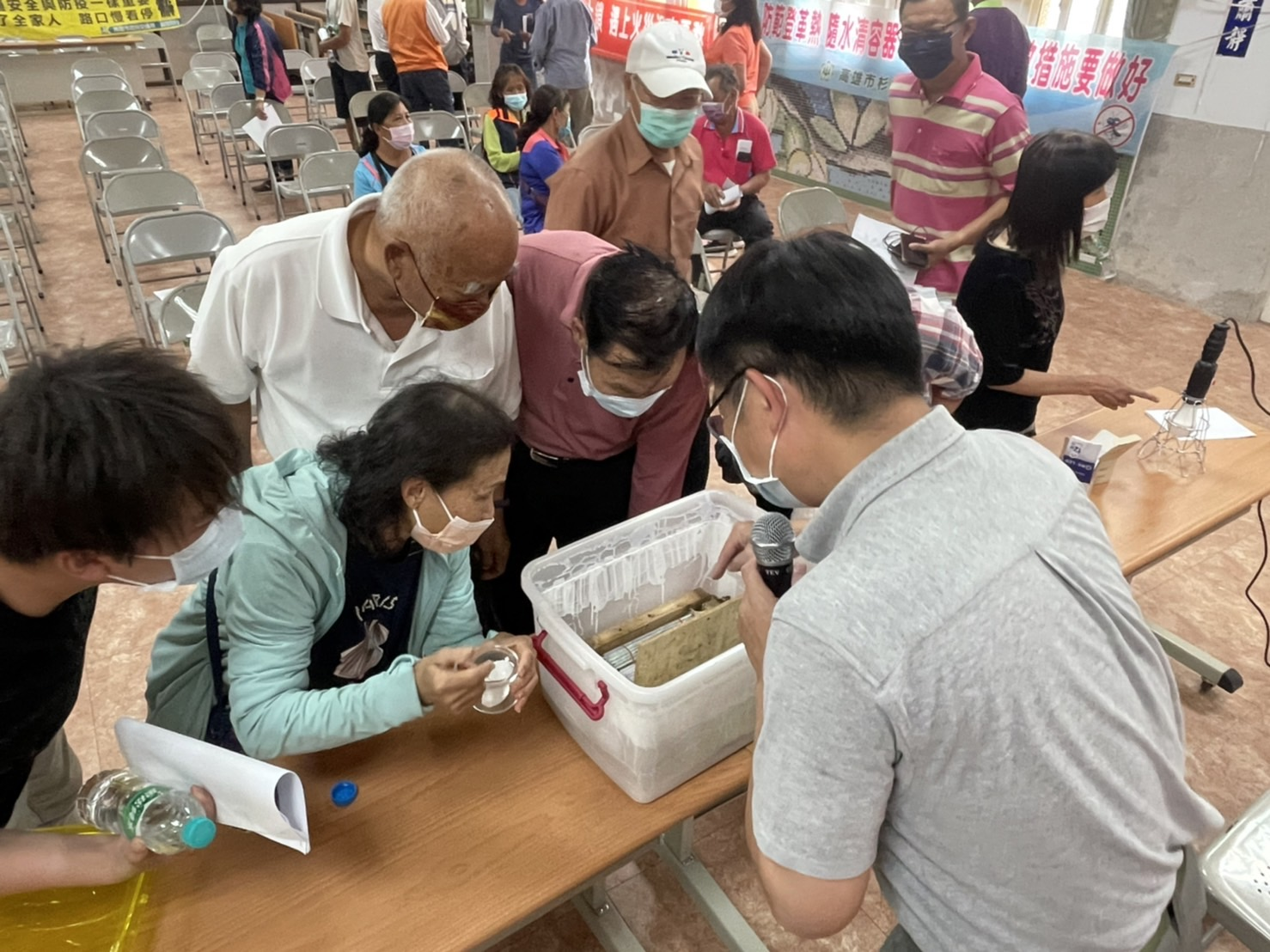
In recent years, the Qimei district of Kaohsiung City has been severely infested by flying ants at night during summer and autumn months, and experts have confirmed that these flying ants (Technomyrmex brunneus) are among the most invasive and pervasive species. During the nuptial flight (mating period), the queen ant and male ants become phototactic. Attracted by the lights at night, these ants invade farmhouses, homes, and business establishments in large swarms, seriously affecting the local residents, and even impacting the local tourism industry. Technomyrmex brunneus has been found in Taiwan since 1912. In 2016, a large number of flying ants began to appear in the city’s Liugui District, and later spread to districts such as Meinong, Jiaxian, and Shanlin from 2019 to 2021, indicating gradual expansion of the ant population. To reduce the menace of Technomyrmex brunneus and prevent the population from expanding and infesting other areas, the project monitors and investigates areas seriously affected by Technomyrmex brunneus and identifies and discusses the reasons for the damage. Control test areas have also been established to develop strategies to control the density of Technomyrmex brunneus colonies and mitigate disruption to public life. Related photos are shown in Figure 6.
|
|
|
Figure 6. Education activities and counseling groups of neighborhood residents for the control of Technomyrmex brunneus in Jiaxian and Shanlin Districts |