SDG 15.2.3 Maintain and extend current ecosystems’ biodiversity
NCUE has undertaken multiple ongoing projects and activities, including: Environmental Education Centre’s “Project of Taoyuan International Airport Corporation/Entrusted Planning and Design for RIFA Control”; “Environmental Educator 24-hour and 33-hour Certification Course”; Biology Department’s “Project of the Division of Science and Technology/Discussion and Solution Strategies on the Ant Infestation Problems in the Qianshan Caused by the Impact of Climate Change on the Ecology of Qianshan and the Changes in the Community”, Science and Technology Division’s projects “Reshape the Prevention and Control of Global Invasive Species: Positioning Taiwan as a Hub for the Prevention and Control, Prediction and Education of RIFA in Asia” and “Microbial Control technology of Agricultural Pest Ant”, a project of the Bureau of Animal and Plant Health Inspection and Quarantine, “Council of Agriculture/Development of Core Technologies and Establishment of Safety Assessment Model of the Agricultural Spraying Drone Industry Chain–Field Trials for Using Agricultural Drones to Control RIFA through the Management of Drone Pesticide Spraying Delegation System”, “Project of the National Natural Park Management Office/Shoushan National Natural Park Plan of Survey, Monitoring and Controlling Yellow Crazy Ants”; Center of General Education’s “Little Purple Crow Butterfly and Its Elf Friends,” and “You Are My Eyes-Walking with Dogs”, as indicated in Table 1.They are briefly introduced in the following section.
Table 1: Related projects and events
|
Project activities |
Subsidized units |
|
Project of Taoyuan International Airport Corporation/Entrusted Planning and Design for Red Imported Fire Ants (RIFA) Control |
Taoyuan International Airport Corporation |
|
Environmental Educator 24-hour and 33-hour Certification Class |
|
|
Discussion and Solutions to the Problem of Pest Ant Damage Caused by the Impact of Climate Change on the Lowland Ecology and the Change of the Lowland Community |
Ministry of Science and Technology |
|
Reshape the Prevention and Control of Global Invasive Species: Positioning Taiwan as a Hub for the Prevention and Control, Prediction and Education of RIFA in Asia |
Ministry of Science and Technology |
|
Development of Microbial Control Technology of Agricultural Pest Ant |
Ministry of Science and Technology |
|
Development of Core Technologies and Establishment of Safety Assessment Model of the Agricultural Spraying Drone Industry Chain–Field Trials for Using Agricultural Drones to Control RIFA through the Management of Drone Pesticide Spraying Delegation System |
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Agency, Ministry of Agriculture |
|
Investigation, Monitoring, and Control Plan for Long-Legged Ants in Shoushan National Nature Park |
National Nature Park Headquarters |
|
“Nuclear Energy and Green Energy” and “Safeguarding Sacred Birds - Conservation Status of the Chinese Crested Tern” |
|
1. Project of Taoyuan International Airport Corporation: “Entrusted Planning and Design for RIFA Control”:
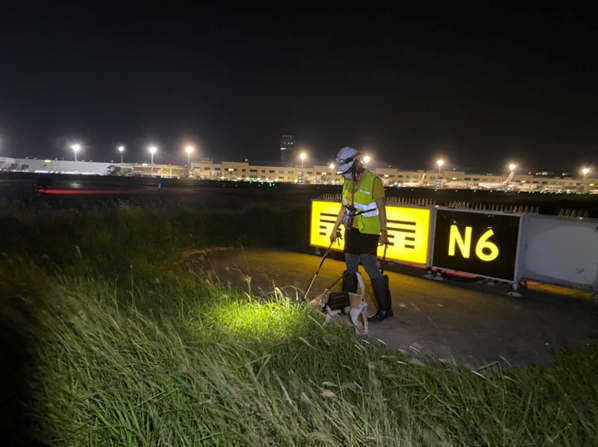
Taoyuan International Airport is located in the Dayuan District. In 2004, Taoyuan International Airport determined that the area around Taoyuan Airport, the airport traffic lane, and some parts of the lawn dividing the running chute were invaded by RIFA. The project team has achieved remarkable results after years of prevention and control work. The entire airport area has been lifted from the list of management by the government in May 2018. However, because Taoyuan International Airport is located in the Dayuan District of Taoyuan City, and the current RIFA population distribution and density in the district is still relatively serious, Taoyuan International Airport is still in an area susceptible to RIFA recurrence. The goal of the project team was to assist Taoyuan International Airport in the prevention and control of RIFA in the entire airport area, including the manpower planning and execution in the control and investigation field operation, planning for the types of prevention and control agents, method suggestion and execution, RIFA monitoring execution and control rate reporting, assistance in reports required by the competent authorities, and checking related matters on RIFA prevention and control, related photos as shown in Figure 1.
|
|
|
Figure 1. NCUE Taoyuan International Airport RIFA Control Team assisting in on-site control work at Taoyuan Intl. Airport (night shift) |
Link to the video of the RIFA detection dog participating in the project: https://www.facebook.com/NCUEEEC/videos/a.1053897732014001/286384779600117.
2. 24-, 33-Hour Courses for Environmental Education Personnel Certification:
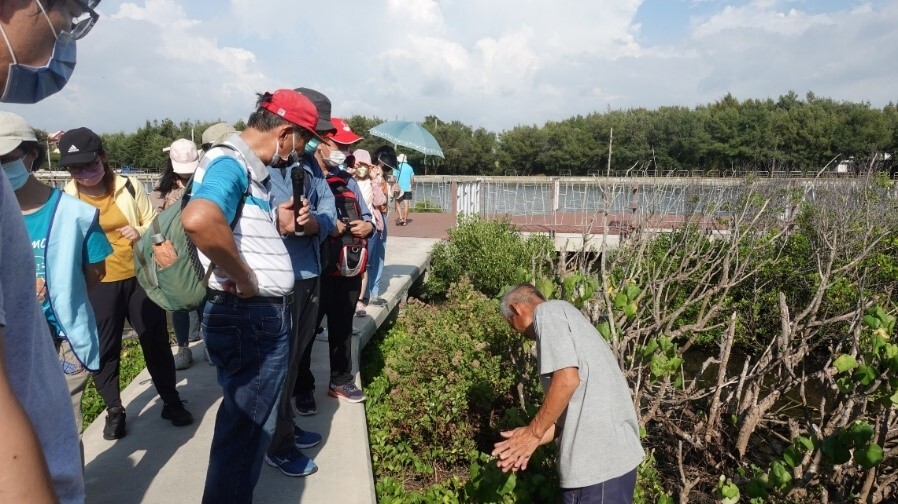
The Environmental Education Center (EEC) nurtures relevant environmental education talents.In conjunction with the project “In-Depth Cultivation of Fangyuan, Working Hand in Hand with Dacheng: Industrial and Environmental Sustainability Plan of the Two Townships of Changhua County” project, EEC provided relevant education courses for the local and nationwide communities from July to August 2022, with the details shown in Table 2 and the activities shown in Figures 2-3.
Table 2. Environmental education course activities
|
Educational activities |
Time |
Number of students |
|
Environmental Educator 24-hour Certification - Dacheng Junior High School Class |
August 2022 |
13 |
|
Environmental Educator 33-hour Certification Class |
July 2022 |
27 |
A total of 40 educators were trained in environmental education and freshwater ecosystem maintenance.
|
|
|
Figure 2. Environmental Educator Certification for Dacheng Junior High School Class |
|
|
|
Figure 3. In-class learning of the Environmental Educator Certification 33-hour Class |
Links to course video information:
https://www.facebook.com/media/set/?set=a.636923044887728&type=3.
https://www.facebook.com/media/set/?set=a.636918504888182&type=3.
3. Project of the Division of Science and Technology: “Discussion and Solution Strategies on the Ant Infestation Problems in the Qianshan Caused by the Impact of Climate Change on the Ecology of Qianshan and the Changes in the Community”:
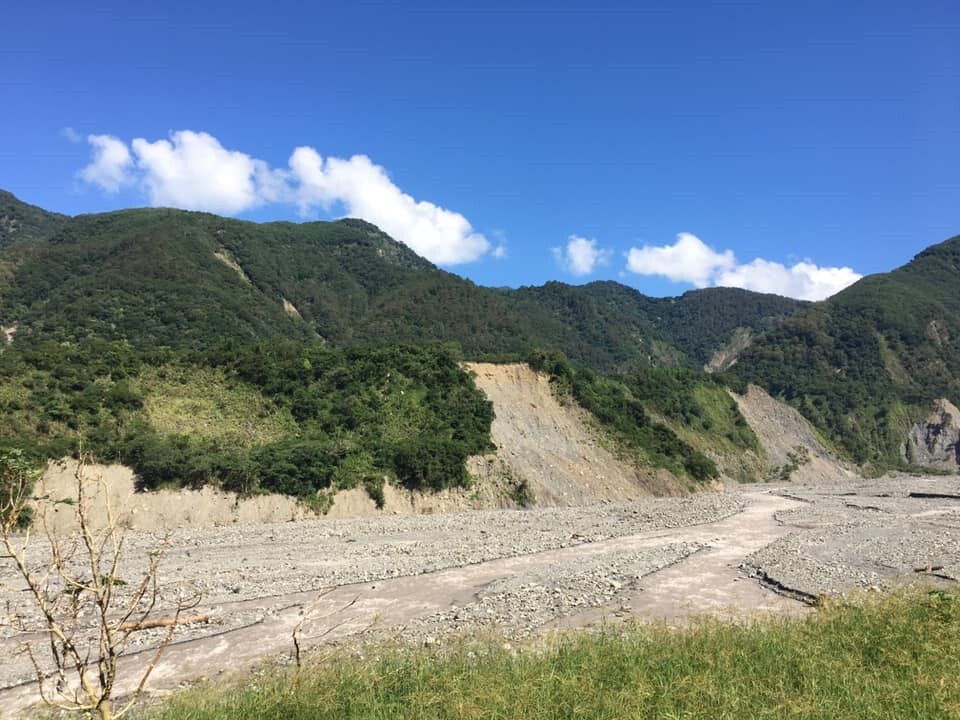
Natural disasters on slopes arose from climate change and man-made development pressure have caused the fragmentation of landscape, ecological fragmentation, and habitat loss, causing slopes in Qianshan, an ecologically fragile area. In addition, recent emerging ant infestation problems have appeared in Qianshan towns in south-central Taiwan. Ants pour into houses like streams, and flying ants invade homes like black mist. Such abnormal ecological responses are warnings of the gradual loss of ecological health in Taiwan. This project integrates multiple domains. It takes the ant infestation problem of the Qianshan residents as the starting point to comprehensively examine the hidden landscape fragmentation, ecological loss, and development pressure behind the ant infestation problem. Using the ecosystem service on the slopes as the research framework, this study investigates key biofacies in the habitat, analyzes landscape changes, establishes indicators, and examines environmental fragility and ecological potential. In addition, in response to the logic of the impact of the ant infestation problem on the industry and tourism in the mountain village communities, a Qianshan agricultural production system with potential for ecosystem services and human well-being are established taking climate change as the background. Related photos are shown in Figure 4.
|
|
|
Figure 4. Collapsed area in Qianshan, Liugui District, Kaohsiung City |
Link for reference information:
https://www.facebook.com/NCUEEEC/photos/a.1053897732014001/1053901572013617.
4. Project of the Division of Science and Technology: “Reshape the Prevention and Control of Global Invasive Species: Positioning Taiwan as a Hub for the Prevention and Control, Prediction, and Education of RIFA in Asia”.
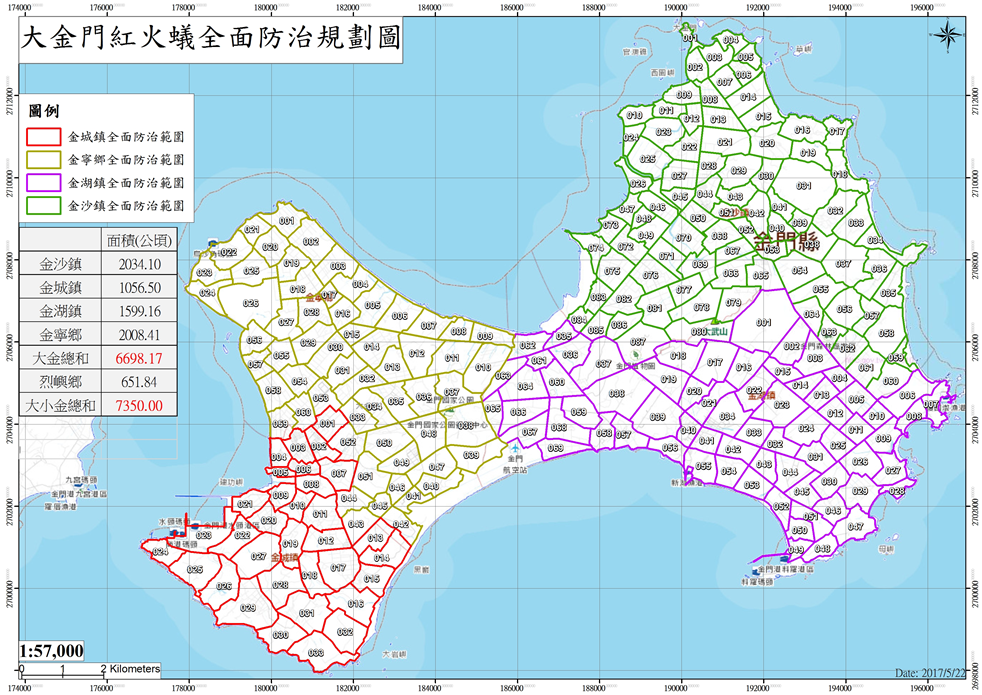
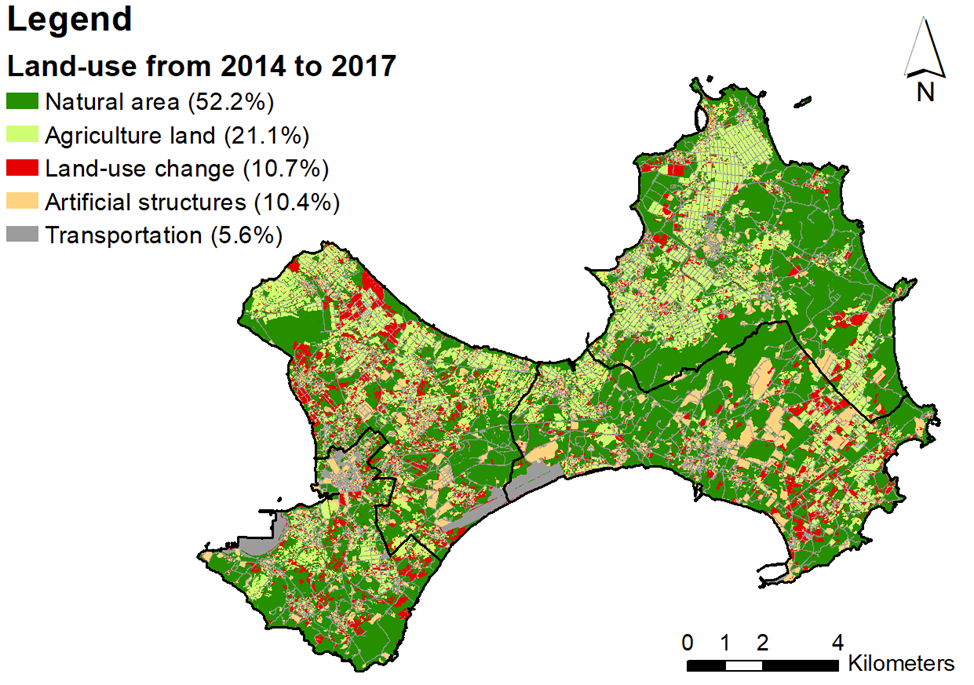
This study uses further data model analysis and establishment of an innovative RIFA invasive platform for the ongoing scientific debate on the causes of the RIFA global invasion, making significant contributions to the prevention of RIFA, its agricultural and economic impacts, and the development of science in Taiwan. This study successfully discovered the pattern of the elimination of RIFA in Taiwan and revealed the proliferation hotspots and paths. In addition, a smart RIFA notification platform was developed, and a harmful ant detection and AI image automatic identification app system was introduced to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the detection of front-line investigators, volunteers, farmers, and the public, so that the sources of infection can be detected early for prevention and control. Through GIS, social network analysis, and foreign and domestic RIFA distribution information, this study has made the following major discoveries: (1)RIFA are mainly distributed across general roads, rice fields, and storage. (2)The way of invasion is through ports with high shipping volume and those having tight connections with high-shipping-volume ports. (3)The main reasons of island-type proliferation in Kinmen were road construction, regional construction, and city development. Therefore, a major part of this research involves assisting the Bureau of Inspection and Quarantine in distributing epidemic prevention resources. This team has been in the inter-departmental meetings of the Bureau of Inspection and Quarantine. Related photos are shown in Figures 5-6.
|
|
|
Figure 5. Kinmen County RIFA Prevention Plan |
|
|
|
Figure 6. Spatial distribution of land-use change variable between 2014 and 2017. The land-use type before dash is the type in 2014, and after dash represents the type in 2017 |
Link for reference information: https://www.facebook.com/photo/?fbid=1053897588680682&set=a.1053897732014001.
5. Project of the Division of Science and Technology: “Development of Microbial Control Technology of Agricultural Pest Ant”.
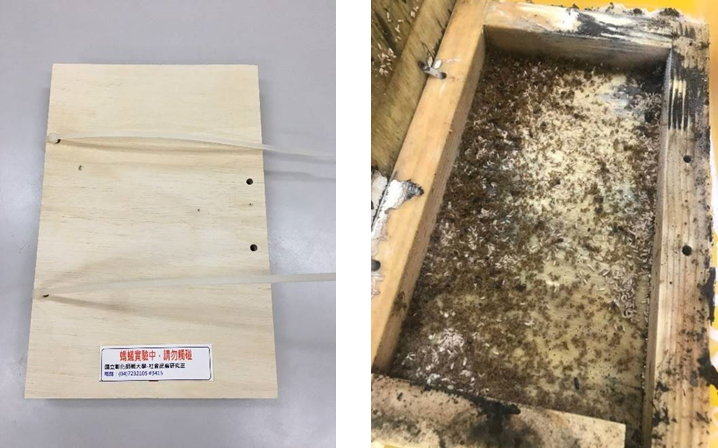
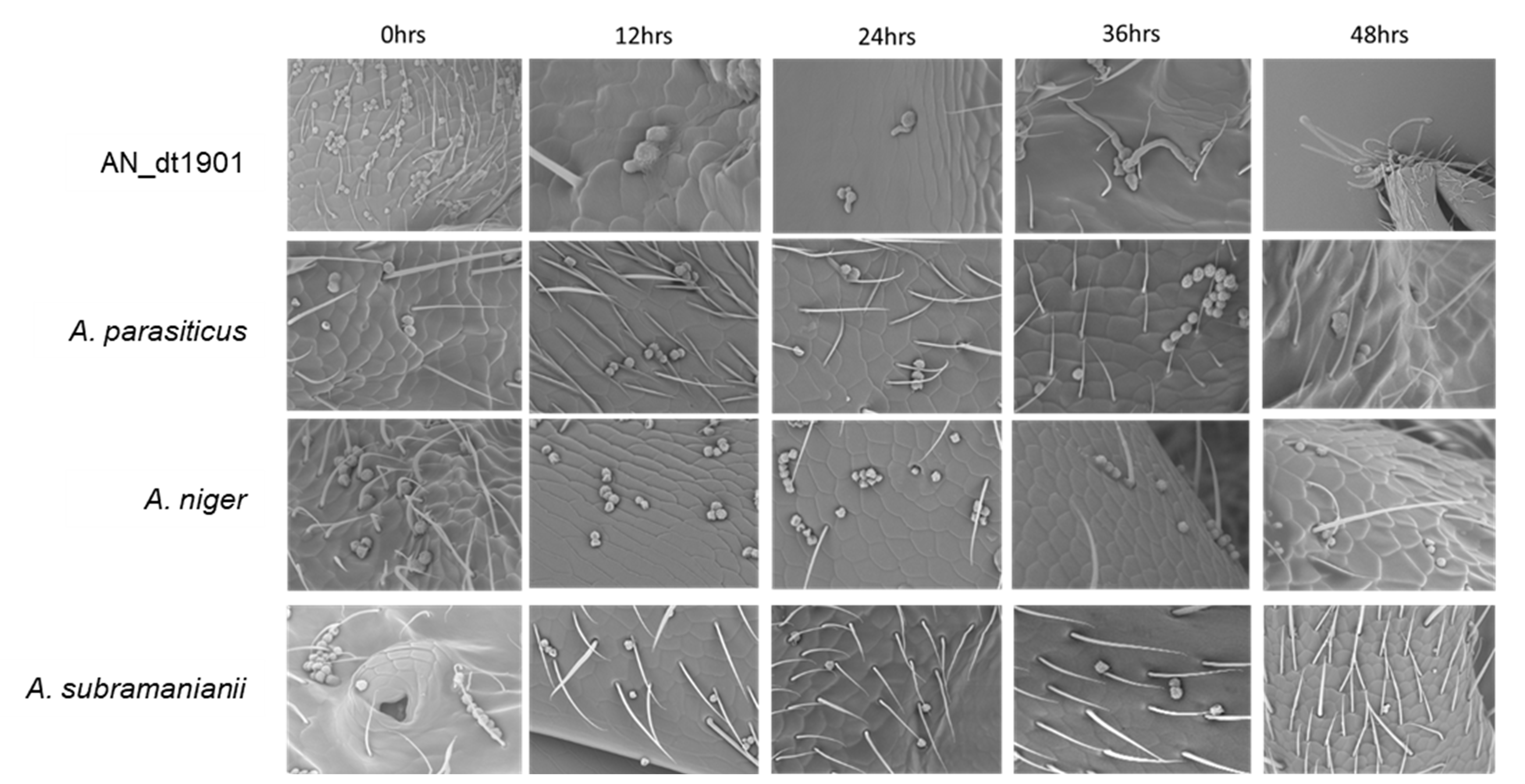
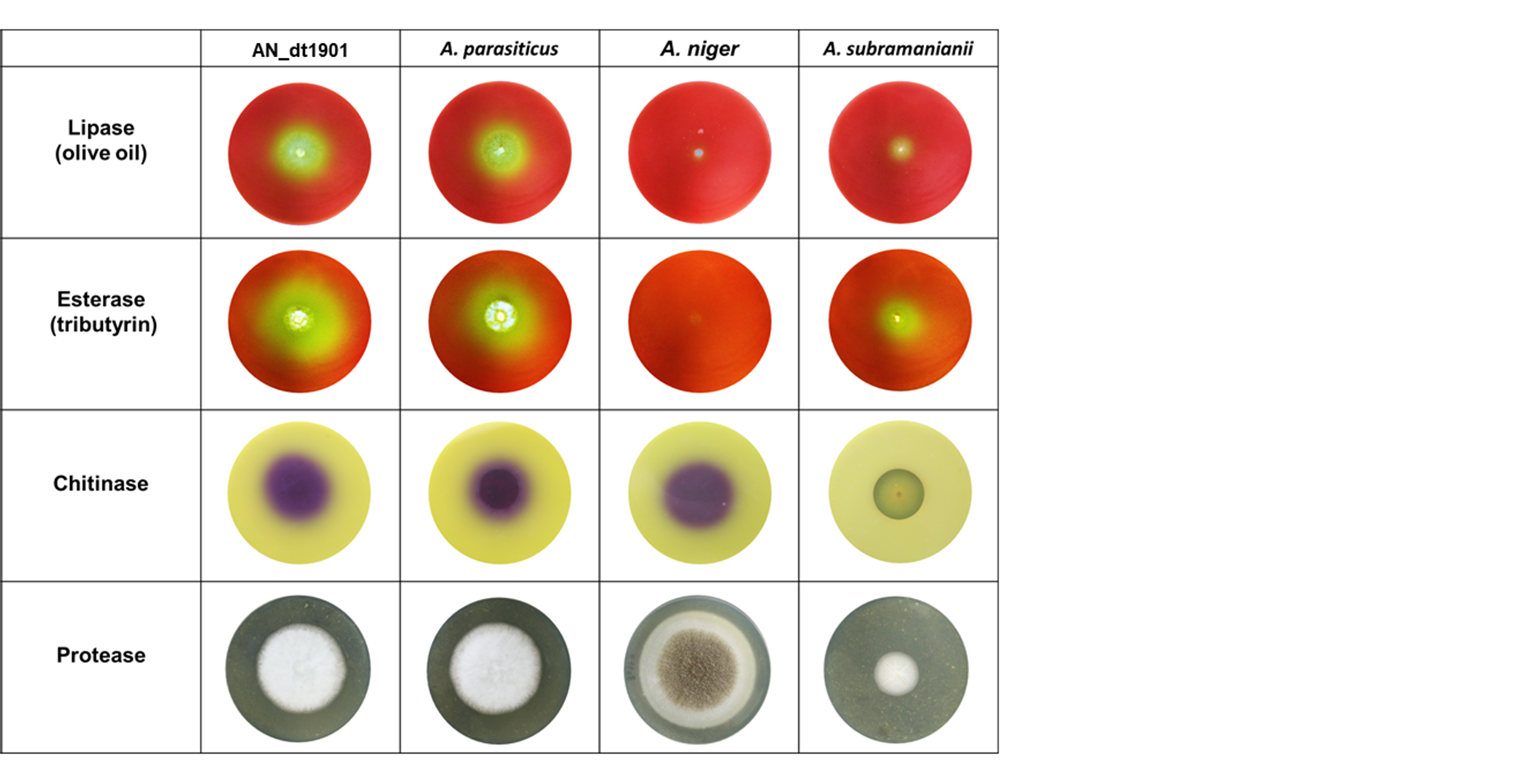
The purpose of this project is the development and application of microbial control for the increasingly serious pest ants in the agricultural environment. Especially considering the development of sustainable agriculture and organic agriculture, this project investigates the design, development, and application of microbial agents for pest ants on crops, and develops its practical value and commercial potential. As biological control is an environmentally acceptable strategy that can reduce the number of pest ants as well as economic losses, entomopathogenic fungi provide an environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides. However, compared with chemical pesticides, the relatively slow action of fungal pathogens hinders their wide use. The project team consists of professional academic research units and vector prevention and control management companies. In addition to the excellent research and development capabilities of academic units, the team has valuable experience in practical applications and commercial development in the industry. On the one hand, the fruitful academic research results can be shared with the industry to promote industrial upgrading; on the other hand, the economic benefits in the market and commercial value of such technology products can be developed so that this technology can truly gain global popularity. The research project has found that the ant pathogen AN_dt1901 (Aspergillus sp. A) has the characteristics of rapidly infecting the nest and killing the major pest ants in the current agricultural environment, Dolichoderus thoracicus. It has the potential to be used in the microbial control of pest ants in agricultural land. These research results have been published in one paper in SCI and have also been used in one submitted SCI paper; they have also been used in two applied for invention patents. Related photos are shown in Figures 7-8.
|
|
|
Figure 7. Dolichoderus thoracicus ant 0-48 hours after pathogenic fungal infection This indicates the phenomenon of conidial germination on the body surface of the Dolichoderus thoracicus ant after infection with the pathogenic fungus AN_dt1901 |
|
|
|
Figure 8. Ability of the ant pathogenic fungus AN_dt1901 and three other species belonging to the same Aspergillus flavus fungus to produce different hydrolase. If lipase is present, the culture medium will change from red to yellow. If esterase is present, the culture medium will change from red to yellow. If chitinase is present, the culture medium will change from yellow to purple. If protease is present, a transparent halo will form on the outer edge of the fungus |
Link for reference information:
https://www.facebook.com/NCUEEEC/photos/a.1053897732014001/1056518568418584.
6. Project of the Bureau of Animal and Plant Health Inspection and Quarantine, Council of Agriculture: “Development of Core Technologies and Establishment of Safety Assessment Model of the Agricultural Spraying Drone Industry Chain-Field Trials for Using Agricultural Drones to Control RIFA through the Management of Drone Pesticide Spraying Delegation System”.
In areas with a large-scale RIFA invasion, bait spreading is currently still the main prevention and control mode. However, in the RIFA prevention and control area, there are still many locations with special terrains (hills and steep slopes, rivers, valleys, fenced farmland, military control areas, etc.), where personnel and current dune buggies cannot perform control tasks. These areas are easily ignored. In many years, due to the terrain restrictions in many prevention and control areas, the coverage rate of prevention and control agents has only reached approximately 70%–75%. Furthermore, these areas may have not been controlled for many years due to terrain factors, resulting in loopholes in the prevention and control and becoming the source of the recurrence of the epidemic. Therefore, this project is mainly to assist in the establishment of the operation specifications for the use of agricultural drones in RIFA pesticide spraying on large areas or special terrains. In addition, the registration and management system for pesticide spraying delegation for prevention and control, through the interface for unmanned aerial vehicle spraying management data, was established. Related photos are shown in Figure 9.
|
|
|
Figure 9. Drone Pesticide Spraying Delegation System website |
Link to the videos of UAV of the project: https://www.facebook.com/NCUEEEC/videos/a.1053897732014001/2572706636208601.
7. The National Nature Park Management Office/Shoushan National Natural Park Plan of Survey, Monitoring, and Controlling Yellow Crazy Ants:
The coastal forests and the Qijin Seawall in the Shoushan National Nature Park of Kaohsiung are the natural habitats of terrestrial crabs. However, Anoplolepis gracilipes (Smith, 1857), commonly known as the yellow crazy ants, have been found in these areas in recent years. A 2018 terrestrial crab survey found that Anoplolepis gracilipes had invaded and spread in the terrestrial crab hotspots of these wetlands. Research reports that these invasive alien ants had infested and had caused serious ecological damage on Christmas Island, west of the Australian mainland, and other Pacific islands, specifically threatening the existence of the local terrestrial crab population. In 2020, the bait trap technique was used to investigate the distribution and density of yellow crazy ants in three terrestrial crab hotspots in the coastal areas and the Qijin Seawall in the Shoushan National Nature Park of Kaohsiung. The results showed that yellow crazy ants appeared in all three terrestrial crab hotspots, and the infestation was the most serious in the windbreaks around the seawall of the Qijin Back Hill. Implementation of the Yellow Crazy Ants Controlling Plan with Insect Traps in Shoushan Nature Park started in 2021 to further investigate ant nests in the windbreaks around the seawall of the Qijin Back Hill, where the population density of these ants was higher. The results showed that the yellow crazy ants in the Qijin Back Hill had formed super colonies. In the 2022 plan, the project focused on areas with high densities of the yellow crazy ants in the windbreaks surrounding the seawall of Qijin Back Hill, and planned to control these high densities of ants with liquid baits and insect growth regulators. To evaluate the control effect, insect traps and baits will be deployed for investigating and monitoring the invasive and foraging yellow ant populations. The distribution of yellow crazy ants will be investigated in the Mount Banping and the Northern Shoushan military control areas, which are the natural habitats of terrestrial crabs. Related photos are shown in Figures 10-12.
|
|
|
Figure 10. Areas of convergence of yellow crazy ant colonies in Shoushan National Nature Park |
|
|
|
Figure 11. Artificial bait boxes for yellow crazy ants in Shoushan National Nature Park |
|
|
|
Figure 12. Monitoring the distribution and density of yellow crazy ants using liquid bait (10% w/v cane sugar solution) method |
8. Center for General Education:
All units of NCUE offered related general education lectures in 2022. The information of the lecture is shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Information on general education lectures
|
Lecture Topics under “USR Green Energy Featured Projects” |
Date |
Number of students |
|
Nuclear and Green Energy |
11/3 |
70 |
|
Green Energy and Net Zero Emissions |
11/17 |
70 |
|
Global Warming and Sustainable Green Energy |
12/8 |
70 |
|
Other Organizations |
Date |
Number of students |
|
[Department of Biology Lecture] “Safeguarding Sacred Birds - Conservation Status of the Chinese Crested Tern” |
4/29 |
200 |
|
[Indigenous Resource Center Online Lecture] Eat Right: The Power of Wild Edible Plants and Seeds |
6/30 |
60 |
|
[Bliss and Wisdom Youth Club Lecture] Turning the World with Vegetarianism - Student Registration Zone |
10/19 |
90 |
|
[Department of Industrial Education and Technology Lecture] The Northerly Wind and the Sun of Sustainable Energy |
11/16 |
150 |
|
[Lecture at the Extracurricular Activities Section] As a Global Citizen, What’s SDGs? |
11/17 |
130 |
|
[NCUE Student’s Association Lecture] – Building a Green and Environmentally Friendly Earth Through Diet |
11/24 |
90 |
|
[Department of Geography Lecture] Child of the Rice Barn |
12/1 |
90 |